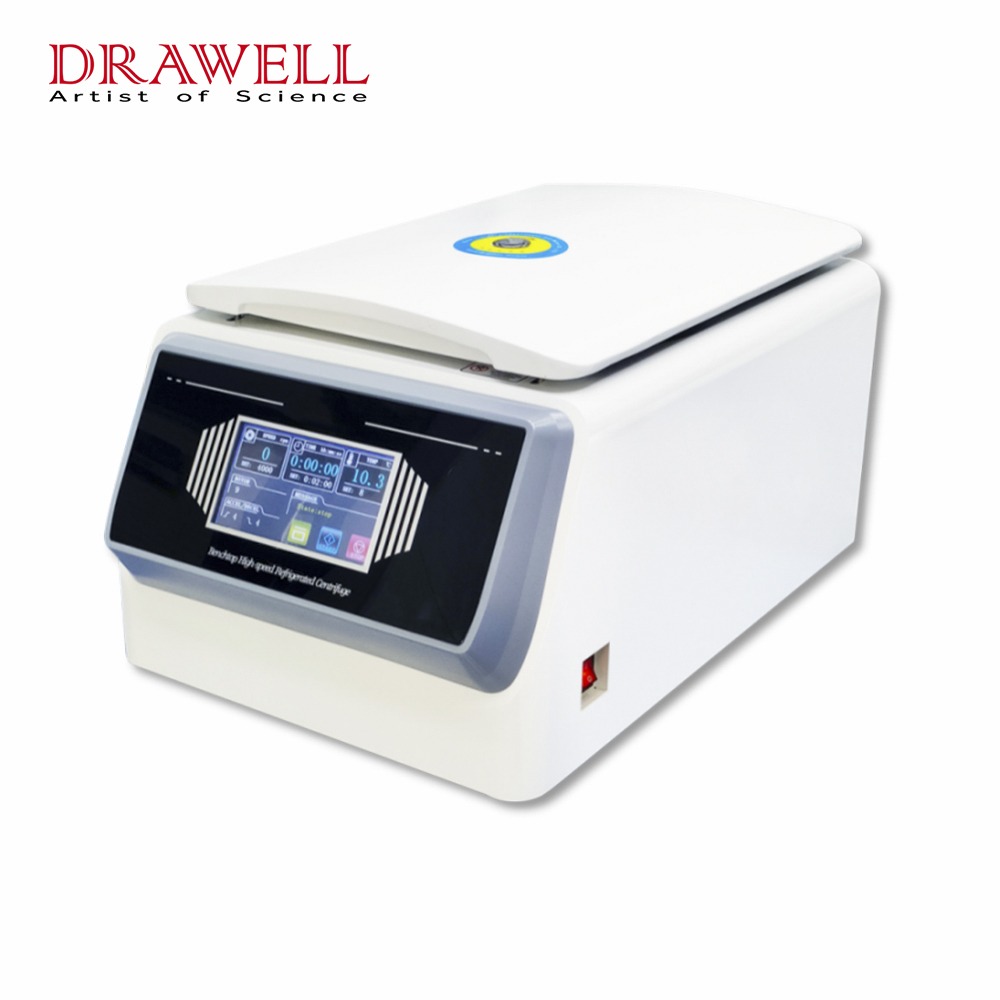
Centrifugation is a fundamental technique used in laboratories to separate substances based on their densities. As laboratory science evolves, the need for precision and efficiency grows, giving rise to sophisticated equipment such as the laboratory refrigerated centrifuge. This technology combines the principles of centrifugation and refrigeration, ensuring that temperature-sensitive samples remain stable throughout the separation process. In this article, we delve into the working principle, components, applications, and maintenance of laboratory refrigerated centrifuges, and introduce you to reliable refrigerated centrifuge suppliers.
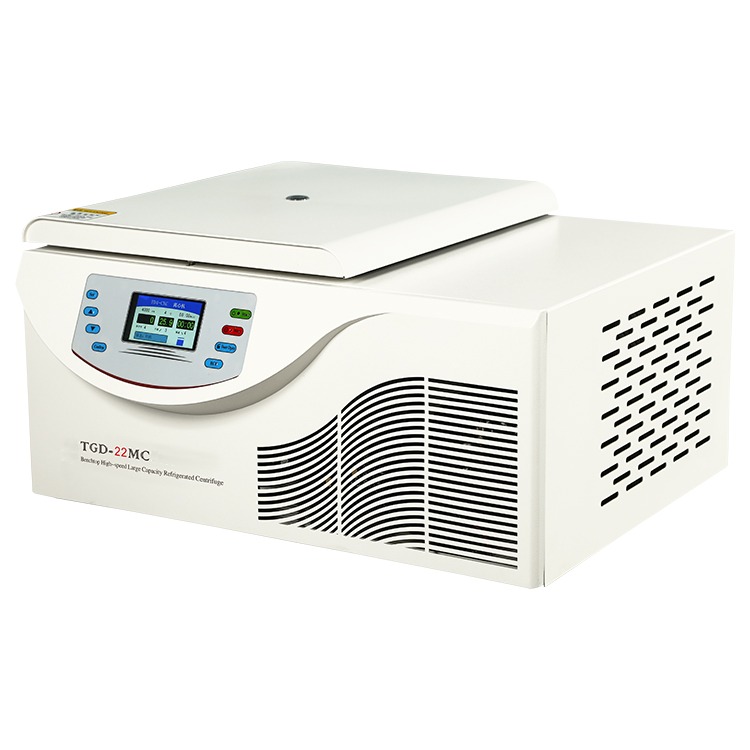

Basic Components of a Laboratory Refrigerated Centrifuge
A laboratory refrigerated centrifuge consists of several key components that work together to achieve precise separation while maintaining sample integrity through temperature control:
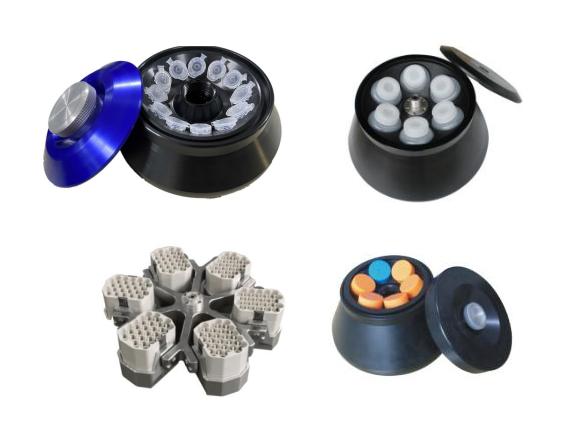
1. Centrifuge Rotor
The rotor holds the sample tubes and spins them at high speeds to generate centrifugal force, which separates the sample components based on density.
Types of Rotors:
- Fixed-Angle Rotors: Hold tubes at a fixed angle relative to the axis of rotation, ideal for rapid separation.
- Swinging Bucket Rotors: Allow tubes to swing out horizontally during centrifugation, suitable for separating components with slight density differences.
- Vertical Rotors: Hold tubes vertically, used for gradient centrifugation.

2. Refrigeration System
The refrigeration system maintains a consistent, low temperature within the centrifuge chamber, ensuring that heat-sensitive samples remain stable during the centrifugation process.
Components:
- Compressor: Pressurizes the refrigerant and circulates it through the system.
- Condenser: Releases heat from the refrigerant to the surroundings.
- Evaporator: Absorbs heat from the centrifuge chamber, cooling the interior.
- Refrigerant: The fluid that circulates through the refrigeration system, transferring heat.
3. Control System
The control system facilitates the precise control and monitoring of the centrifuge’s operating conditions, ensuring accurate and repeatable results.
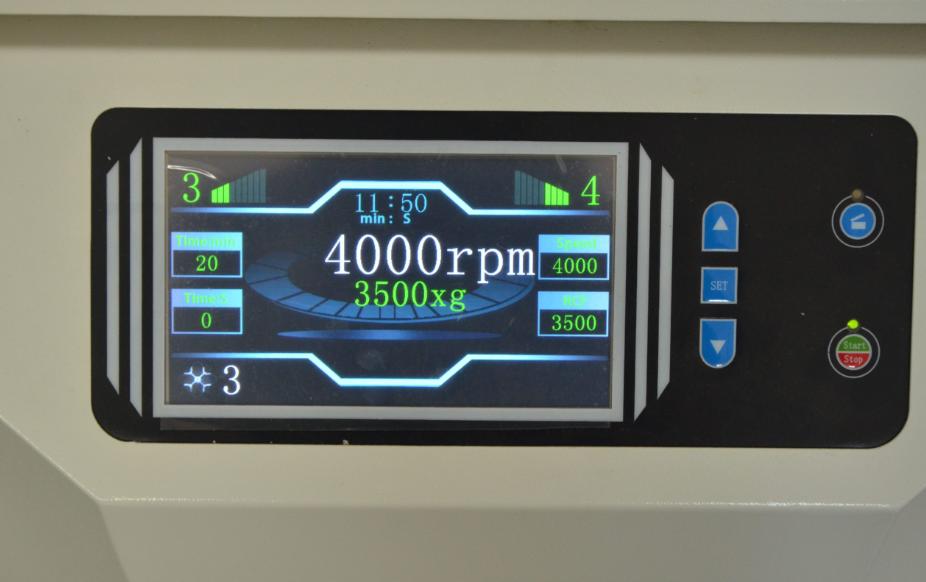
User Interface:
- Control Panel: Allows the user to set parameters such as speed, temperature, and time.
- Digital Display: Provides real-time information about the operating conditions.

4. Centrifuge Chamber
The centrifuge chamber houses the rotor and samples, ensuring that the cooling effect of the refrigeration system is evenly distributed throughout the chamber.
Design:
- Insulated Chamber: Helps maintain a stable temperature by reducing heat exchange with the external environment.
- Sealed Environment: Prevents contamination and ensures consistent cooling.
5. Drive System
The drive system provides the mechanical force needed to spin the rotor at high speeds, generating the centrifugal force necessary for sample separation.
Components:
- Motor: Powers the rotation of the rotor.
- Drive Shaft: Connects the motor to the rotor.
6. Monitoring and Safety Features
These features enhance the safety and reliability of the centrifuge, protecting both the samples and the equipment.
Sensors:
- Temperature Sensors: Monitor the internal temperature to ensure it stays within the set range.
- Speed Sensors: Ensure that the rotor spins at the set speed.
Safety Mechanisms:
- Imbalance Detection: Stops the centrifuge if an imbalance is detected to prevent damage.
- Automatic Shutoff: Engages in case of overheating or other malfunctions.
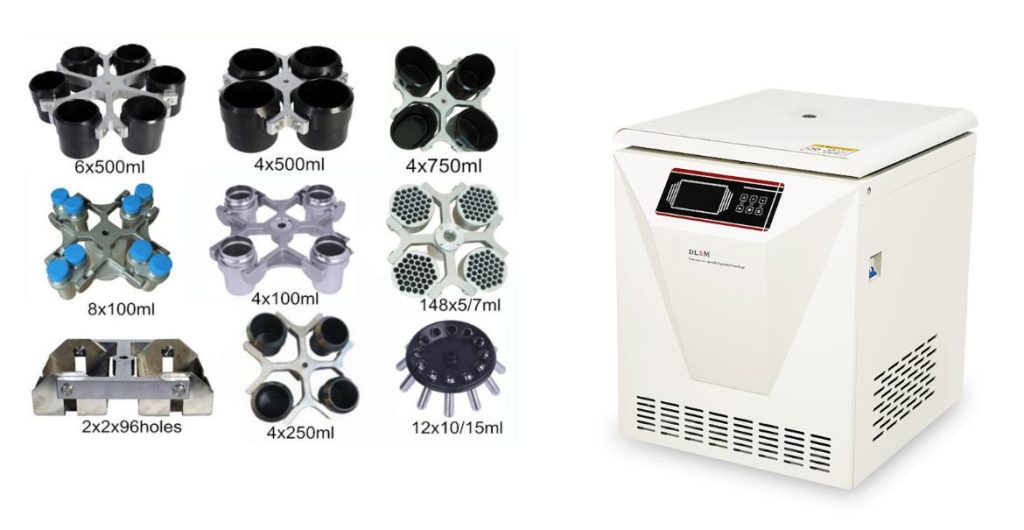

7. Sample Holders and Accessories
These accessories ensure that samples are securely and appropriately positioned within the rotor for optimal separation.
- Tube Holders: Securely hold the sample tubes in the rotor.
- Adapters and Cushions: Accommodate different tube sizes and provide cushioning to prevent tube breakage.
These components work together to provide precise temperature control and efficient sample separation, making laboratory refrigerated centrifuges essential tools in many scientific and clinical applications.
Working Principle of a Lab Refrigerated Centrifuge
The working principle of a lab refrigerated centrifuge involves several key steps to ensure effective separation of sample components while maintaining a controlled, low-temperature environment. Here is a detailed breakdown of the process:
1. Sample Preparation and Loading
Preparation: Samples are prepared and placed into appropriate centrifuge tubes. This may involve adding specific reagents or ensuring the sample is at a particular volume.
Balancing: To prevent imbalance and potential damage, sample tubes must be balanced within the rotor. This typically involves placing tubes of equal weight opposite each other.
2. Temperature Regulation Mechanism
Cooling Activation: Once the samples are loaded and the centrifuge is closed, the refrigeration system activates. The compressor pressurizes the refrigerant, which circulates through the condenser, evaporator, and other components.
Heat Absorption: The evaporator absorbs heat from the centrifuge chamber, effectively lowering the internal temperature. This cooling process is crucial for maintaining the integrity of temperature-sensitive samples.
Temperature Monitoring: Sensors continuously monitor the chamber temperature, ensuring it remains within the set range. If any deviation occurs, adjustments are made automatically to maintain stability.

3. Centrifugation Process
Rotor Acceleration: The motor powers the rotor to accelerate it to the desired speed, which can range from a few hundred to several thousand revolutions per minute (RPM), depending on the application.
Centrifugal Force Generation: As the rotor spins, centrifugal force is generated, pushing the sample components outward. Denser components move further from the axis of rotation, while less dense components stay closer.
Separation: The centrifugal force causes the sample components to separate based on their densities. For example, in blood samples, red blood cells (denser) move outward, while plasma (less dense) remains near the center.
Maintaining Low Temperature: Throughout the centrifugation process, the refrigeration system continues to work, ensuring that the temperature remains low and stable, preventing heat-sensitive components from degrading.
4. Monitoring and Safety Features
Speed Monitoring: Speed sensors continuously monitor the rotor speed, ensuring it matches the set parameters. Any significant deviations result in automatic adjustments or shut down to prevent accidents.
Imbalance Detection: The centrifuge is equipped with imbalance detection systems that monitor the distribution of weight within the rotor. If an imbalance is detected, the centrifuge stops automatically to prevent damage.
Overheating Protection: The refrigeration system prevents overheating by maintaining a constant low temperature. If the system detects overheating, it triggers an automatic shutoff to protect both the samples and the equipment.
5. Completion and Sample Retrieval
Deceleration: After the set centrifugation time, the rotor gradually decelerates to a stop. Rapid deceleration is avoided to prevent disturbance of the separated components.
Sample Retrieval: Once the rotor stops, the centrifuge lid can be opened, and the samples are carefully retrieved. The separated components can then be further analyzed or processed as needed.
By combining these steps, laboratory refrigerated centrifuges ensure precise and reliable separation of samples while maintaining the necessary low-temperature conditions to preserve the integrity of temperature-sensitive components. This combination of centrifugation and refrigeration makes them indispensable tools in various scientific, medical, and industrial applications.

Applications and Benefits
Laboratory refrigerated centrifuges are essential in various fields, including:
Common Applications
They are widely used in biochemistry, molecular biology, and clinical diagnostics for processing biological samples such as blood, urine, and cell cultures. Pharmaceutical industries also rely on these centrifuges for drug development and quality control.
Advantages of Refrigerated Centrifuges
The primary benefit of refrigerated centrifuges is the preservation of sample integrity. By maintaining low temperatures, they prevent the degradation of temperature-sensitive components, ensuring accurate and reliable results. Additionally, the ability to control temperature and speed enhances the precision of separations.
Maintenance and Best Practices
Proper maintenance and adherence to best practices are vital for the longevity and optimal performance of laboratory refrigerated centrifuges:
Regular Maintenance Procedures: Routine cleaning and disinfection of the centrifuge chamber, rotor, and accessories are essential. Regular checks and calibration ensure that the equipment functions correctly and consistently.
Troubleshooting Common Issues: Addressing issues such as temperature fluctuations, imbalances, and mechanical wear promptly can prevent more significant problems. Consulting the user manual and manufacturer guidelines can provide solutions to common operational challenges.
Operational Best Practices: Following best practices, such as balancing samples, using appropriate rotors, and setting correct parameters, is crucial. Operators should also be trained to handle the equipment safely and effectively.

Get Refrigerated Centrifuges from Drawell
For high-quality laboratory refrigerated centrifuges, Drawell offers a range of reliable and efficient models tailored to meet diverse laboratory needs including high or low speed refrigerated centrifuges, benchtop or floortype refrigerated centrifuges. With a commitment to innovation and excellence, Drawell’s centrifuges are designed to provide precise temperature control and robust performance, ensuring that your samples are handled with the utmost care.
In conclusion, laboratory refrigerated centrifuges are indispensable tools in modern scientific research and diagnostics. By combining centrifugation and refrigeration, they enable accurate and efficient separation of samples while preserving their integrity. Proper maintenance and adherence to best practices ensure the longevity and optimal performance of these sophisticated devices. For those seeking reliable refrigerated centrifuges supplier, Drawell provides cutting-edge solutions that meet the highest standards of quality and performance.
Related Products Recommendation