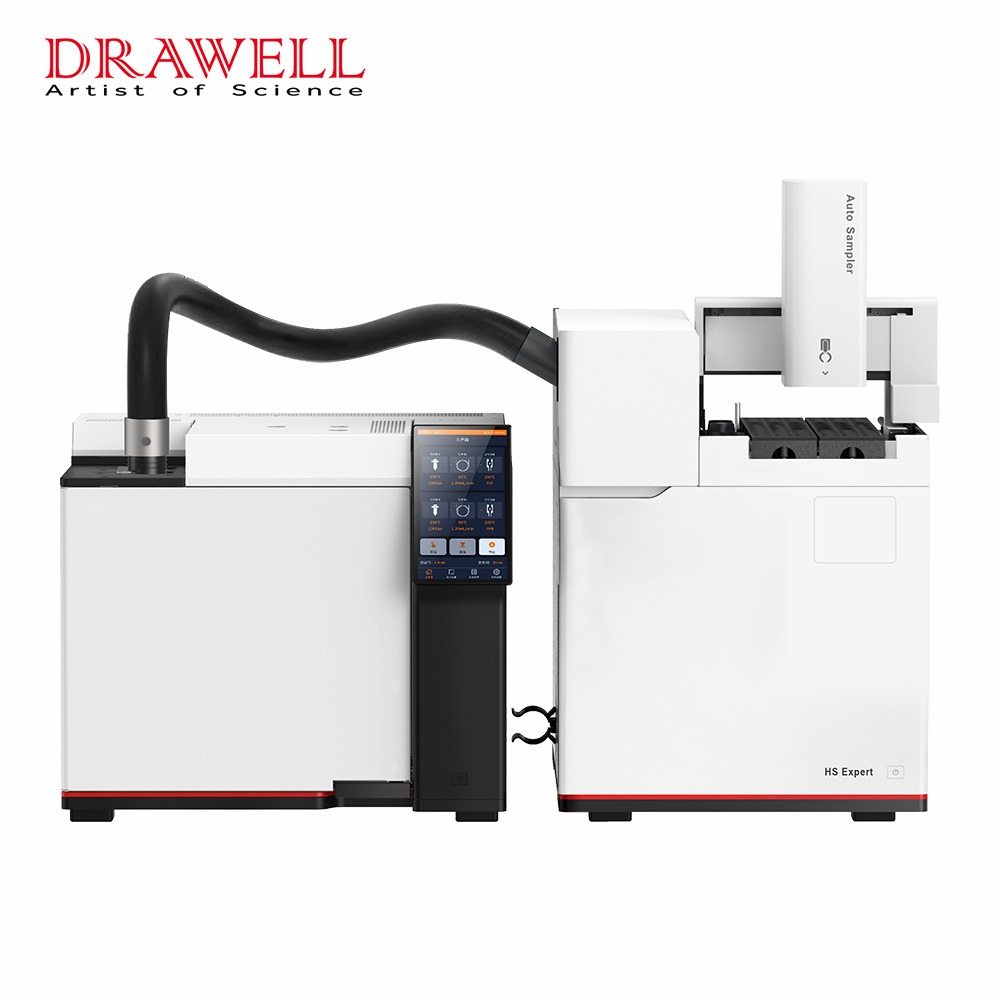
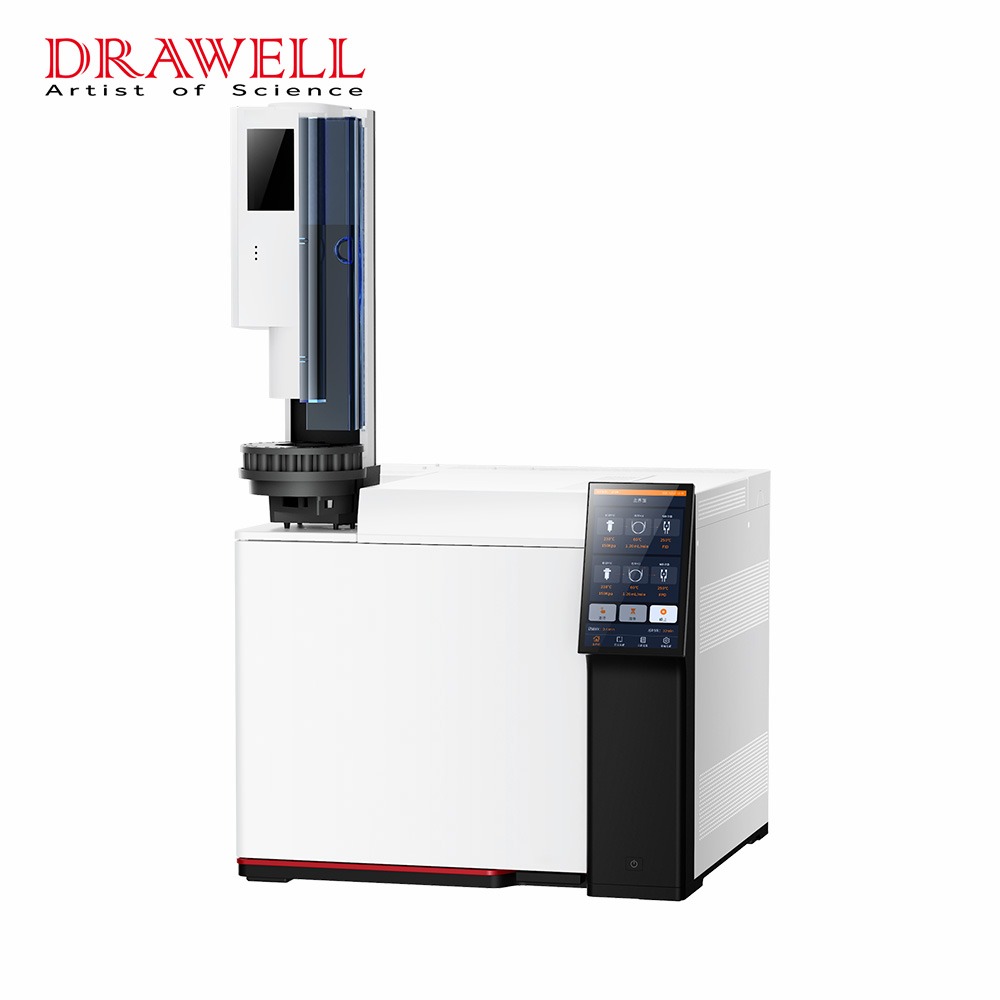
Because of its extraordinary capacity to separate, identify, and measure chemical components within complicated mixtures, gas chromatography (GC) is a strong analytical technique widely employed in a variety of scientific domains and enterprises. This technology, which is based on the principles of gas-solid or gas-liquid chromatography, is an invaluable tool for both researchers and professionals. In this article, we’ll explore the diverse applications of gas chromatography, showcasing its importance in various industries.

Common Applications of Gas Chromatography

1. Pharmaceuticals and Medicine
Gas chromatography is extremely important in pharmaceutical research and quality control. It is used to examine drug compositions, determine drug purity, and detect contaminants. GC is useful in pharmacokinetics investigations because it helps researchers understand how medicines are absorbed, processed, and removed in the body. Furthermore, it is used in forensic toxicology to detect drugs and toxins in biological materials.
2. Environmental Analysis
Gas chromatography is used by environmental scientists to test the quality of air and water. It assists in the identification and quantification of contaminants such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), insecticides, and industrial chemicals. GC is also used to assess soil pollution and analyze samples collected from hazardous waste sites.
3. Food and Beverage Industry
Food analysis relies on Gas chromatography to evaluate the composition of flavors and perfumes, assess food quality, and discover pollutants. It is commonly used to measure components such as fatty acids, vitamins, and dietary additives. The investigation of volatile chemicals responsible for the scent and flavor of diverse food products is also aided by GC.
4. Petrochemical Industry
For studying hydrocarbon mixtures, gas chromatography is a pillar of the petrochemical sector. It aids in refining operations, determining the composition of fuels, and assuring environmental compliance. GC is crucial for characterizing crude oil, assessing the quality of petroleum products, and monitoring emissions from refineries.
5. Chemical Research
Chemists rely on Gas chromatography for a wide range of applications, from analyzing reaction products to identifying and quantifying organic compounds. GC helps researchers investigate chemical kinetics, study reaction mechanisms, and assess the purity of synthesized compounds. It is also used in the analysis of polymers, paints, and coatings.
6. Clinical and Healthcare
In clinical laboratories, GC is utilized for analyzing blood, urine, and other bodily fluids to diagnose diseases, assess metabolic disorders, and measure hormone levels. It is instrumental in detecting volatile organic compounds associated with various medical conditions, including diabetes and cancer.
7. Material Science
GC is used to analyze materials such as polymers, plastics, and textiles in order to evaluate their chemical composition and quality. Researchers utilize GC to research degradation processes, find additives, and investigate material performance under various situations.
8. Cosmetics and Fragrance Industry
The composition of perfumes, scents, and cosmetics is analyzed using gas chromatography. It aids in the identification and quantification of volatile molecules responsible for the aroma of these items. Additionally, GC aids in quality control by assuring uniformity in fragrance formulations.
9. Forensic Science
GC is used by forensic experts to evaluate volatile substances found at crime scenes or in evidence. It aids in the identification of accelerants in arson investigations, the detection of narcotics in bodily fluids, and the analysis of volatile substances in decomposing remains.
10. Biotechnology and Life Sciences
Gas chromatography is used in biotechnology to investigate metabolic pathways, analyze fermentation products, and evaluate gas composition in biological systems. It is also used in plant biology and microbiology research to analyze volatile chemicals.

The significance of Gas chromatography in Various Industrial Applications
The versatility, precision, and ability to separate and analyze complex mixtures of chemical compounds make gas chromatography an indispensable analytical technique across diverse fields.
Analytical Precision
Gas chromatography has high analytical precision, allowing for precise measurement and identification of individual components in a mixture. This precision is critical in areas such as medicines, environmental monitoring, and food analysis, where minute differences in chemical composition can have large consequences.
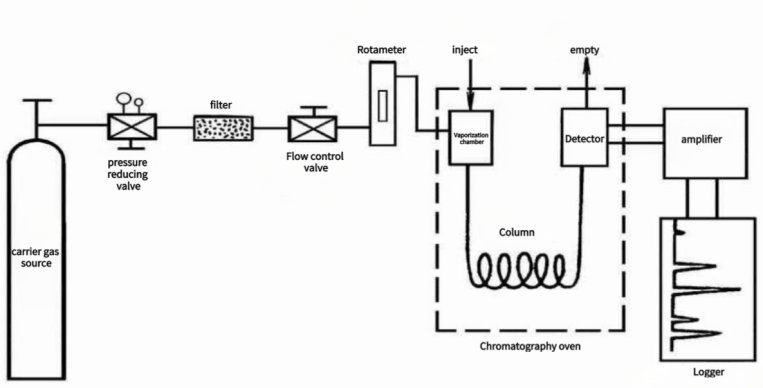
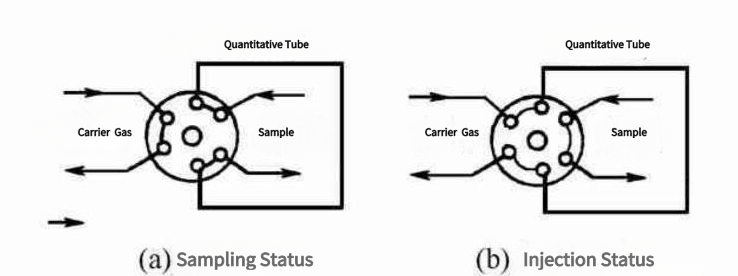
Separation of Complex Mixtures
Many industries deal with complex chemical combinations. The ability of GC to separate and resolve complex mixtures into distinct components simplifies analysis and allows for a more in-depth understanding of sample composition. This is especially useful in the petrochemical, environmental, and pharmaceutical industries.
Quantitative Analysis
GC is renowned for its quantitative capabilities. It allows for the precise measurement of compound concentrations, making it essential in quality control, compliance testing, and research and development efforts across industries, including pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, and materials science.
Identification of Unknown Compounds
Gas chromatography is essential in research and investigative applications for detecting unknown chemicals. Its ability to compare retention times and spectra to reference standards or databases aids in characterizing unknown chemicals, which is important in forensic science, pharmaceutical research, and environmental investigation.
Conclusion
Gas chromatography is a versatile analytical technique with extensive applications in a variety of industries. The capacity of gas chromatography to perform exact, quantitative, and qualitative chemical analysis makes it a vital tool for quality control, research, and regulatory compliance in a variety of disciplines.




