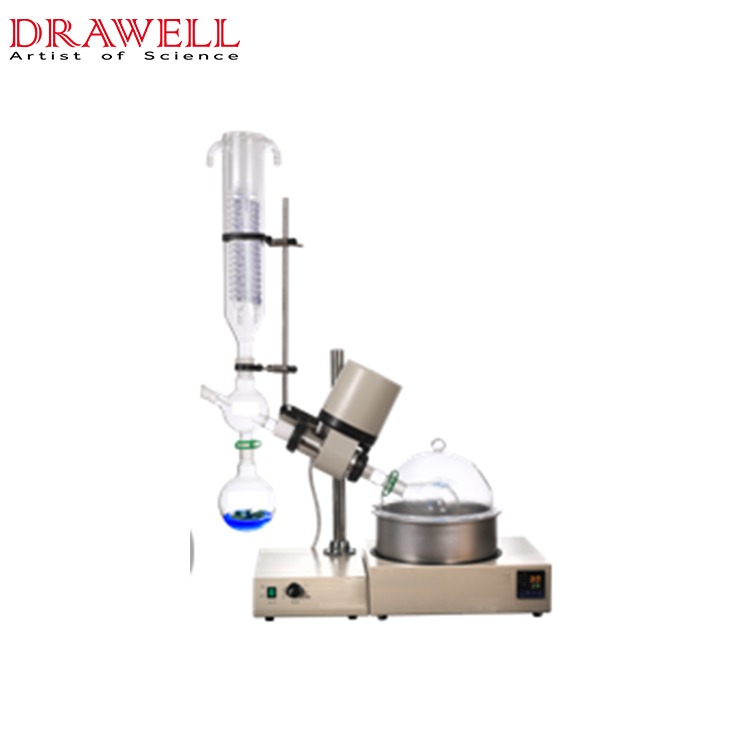
In laboratory settings, the ability to separate and purify compounds is essential for various processes, from chemical analysis to product development. Two commonly used pieces of equipment for this purpose are the Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap) and the Distillation Apparatus. While both serve similar functions, they differ significantly in design, applications, and performance. This article aims to explore the differences between Rotovap and Distillation Apparatus, outline their pros and cons, and help guide you in choosing the most appropriate tool for your laboratory’s specific needs.
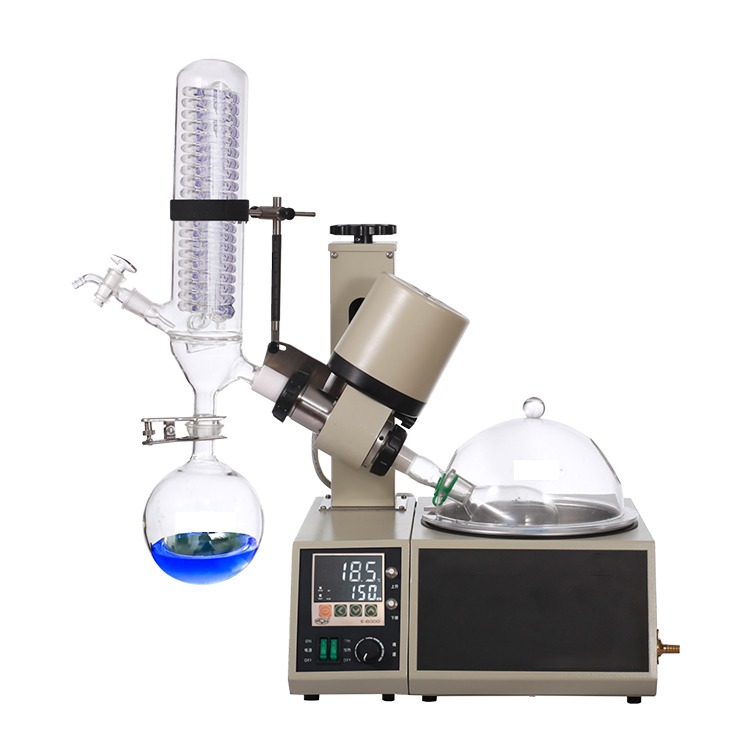

What is Rotovap and Distillation Apparatus?
Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap)
A Rotary Evaporator, often referred to as a Rotovap, is a device primarily used for the efficient removal of solvents from samples by evaporation. It consists of a rotating flask submerged in a heated water bath, connected to a vacuum system, which reduces the pressure inside the flask. The reduced pressure lowers the boiling point of the solvent, allowing it to evaporate at a much lower temperature. A condenser cools the evaporated solvent, which is then collected for reuse or disposal.
Distillation Apparatus
A Distillation Apparatus is a more traditional piece of lab equipment used to separate components of a mixture based on differences in their boiling points. The mixture is heated in a distillation flask, and as each component reaches its boiling point, it vaporizes, travels through a condenser, and is collected in a separate receiver.
Key Differences Between Rotovap and Distillation Apparatus
While both the Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap) and Distillation Apparatus are designed for separating substances, they differ significantly in their operation, applications, and efficiency. Below are the key distinctions:
1. Operating Principle
Rotovap: A Rotovap uses a combination of heat, rotation, and vacuum pressure to speed up the evaporation process. The rotating flask increases the surface area of the liquid, allowing solvents to evaporate more quickly and efficiently under reduced pressure.
Distillation Apparatus: In contrast, a traditional distillation setup separates mixtures based on their boiling points. The liquid is heated until it reaches its boiling point, turning into vapor, which then condenses into a separate container. This process is slower and depends entirely on the temperature and boiling point differences of the components in the mixture.
2. Temperature Control
Rotovap: The use of reduced pressure in a Rotovap lowers the boiling point of solvents, allowing evaporation to occur at much lower temperatures. This makes it ideal for handling temperature-sensitive compounds that could degrade at high temperatures.
Distillation Apparatus: Traditional distillation typically requires higher temperatures to boil off the different components of a mixture. This can pose challenges when working with heat-sensitive substances, as the risk of thermal degradation is higher.
3. Speed and Efficiency
Rotovap: A Rotovap is designed to be faster and more efficient for solvent removal. The continuous rotation of the flask increases the evaporation rate, making it ideal for rapid solvent removal and sample concentration.
Distillation Apparatus: Distillation is generally a slower process because each component in a mixture must be vaporized and condensed separately. The efficiency of the distillation process is determined by the difference in boiling points, with smaller differences resulting in a longer process.
4. Scalability
Rotovap: Typically, Rotovaps are used for small- to medium-scale operations, making them suitable for research labs, academic settings, or smaller industrial processes. Their capacity is limited by the size of the rotating flask.
Distillation Apparatus: A distillation apparatus is more scalable and can handle larger volumes of liquids. This makes it the preferred choice for large-scale separations, industrial laboratories, and applications where larger quantities of material are processed.
5. Application Versatility
Rotovap: Rotovaps are primarily used for solvent removal, concentration of samples, and recovery of solvents. They are particularly valuable in organic chemistry, pharmaceuticals, and natural product extraction.
Distillation Apparatus: Distillation apparatuses are more versatile when it comes to separating complex mixtures, purifying chemicals, and separating high-boiling-point substances. They are often used in petrochemical industries, chemical engineering, and large-scale purification processes.
In summary, the main differences between a Rotovap and a Distillation Apparatus lie in their operational speed, temperature control, scalability, and specific applications. While the Rotovap excels in fast solvent removal at low temperatures, the Distillation Apparatus offers versatility and precision for larger-scale separations and mixtures with a wider range of boiling points.
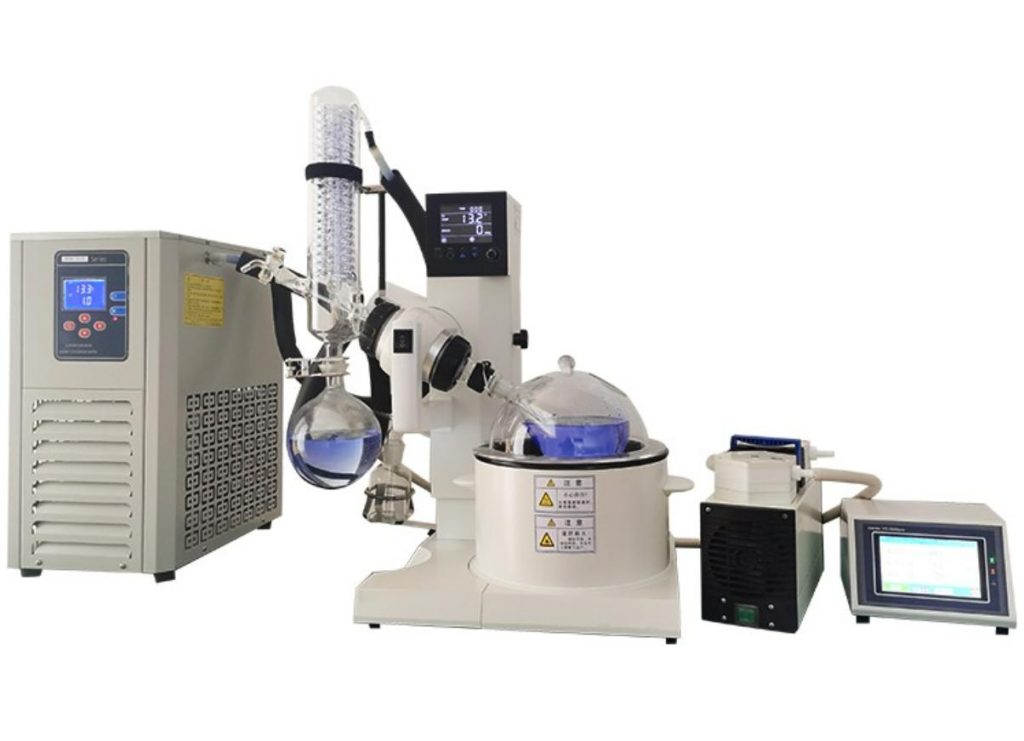

Choosing Considerations Between Rotovap and Distillation Apparatus
When deciding between a Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap) and a Distillation Apparatus, it’s essential to consider the pros and cons of each device based on your lab’s specific requirements. The choice largely depends on factors like the type of substances you’re working with, the volume of materials, and the precision needed for your distillation or evaporation processes. Below is a table comparing the pros and cons of each apparatus, followed by recommendations on when to choose each.
Pros and Cons of Rotovap vs. Distillation Apparatus
| Aspect | Rotovap (Rotary Evaporator) | Distillation Apparatus |
| Pros | Fast and efficient solvent removal | Ideal for separating complex mixtures |
| Low-temperature operation protects heat-sensitive compounds | Suitable for large-scale purifications | |
| Simple and user-friendly for routine lab use | Handles high-boiling-point compounds | |
| Reduces risk of thermal degradation | Versatile for separating mixtures with wide boiling points | |
| Cons | Limited scalability (smallto medium-scale only) | Slower process compared to Rotovap |
| Not ideal for high-boiling-point compounds | Higher temperatures may degrade heat-sensitive compounds | |
| Less precise separation for mixtures with close boiling points | More complex setup, requiring more monitoring |
When to Choose a Rotovap?
A Rotovap is the best choice when your primary need is for fast solvent removal, concentration, or sample preparation. It is particularly useful for handling temperature-sensitive compounds that could degrade at higher temperatures. If you’re working with small-to-medium sized samples or need to perform routine solvent evaporation, a Rotovap will offer the efficiency and control you need.
Best for:
- Solvent removal and recovery
- Organic synthesis
- Concentration of natural extracts
- Pharmaceutical applications
When to Choose a Distillation Apparatus?
Applications: A Distillation Apparatus should be chosen when you need to separate mixtures with components that have wide differences in their boiling points, particularly when dealing with high-boiling-point or thermally stable compounds. This apparatus is more suited for large-scale operations, chemical refinement, or purification of industrial chemicals. It also excels when you need a more precise separation of components.
Best for:
- Chemical purification and separation
- Petrochemical refinement
- Industrial-scale distillations
- Separating mixtures with high-boiling-point substances
Both the Rotary Evaporator (Rotovap) and Distillation Apparatus are valuable tools for laboratory separation and purification tasks, but they are suited for different types of work. The Rotovap is ideal for fast solvent evaporation and working with heat-sensitive substances, making it perfect for smaller lab operations. On the other hand, the Distillation Apparatus shines in large-scale purifications and precise separations, especially when dealing with high-boiling-point compounds. By understanding the differences and advantages of each apparatus, you can make an informed decision on which tool best suits your laboratory’s needs.






