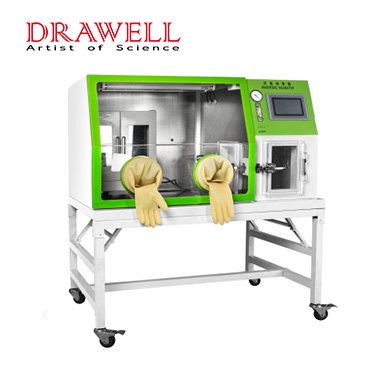
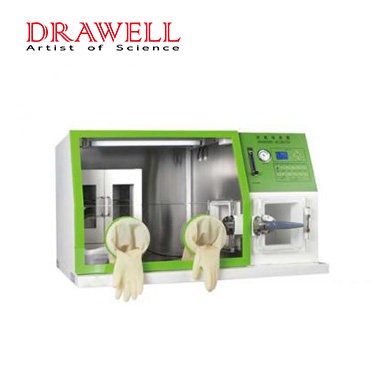
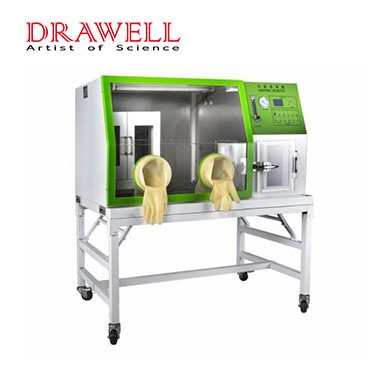
Anaerobic incubators are essential tools for the cultivation and handling of anaerobic microorganisms. They provide a controlled environment that allows these organisms to grow and thrive.
This article will provide a guide to the features, gases, and use of anaerobic incubators. We will discuss the different types of gases used in anaerobic incubators, the features that are important to consider when choosing an anaerobic incubator, and how to use an anaerobic incubator safely and effectively.
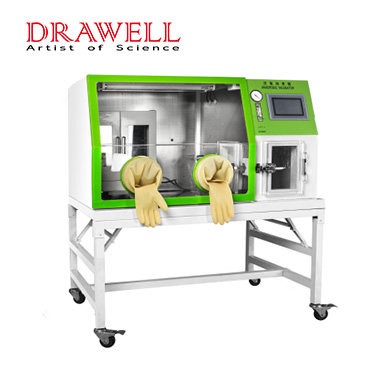
What are the features of an anaerobic incubator?
Anaerobic incubators come with various features to ensure precise control over the incubation conditions and provide a suitable environment for anaerobic cultures. The specific features of anaerobic incubators may vary among different models and manufacturers, but here are some common features you can find in these devices:
- Airtight Seal: Anaerobic incubators have a secure and airtight seal to prevent the entry of oxygen from the external environment. This seal ensures that the chamber maintains an anaerobic atmosphere during operation.
- Gas Inlet and Outlet Ports: Anaerobic incubators have gas inlet and outlet ports to connect the gas supply, allowing the introduction of anaerobic gas mixtures (usually nitrogen and carbon dioxide) and the venting of gases during operation.
- Gas Flow Control: These incubators feature controls to adjust the flow rate of the anaerobic gas mixture. Proper gas flow control is essential for creating and maintaining the desired oxygen-free environment.
- Gas Mixing System: Some anaerobic incubators have built-in systems that automatically mix the nitrogen and carbon dioxide gases to achieve the desired gas composition within the chamber.
- Temperature Control: Anaerobic incubators allow precise temperature control to maintain the optimal growth conditions for anaerobic microorganisms. They typically have a digital control panel to set and monitor the temperature.
- Humidity Control: Some models of anaerobic incubators offer humidity control to ensure the appropriate moisture level for cultures that require specific humidity conditions.
- Anaerobic Indicators: Many anaerobic incubators come with built-in anaerobic indicators, such as methylene blue strips or anaerobic indicator solutions. These indicators change color in the presence of oxygen, providing a visual confirmation of the anaerobic environment.
- Safety Features: Anaerobic incubators are equipped with safety features to protect both the user and the cultures. These may include alarms for gas leaks, temperature deviations, and overpressure conditions.
- Interior Shelving or Racks: The interior of the incubator usually contains shelving or racks to hold the culture vessels, such as Petri dishes, culture tubes, or plates.
- Observation Window: Some anaerobic incubators have an observation window or a clear panel that allows researchers to view the cultures without opening the chamber and disrupting the anaerobic environment.
- User-Friendly Interface: The control panel of the incubator is designed to be user-friendly, with easy-to-understand settings and displays for temperature, gas flow, and other parameters.
- Data Logging and Connectivity: Advanced models may have data logging capabilities, allowing researchers to record and analyze environmental conditions and incubation parameters. Additionally, some incubators may offer connectivity options to interface with a computer or a central monitoring system.
Remember that the specific features and capabilities of an anaerobic incubator may vary based on the model and the intended applications. When selecting an anaerobic incubator, it’s essential to consider the specific research needs and the types of anaerobic microorganisms to be cultured.

What gases are in an anaerobic incubator?
In anaerobic incubators, the most common gases used to create an oxygen-free environment are nitrogen (N2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). These gases are used in combination to displace and replace the oxygen present in the incubator chamber, creating the desired anaerobic conditions for the growth and study of anaerobic microorganisms.
- Nitrogen (N2): Nitrogen gas is the primary gas used to purge the incubator chamber of oxygen. It is an inert gas, meaning it does not participate in chemical reactions with other substances within the chamber. By filling the chamber with nitrogen gas and allowing it to flow for a period, the oxygen is effectively removed, creating an oxygen-free atmosphere.
- Carbon Dioxide (CO2): Carbon dioxide is often used in combination with nitrogen to maintain a low redox potential in the incubator. While nitrogen displaces the oxygen, carbon dioxide serves as a secondary gas to maintain the desired anaerobic conditions. It helps to prevent the buildup of highly reducing compounds and ensures the microorganisms’ metabolic processes can proceed efficiently.
The specific ratio of nitrogen to carbon dioxide used in anaerobic incubators may vary depending on the type of microorganisms being studied, the experimental requirements, and the equipment specifications. Additionally, some anaerobic incubators may offer the flexibility to adjust the gas mixture to meet specific research needs.
It is essential to note that when working with gases, safety precautions should be taken to prevent leaks and ensure proper ventilation in the laboratory setting. Regular maintenance and calibration of the anaerobic incubator are also crucial to maintain a consistent and accurate anaerobic environment for experiments and cultures.
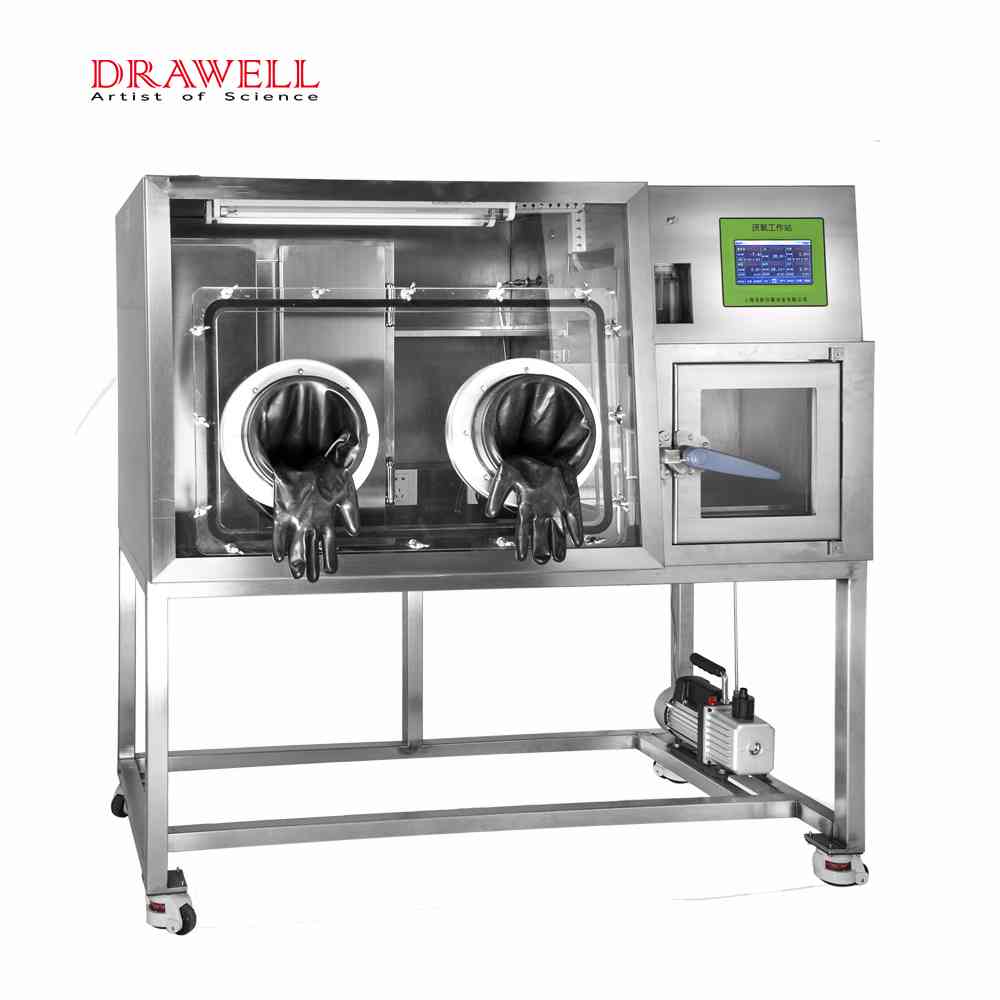

What are the uses of an anaerobic incubator?
Anaerobic incubators are used to create an oxygen-free environment for the growth and cultivation of anaerobic microorganisms. Anaerobic microorganisms are organisms that do not require oxygen to survive. They can be found in a variety of environments, including the human body, soil, and water.
Anaerobic incubators are used in a variety of applications, including:
- Clinical microbiology: Anaerobic incubators are used to culture and identify anaerobic bacteria that can cause infections in humans.
- Food microbiology: Anaerobic incubators are used to study the growth of anaerobic bacteria in food. This information can be used to prevent food spoilage and foodborne illness.
- Environmental microbiology: Anaerobic incubators are used to study the diversity and abundance of anaerobic microorganisms in the environment. This information can be used to understand the role of these organisms in the cycling of nutrients and the decomposition of organic matter.
- Biotechnology: Anaerobic incubators are used to grow and produce enzymes, antibiotics, and other products from anaerobic microorganisms.
The use of anaerobic incubators is essential for the study and manipulation of anaerobic microorganisms. These incubators provide a controlled environment that allows these organisms to grow and thrive.
Here are some of the specific uses of anaerobic incubators:
- Culturing anaerobic bacteria: Anaerobic incubators are used to culture anaerobic bacteria from clinical specimens, food samples, and environmental samples. This allows scientists to identify and characterize these bacteria.
- Studying the growth of anaerobic bacteria: Anaerobic incubators can be used to study the growth of anaerobic bacteria under different conditions, such as different temperatures, pH levels, and gas mixtures. This information can be used to understand the factors that affect the growth of these bacteria.
- Producing enzymes and antibiotics: Anaerobic incubators can be used to produce enzymes and antibiotics from anaerobic microorganisms. These products can be used in a variety of applications, such as food processing, medicine, and environmental remediation.
Anaerobic incubators are an essential tool for the study and manipulation of anaerobic microorganisms. They provide a controlled environment that allows these organisms to grow and thrive.
Conclusion
In conclusion, anaerobic incubators are essential tools for the cultivation and handling of anaerobic microorganisms. They provide a controlled environment that allows these organisms to grow and thrive.
When choosing an anaerobic incubator, it is important to consider the type of gas mixture you need, the temperature and humidity range you need, and the size of the incubator. You should also make sure that the incubator has a safety system to prevent the buildup of hazardous gases.
Anaerobic incubators are relatively easy to use. However, it is important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure that the incubator is used safely and effectively. If you buy Drawell Anaerobic Incubators, we will provide you with manual and brochure. And we will get connected with you once you have questions. Believe our products will not let you down.