pH, a measure of acidity or alkalinity, plays a crucial role in various fields such as agriculture, food production, environmental monitoring, and research. pH meters are indispensable tools for accurate pH measurement. Understanding the different types of pH meters and their applications is essential for selecting the right one for your needs.
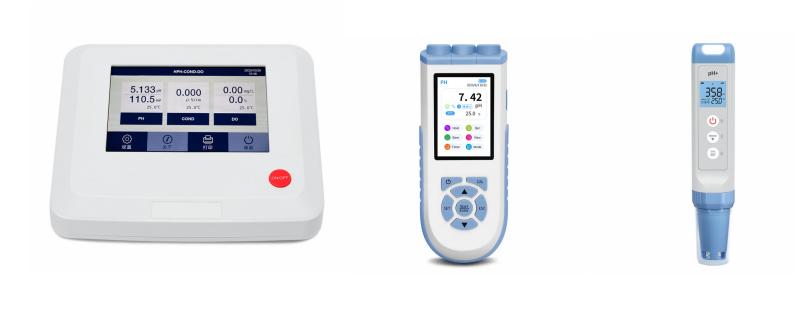
Types of pH Meters
pH meters come in various types, each suited for different applications and environments. Here are some common types:
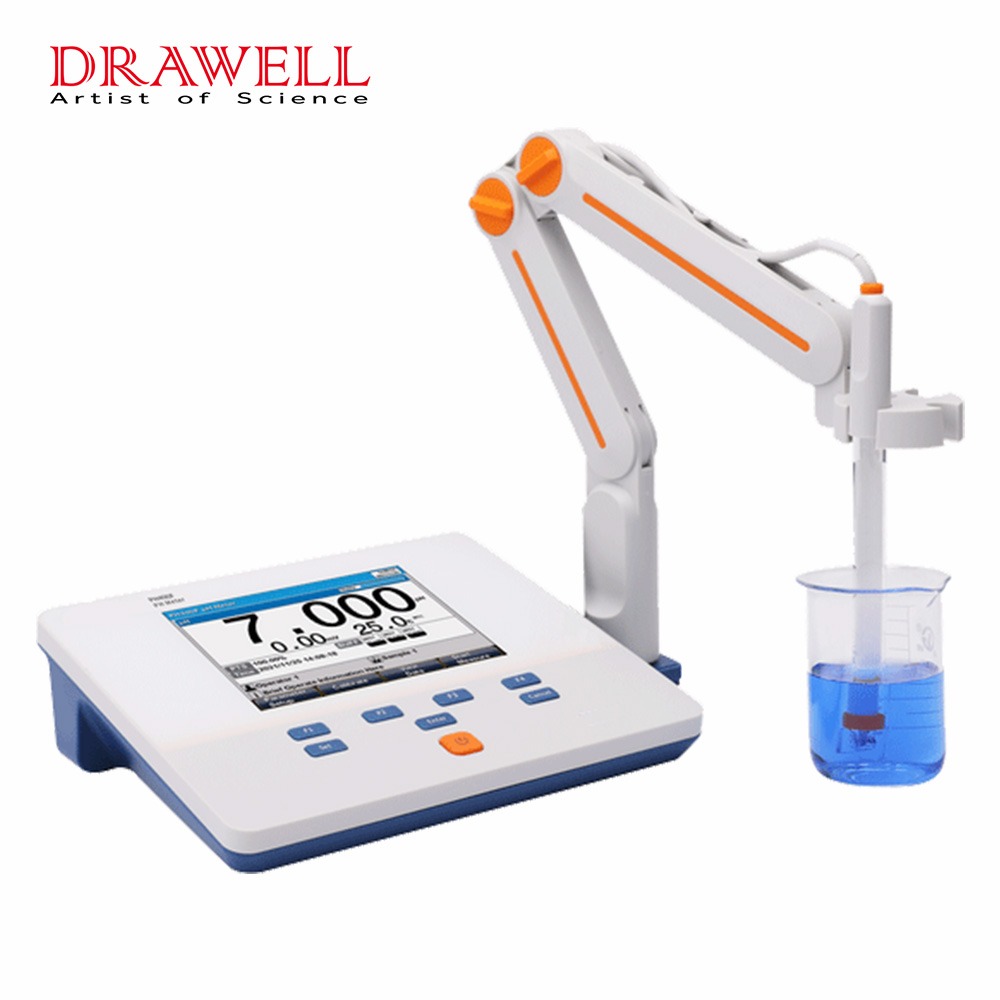
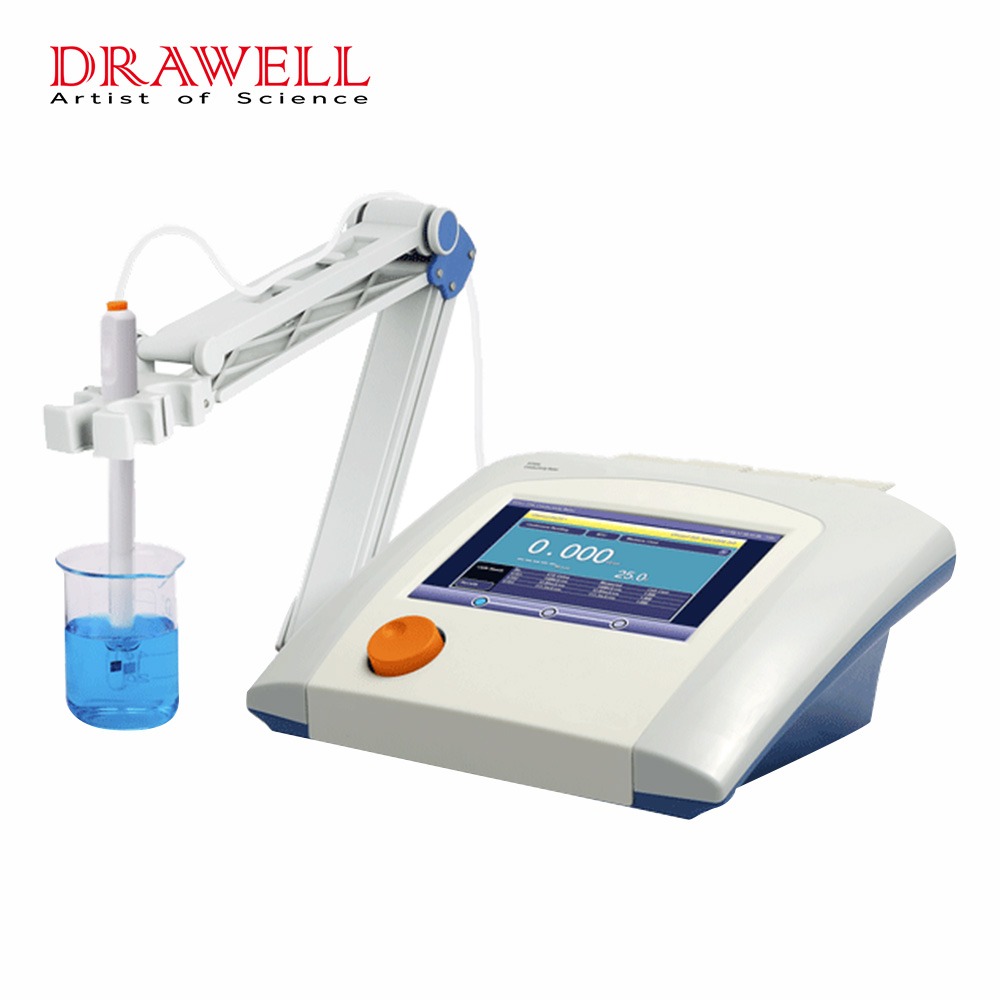
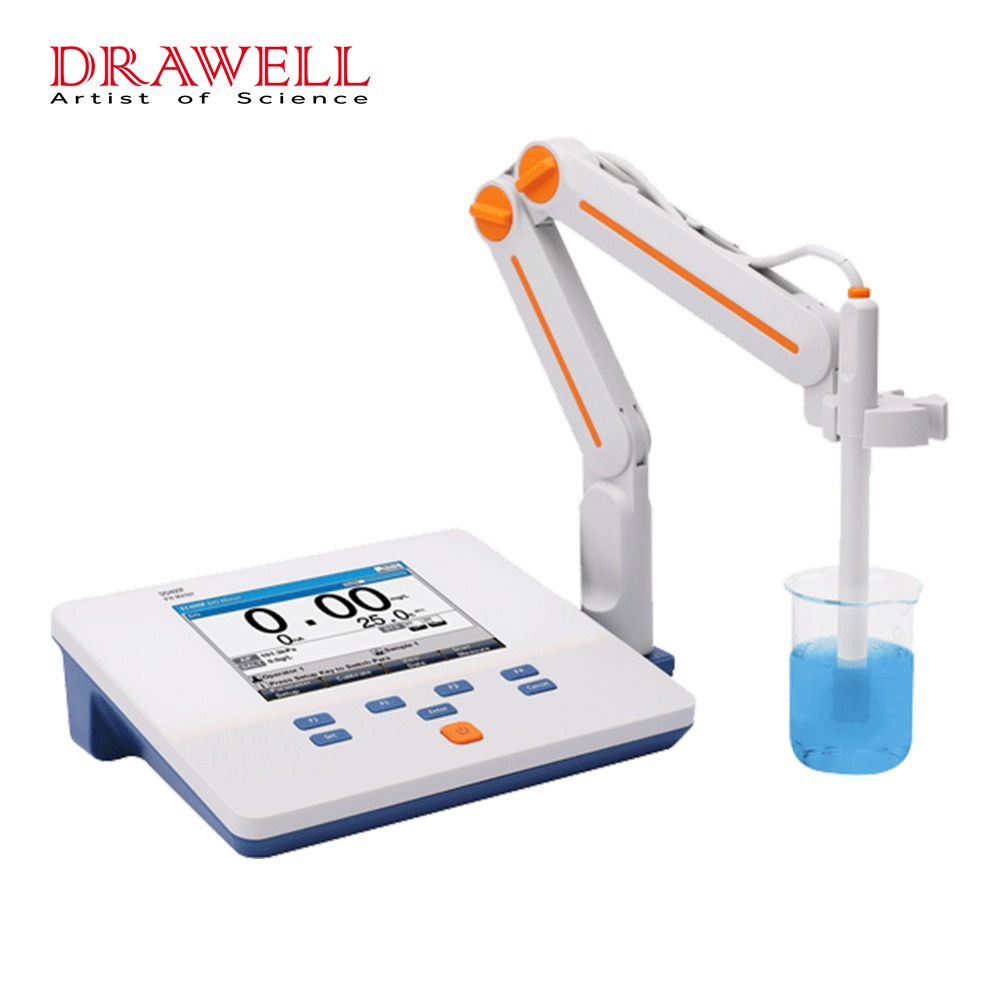
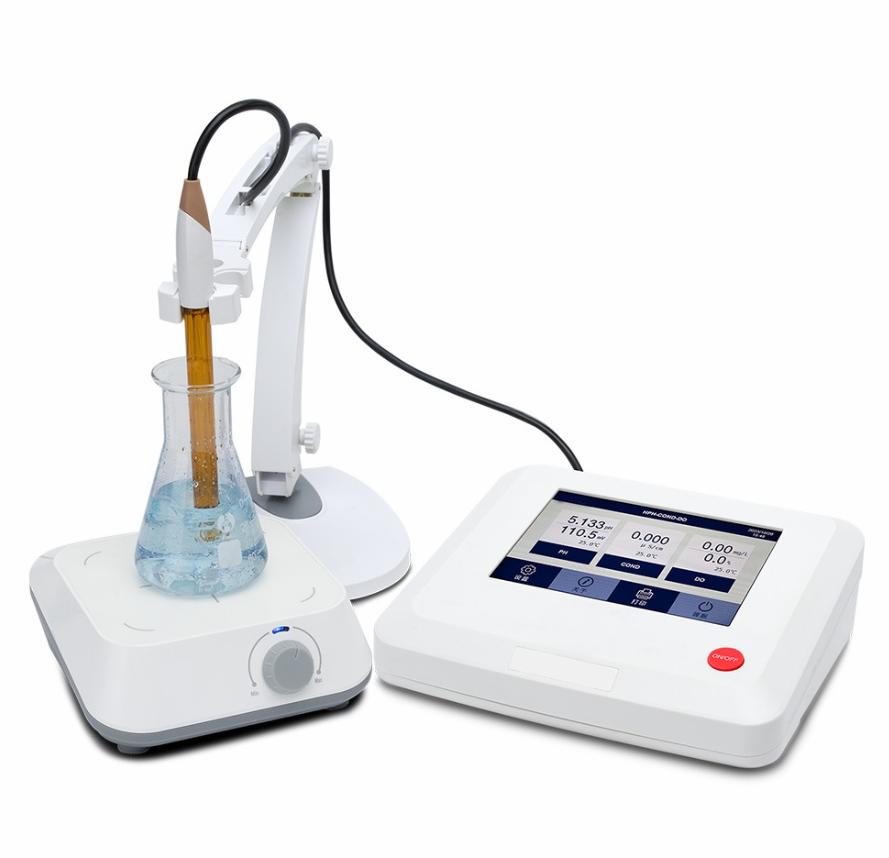
Benchtop pH Meters:
- Design: These are larger, stationary devices typically used in laboratory settings or industrial environments where accuracy and precision are paramount.
- Features: Benchtop pH meters usually offer advanced features such as multiple calibration points, temperature compensation, data logging capabilities, and often have a larger display for easier reading of measurements.
- Accuracy: They tend to provide highly accurate pH measurements due to their stable setup and precise calibration options.
- Applications: Commonly used in scientific research, quality control processes, and educational laboratories where consistent and reliable pH measurements are required.
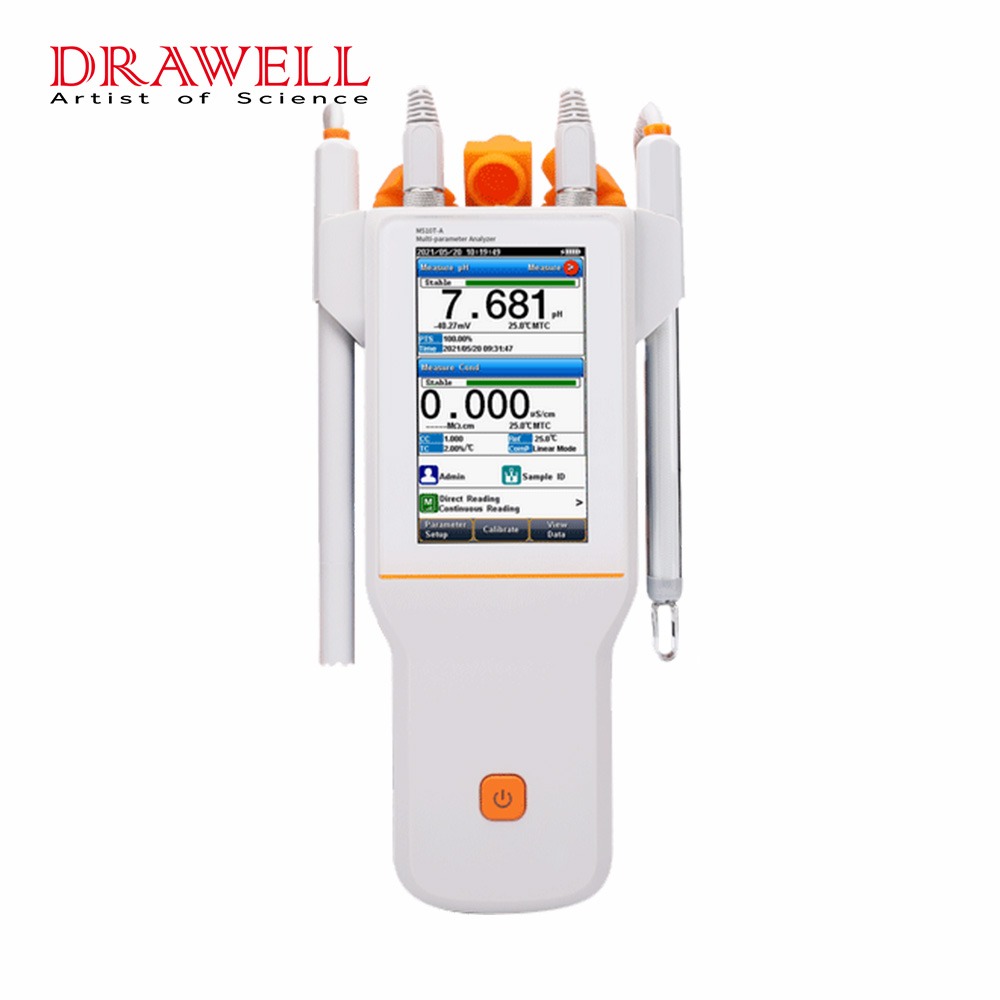
Portable pH Meters:
- Design: These pH meters are designed to be easily transported and used in various locations. They are more compact and lightweight compared to benchtop models.
- Features: Portable pH meters often offer basic to intermediate features such as single or dual-point calibration, automatic temperature compensation, and digital displays.
- Accuracy: While they may not offer the same level of precision as benchtop models, portable pH meters still provide reliable pH measurements suitable for fieldwork or on-the-go testing.
- Applications: Widely used in environmental monitoring, agriculture, food and beverage production, water treatment facilities, and other field applications where portability is essential.
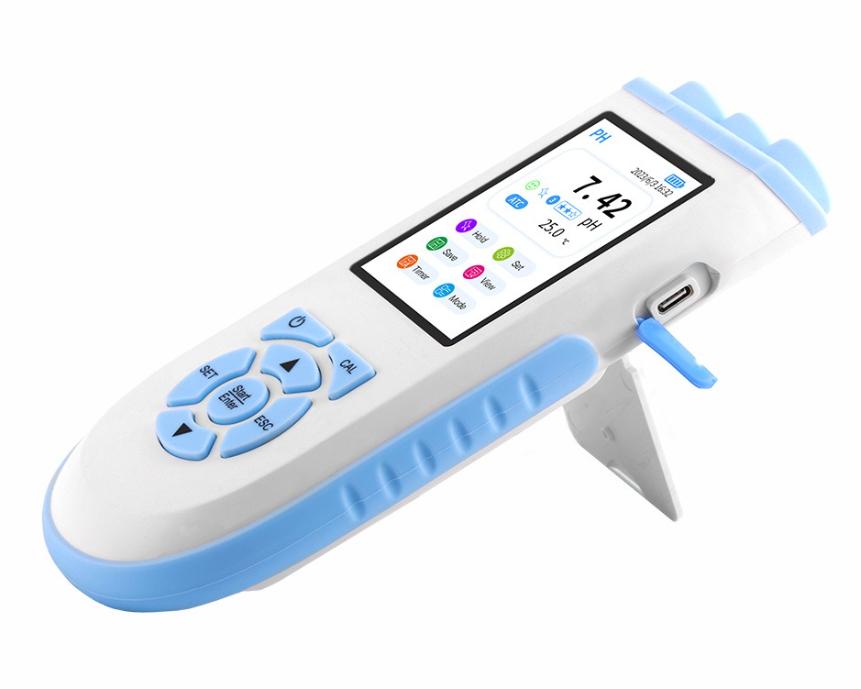

Pocket pH Testers:
- Design: These pH meters are extremely compact and handheld, resembling a pen or a small device that can fit in a pocket.
- Features: Pocket pH testers typically offer basic functionality with a single-button operation for simplicity. They may have limited calibration options and basic temperature compensation.
- Accuracy: While convenient for quick pH checks, pocket pH testers may not provide the same level of accuracy and precision as benchtop or portable models. They are more suitable for rough estimation rather than precise measurements.
- Applications: Ideal for home use, hobbyists, and situations where portability and convenience are prioritized over laboratory-grade accuracy. They are commonly used for aquarium maintenance, pool testing, and simple pH checks in household applications.
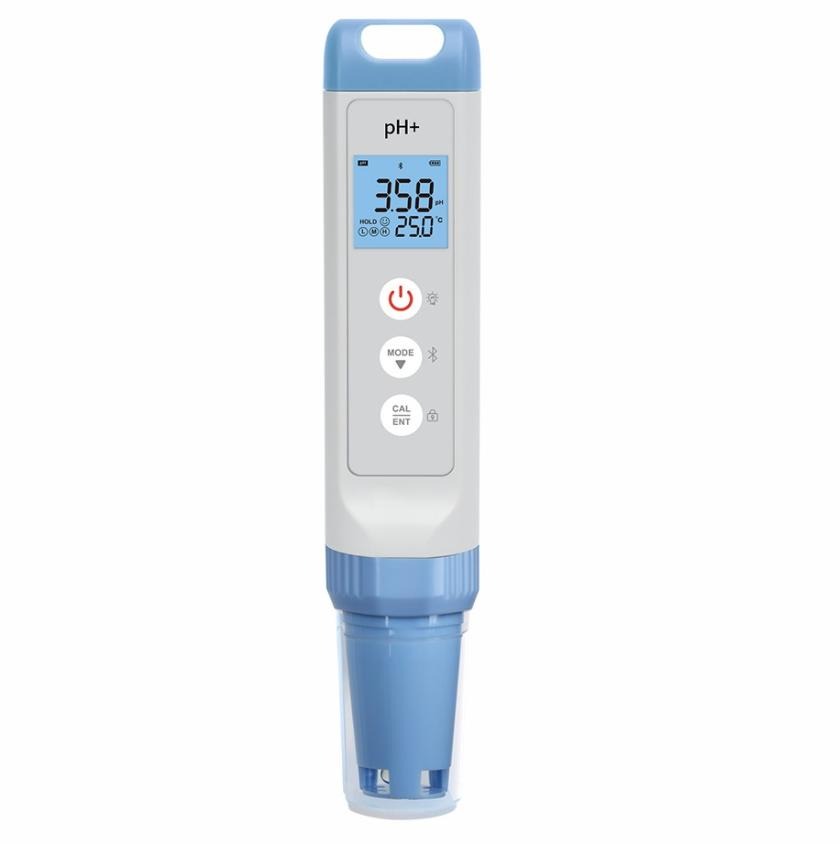

Each type of pH meter serves specific needs, ranging from high-precision laboratory work to quick, on-the-spot measurements in various environments. The choice depends on factors such as the required level of accuracy, portability, and intended application.
Pros and Cons, and Application among these pH Meters
| Type of pH Meter | Pros | Cons | Applications |
| Benchtop pH Meter | High accuracy and precision | Bulky and not portable | Scientific research |
| Advanced features (e.g., data logging) | Limited mobility | Quality control processes | |
| Stable setup | Higher cost compared to portable and pocket meters | Industrial laboratories | |
| Portable pH Meter | Portability | May sacrifice some accuracy compared to benchtop | Environmental monitoring |
| Suitable for fieldwork | Limited features compared to benchtop | Agriculture | |
| Versatility in various environments | May require more frequent calibration | Water treatment facilities | |
| Pocket pH Meter | Extremely compact and portable | Limited accuracy and precision | Home use (e.g., aquarium maintenance, pool testing) |
| Simple and easy to use | Basic features | Hobbyist applications | |
| Affordable | Not suitable for high-precision laboratory work | Quick pH checks in household applications |
This table provides a quick overview of the strengths, weaknesses, and typical applications of each type of pH meter, helping to guide the selection process based on specific needs and requirements.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a pH Meter
When choosing a pH meter, several factors should be taken into consideration to ensure that it meets your specific needs and requirements. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Accuracy and Precision: The level of accuracy and precision required for your pH measurements depends on the application. For critical scientific research or quality control processes, high accuracy and precision are essential, while rough estimations may suffice for general testing purposes.
- Measurement Range: Ensure that the pH meter’s measurement range covers the pH values you intend to measure. Some applications may require measurement of acidic solutions, while others may involve alkaline or neutral solutions.
- Calibration: Consider the calibration process of the pH meter. Most pH meters require regular calibration using pH buffer solutions. Check if the meter supports single-point or multi-point calibration and how easy it is to perform calibration procedures.
- Temperature Compensation: pH measurements are temperature-sensitive, so temperature compensation is crucial for accurate results, especially in environments where temperature fluctuations occur. Look for pH meters with automatic temperature compensation (ATC) to ensure accurate readings across different temperatures.
- Portability: Determine whether you need a benchtop, portable, or pocket-sized pH meter based on your intended application and mobility requirements. Benchtop models offer high accuracy but are stationary, while portable and pocket-sized meters provide flexibility for fieldwork and on-the-go testing.
- Durability and Build Quality: Consider the durability and build quality of the pH meter, especially if it will be used in harsh or demanding environments. Look for meters with rugged construction and waterproof or splash-proof features for long-lasting performance.
- Ease of Use: Choose a pH meter with a user-friendly interface and intuitive controls for easy operation. Features such as digital displays, one-touch calibration, and simple button layouts can enhance usability, especially for inexperienced users.
- Additional Features: Assess the additional features offered by the pH meter, such as data logging capabilities, connectivity options (e.g., USB, Bluetooth), and compatibility with external accessories (e.g., electrodes, probes). These features can enhance functionality and versatility for specific applications.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of the pH meter relative to your budget and the features it offers. While high-end models may provide advanced functionality, more affordable options may suffice for basic pH testing needs.
- Support and Warranty: Check the manufacturer’s reputation for product support and warranty coverage. Ensure that the pH meter is backed by reliable customer service and warranty policies to address any issues or concerns that may arise after purchase.
By considering these factors, you can select a pH meter that best suits your requirements and ensures accurate and reliable pH measurements for your specific applications.
Conclusion
By understanding the different types of pH meters and the factors influencing choice, you’ll be well-equipped to select the ideal tool for your specific application. Remember, prioritize accuracy for critical lab work while portability might be key for field measurements. If you are not sure about the selection, please feel free to contact a pH meter supplier, believe Drawell is your disirable choice. With the right pH meter in hand, you’ll have a powerful tool to unlock a world of pH insights!