Water quality is essential for public health, environmental protection, and industrial processes. To ensure the safety and purity of our water sources, accurate and reliable analysis techniques are essential. Inductively Coupled Plasma Optical Emission Spectroscopy (ICP-OES) is a powerful analytical tool that can uncover a wealth of information about the composition of water samples by providing precise elemental analysis.

Why Choose ICP-OES for Water Analysis
ICP-OES is a powerful analytical technique that uses plasma—a highly energized state of matter—to excite atoms and ions in a sample. When these atoms return to their lower energy states, they emit light at specific wavelengths. Each element has a unique emission spectrum, enabling ICP-OES to identify and quantify multiple elements simultaneously. When use it for water analysis, there are some advantages:
- Multi-Element Detection: ICP-OES can analyze dozens of elements simultaneously, making it highly efficient.
- High Sensitivity: It detects trace elements at parts per billion (ppb) or even parts per trillion (ppt) levels.
- Wide Dynamic Range: Capable of measuring low and high concentrations without compromising accuracy.
- Rapid Results: The analysis process is fast, providing quick turnaround times.
- Minimal Interference: Advanced optical systems minimize interference from complex matrices.
When comparied with other water analysis methods like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or UV-Vis Spectrophotometry, ICP-OES has also stands out. While AAS is effective for single-element detection, ICP-OES outperforms it in multi-element analysis and speed. UV-Vis is limited to detecting specific compounds, such as nitrates or organic matter, whereas ICP-OES provides a broader elemental analysis.
In summary, ICP-OES offers unparalleled efficiency, accuracy, and versatility, making it a superior choice for comprehensive water analysis.
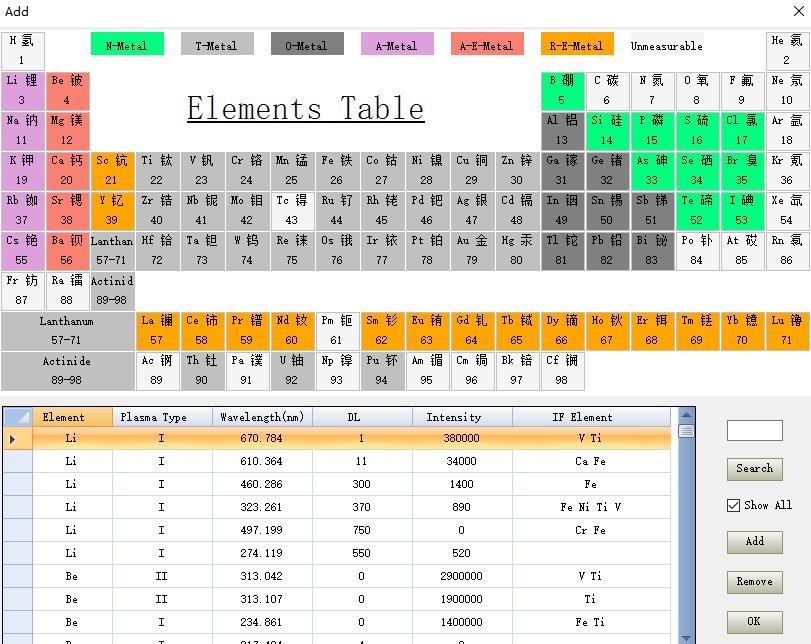
What Can ICP-OES Detect in Water?
ICP-OES is renowned for its ability to detect and quantify a wide range of elements in water, making it an indispensable tool in water analysis. Its versatility and sensitivity allow it to analyze both major and trace elements, ensuring comprehensive insights into water quality. Here’s a detailed look at what ICP-OES can detect in water:
1. Heavy Metals
Heavy metals are among the most critical contaminants in water due to their toxicity and potential harm to both humans and ecosystems. ICP-OES excels at detecting these metals, even at trace levels, ensuring safety and regulatory compliance.
- Lead (Pb): A significant public health concern, especially in drinking water systems, where even low levels can cause severe health problems, particularly in children.
- Arsenic (As): Common in groundwater, especially in regions with natural mineral deposits, arsenic is toxic and carcinogenic.
- Mercury (Hg): Often found in industrial effluents and contaminated water bodies, mercury poses a severe threat to aquatic life and human health.
- Cadmium (Cd): Typically a byproduct of industrial processes, cadmium can accumulate in the body, causing kidney damage and other health issues.
2. Essential Nutrients
In agricultural and ecological contexts, analyzing water for essential nutrients is vital to ensure its suitability for plant growth and ecosystem health.
- Calcium (Ca): A critical component of water hardness, calcium analysis helps in understanding the scaling potential in industrial or domestic systems.
- Magnesium (Mg): Along with calcium, magnesium contributes to water hardness and is crucial for assessing water suitability for drinking and irrigation.
- Potassium (K) and Phosphorus (P): Important nutrients for plant growth, their presence in irrigation water can impact agricultural productivity.
3. Toxic Elements
ICP-OES can detect toxic elements that pose risks to human health and the environment.
- Selenium (Se): While selenium is essential in trace amounts, excessive levels can cause toxicity, especially in agricultural drainage water.
- Chromium (Cr): Chromium, particularly its hexavalent form (Cr-VI), is a known carcinogen and often linked to industrial pollution.
- Antimony (Sb): Found in some industrial waste, antimony can leach into water supplies and pose health risks when consumed over long periods.

4. Trace Elements
Trace elements, though present in minute quantities, can significantly affect water quality, taste, and safety. ICP-OES provides the precision required to analyze these elements accurately.
- Iron (Fe): A common element in water that, when present in high concentrations, can cause discoloration and affect taste.
- Copper (Cu): Often found in water due to corroding plumbing systems, excessive copper levels can lead to health concerns and water quality issues.
- Zinc (Zn): Typically non-toxic, but elevated zinc levels can impart an unpleasant taste to water.
5. Rare Earth Elements and Emerging Contaminants
With its high sensitivity, ICP-OES is also capable of detecting rare earth elements and other emerging contaminants that are gaining attention in environmental studies.
- Lanthanides: Elements like cerium (Ce) and neodymium (Nd) are increasingly monitored due to their use in advanced technologies and potential leaching into water systems.
- Emerging Trace Metals: Elements like cobalt (Co) and molybdenum (Mo), which have industrial and agricultural significance, are also detectable with ICP-OES.
6. Salinity and Mineral Content
Salinity impacts the usability of water in agriculture and industry. ICP-OES can measure elements contributing to salinity, such as:
- Sodium (Na): High levels can harm crops and affect the potability of water.
- Chloride (Cl): A component of salinity that can cause corrosion in pipelines and equipment.
- Sulfur (S): Found in sulfates, which can impact water taste and scaling potential.
ICP-OES’s ability to detect a diverse array of elements—ranging from heavy metals and toxic substances to essential nutrients and trace elements—makes it a comprehensive solution for water analysis.
Applications of ICP-OES in Water Testing
The application of ICP-OES span a wide range of industries and scenarios, and it has become an essential tool in water quality testing.
1. Environmental Monitoring
Monitoring the quality of natural water sources is vital for ecological health and human safety. ICP-OES plays a crucial role in environmental studies by detecting pollutants and trace elements in rivers, lakes, oceans, and groundwater.
- Tracking Industrial Pollution: ICP-OES helps identify heavy metals such as cadmium, mercury, and lead in water bodies near industrial zones. Regular monitoring ensures compliance with environmental regulations and aids in pollution control.
- Assessing Ecosystem Health: Elevated levels of elements like selenium or copper can harm aquatic life. ICP-OES enables precise measurements to track these changes over time.
- Groundwater Contamination: By analyzing groundwater samples, ICP-OES can detect contaminants from agricultural runoff, such as nitrates or pesticides, helping address potential risks to drinking water supplies.
2. Drinking Water Safety
Ensuring the safety of drinking water is a primary concern for public health authorities worldwide. ICP-OES is instrumental in testing municipal water supplies and identifying harmful contaminants.
- Detection of Heavy Metals: Lead, arsenic, and chromium are toxic even at trace levels. ICP-OES provides accurate measurements to ensure compliance with health standards set by organizations like the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) and WHO (World Health Organization).
- Monitoring Water Hardness: Essential elements like calcium and magnesium are measured to determine water hardness, which can affect plumbing systems and appliance efficiency.
- Emergency Response: In cases of contamination due to natural disasters or industrial accidents, ICP-OES facilitates rapid testing to determine water safety and guide remediation efforts.

3. Industrial Applications
Industries rely on water for various processes, from manufacturing to cooling systems. Monitoring and managing water quality are critical to maintaining operational efficiency and environmental responsibility.
- Effluent Discharge Monitoring: Industrial facilities must ensure their wastewater complies with environmental discharge standards. ICP-OES detects toxic elements like cadmium and nickel, ensuring adherence to regulations and reducing environmental impact.
- Process Water Analysis: In industries like food and beverage or pharmaceuticals, water quality directly affects product safety. ICP-OES helps maintain strict quality control by analyzing trace contaminants.
- Boiler and Cooling Water: Metals like iron and copper in process water can cause scaling and corrosion in industrial equipment. ICP-OES aids in identifying these elements, enabling preventive maintenance.
4. Agricultural Use
Water quality is a key factor in agricultural productivity. Farmers and agricultural scientists use ICP-OES to assess water suitability for irrigation and other applications.
- Nutrient Analysis: ICP-OES measures essential nutrients such as potassium, magnesium, and phosphorus in water, ensuring it supports plant growth without causing nutrient deficiencies.
- Salinity and Toxicity Assessment: Excessive salts or toxic elements like boron can harm crops and soil. ICP-OES enables precise monitoring, helping farmers mitigate risks and optimize crop yield.
- Sustainable Practices: With increasing pressure on freshwater resources, ICP-OES helps implement sustainable irrigation practices by evaluating water quality and ensuring minimal environmental impact.
5. Research and Development
Beyond routine testing, ICP-OES is widely used in research and development for studying water quality trends and developing innovative water treatment solutions.
- Pollution Studies: Researchers use ICP-OES to identify emerging pollutants and understand their distribution in water bodies.
- Treatment Technology Validation: New water treatment methods, such as advanced filtration or desalination, are tested using ICP-OES to evaluate their efficiency in removing contaminants.
From protecting ecosystems to ensuring safe drinking water, ICP-OES offers unparalleled accuracy and reliability in water testing applications. Its ability to detect a broad range of elements, combined with its rapid analysis capabilities, makes it indispensable in addressing the growing challenges of water quality management.


2.jpg)