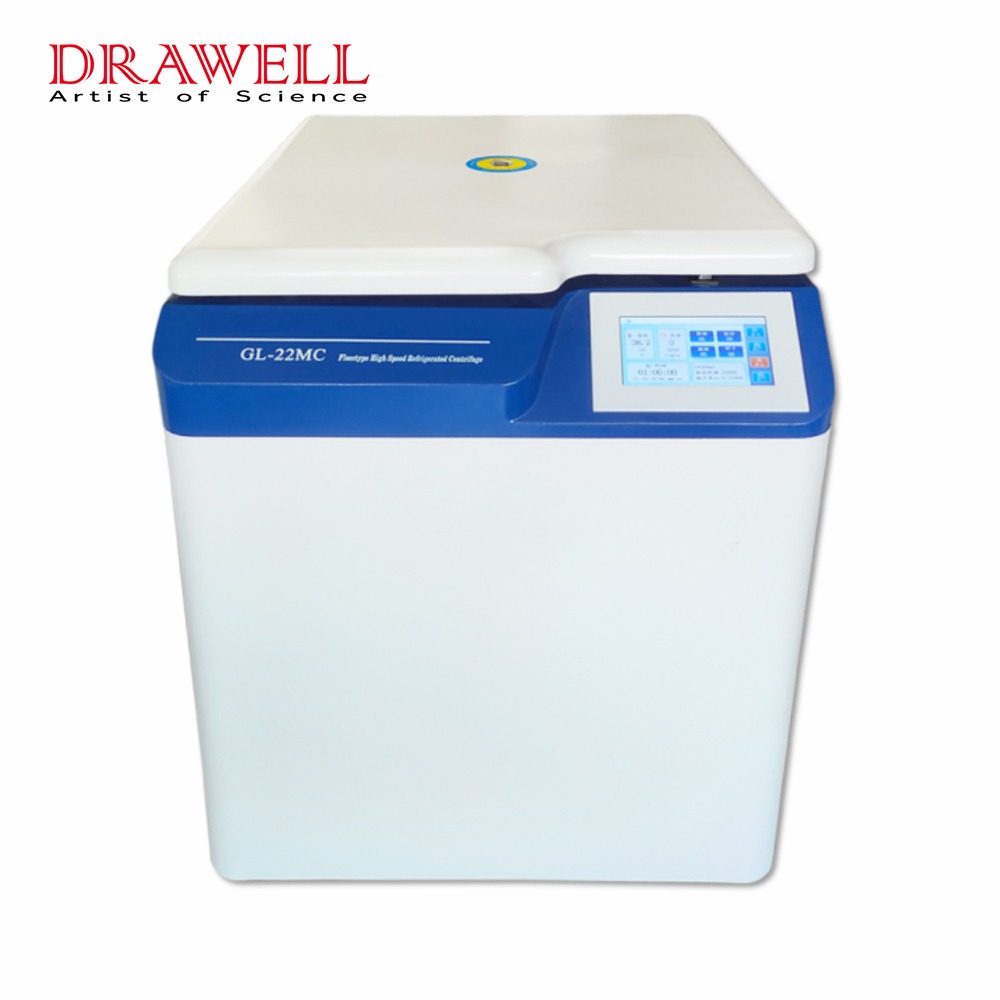
A refrigerated centrifuge is a powerful tool used in various scientific research and industrial applications. It combines the function of a regular centrifuge with the benefit of temperature control, making it ideal for separating particles sensitive to heat or requiring specific processing temperatures. This article will delve into the different types of refrigerated centrifuges, their key features, and basic information you should know before using one.
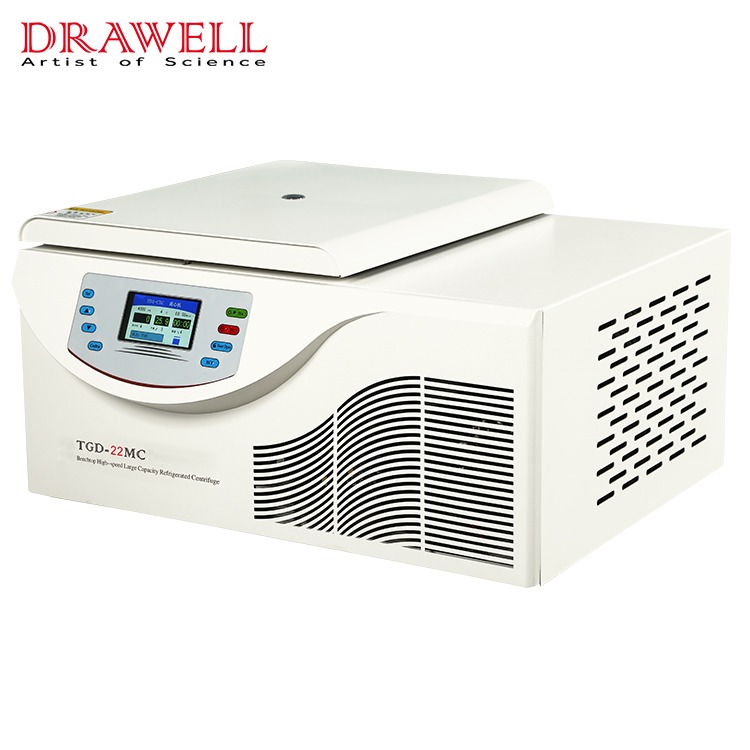

What are the Types of Refrigerated Centrifuges?
Refrigerated centrifuges come in various types, each designed for specific applications. They are classified based on several key factors, here are some common types:
1. Speed:
- Low-speed centrifuges: Up to 6,000 rpm, 4,412 x g, used for separating large volumes of samples such as blood, urine, and cell cultures.
- High-speed centrifuges: Up to 25,000 rpm, 75,000 x g, used for separating high-density particles such as viruses and subcellular organelles.
- Ultracentrifuges: Up to 150,000 rpm, 1,000,000 x g, used for separating very small particles such as macromolecules and viruses.
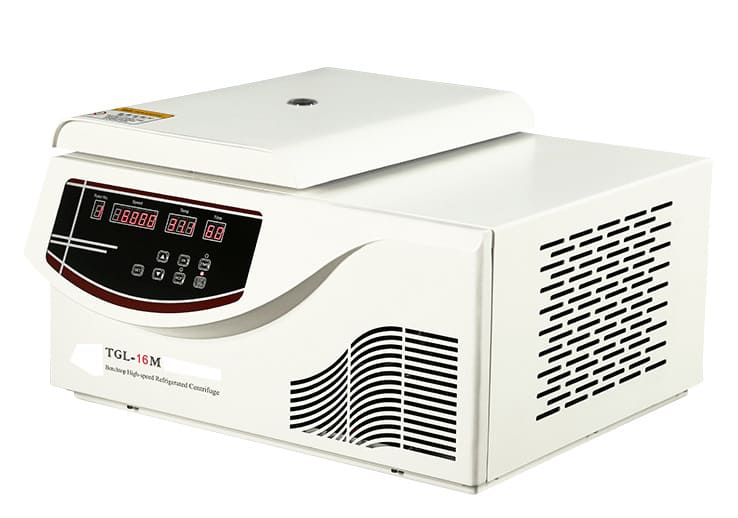

2. Capacity:
- Microcentrifuges: Accommodate small volumes of samples (typically 1.5-2 mL tubes) and ideal for separating nucleic acids, proteins, and cell lysates.
- Benchtop centrifuges: Handle larger volumes and various tube sizes, suitable for general laboratory use.
- Floor centrifuges: Highest capacity, designed for high-throughput applications and accommodating large bottles.
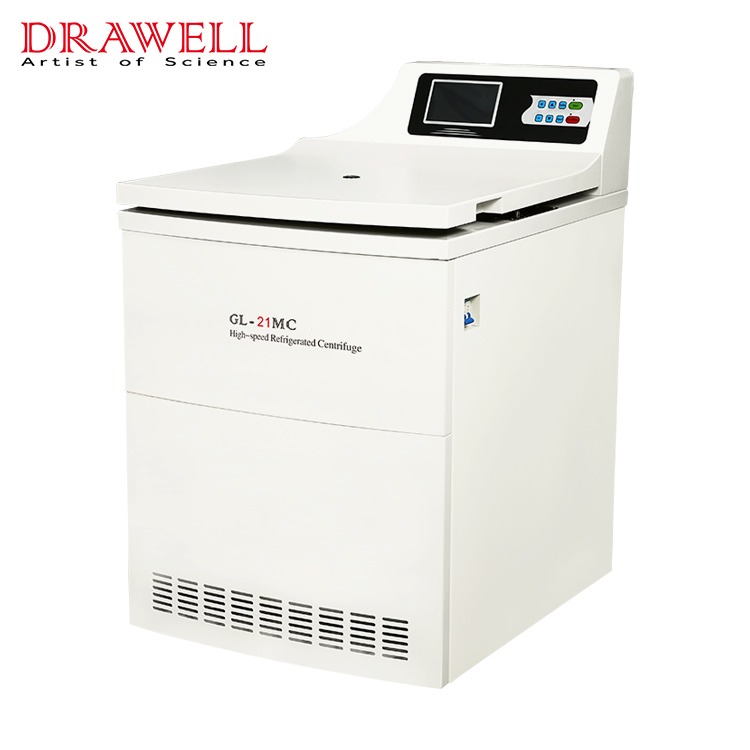

What are the Key Features of Refrigerated Centrifuges?
Here are some key features to consider when choosing a refrigerated centrifuge:
- Speed range: The speed range will determine the types of separations you can perform. Higher speeds are required for separating smaller or denser particles.
- Temperature range: Refrigerated centrifuges typically offer a temperature range between -10°C and 40°C. Choose a model with a temperature range suitable for your samples and applications.
- Rotors and buckets: Different rotors and buckets are available for different types of tubes and sample volumes. Select the appropriate combination based on your needs.
- Safety features: Look for safety features such as automatic lid locking, over-speed protection, and imbalance detection.

How to Use a Refrigerated Centrifuge?
Here are some basic points to consider before using a refrigerated centrifuge:
- Read the manufacturer’s manual carefully. This will provide specific instructions for operating your model safely and effectively.
- Balance the samples evenly. This is crucial for safe operation and prevents damage to the centrifuge.
- Use the appropriate tubes and adapters. Ensure your tubes are rated for the centrifuge’s maximum speed.
- Never open the lid while the centrifuge is running. This can cause injury and damage the samples.
- Clean and disinfect the centrifuge regularly. This helps prevent contamination and ensures optimal performance.
What are the Benefits of Using a Refrigerated Centrifuge?
Refrigerated centrifuges offer various benefits over non-refrigerated models:
- Preserves sample integrity: Refrigeration prevents heat-induced degradation of samples, especially biological materials.
- Improves separation efficiency: Maintaining low temperatures can improve the separation of certain particles.
- Increases versatility: Refrigerated centrifuges are suitable for a wider range of applications.
- Provides precise temperature control: Ensure consistent and reproducible results.
Conclusion
Refrigerated centrifuges are essential tools for various scientific and industrial applications. Understanding their types, features, and basic operation guidelines is crucial for their safe and effective use. By choosing the appropriate model and following best practices, you can ensure optimal results and protect the integrity of your samples.