Pipette
What is Pipette?
A pipette is a device used to transfer liquid quantitatively. It is widely used in biology, chemistry and other fields and in clinical diagnostic laboratories, biotechnology laboratories, pharmaceutical and chemical laboratories, environmental laboratories, and food laboratories. Commonly used pipettes include manual adjustable pipettes and electric ones. There are many optional specifications depending on the volume of the liquid to be transferred.
Working Principle: The working principle of the pipette is that the piston achieves liquid suction and discharge through the expansion and contraction movement of the spring. Under the push of the piston, some air is expelled, the liquid is sucked in by the atmospheric pressure, and then the piston pushes the air to discharge the liquid.
Pipette Types
Single-channel Pipette (Manual&Electronic)
Single-channel pipette is the most common type of pipette and is suitable for most routine experiments. It is easy to operate and maintain, and is an essential tool in the laboratory.
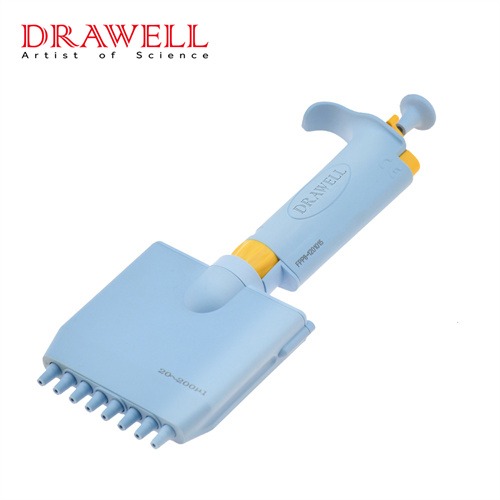
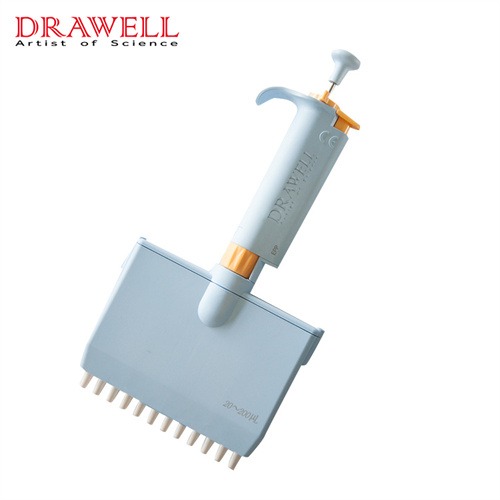
Multi-chnnel Ppipette
Multi-channel pipette is usually used in experiments that require processing multiple samples at the same time, such as high-throughput screening, DNA sequencing, etc. It can transfer multiple samples at one time, greatly improving the efficiency of the experiment.
Features of Pipette
Manual Pipette:
- Lightweight, ergonomic, low force design
- Digital display clearly reads volume setting
- The pipettes cover a wide volume range
- Easy to calibrate and maintain with tool supplied
- Design helps avoid repetitive strain injuries
EP/EPP Adjustable Autoclavable Pipette
• Non-Autoclavable/Fully autoclavable(121℃ for 20min)
• Volume Options: 0.1-2ul, 1-10ul, 2-20ul, 5-50ul, 10-100ul, 20-200ul, 50-300ul, 100-1000ul, 1000-5000ul
IP/IPP Adjustable Autoclavable Pipette
• IPP series fully autoclavable. ( 121℃ for 20 minutes )
• Volume Options: 0.1-2ul, 1-10ul, 2-20ul, 5-50ul, 10-100ul, 20-200ul, 50-300ul, 100-1000ul, 1000-5000ul, 1000-10000ul
EPP8 MultiChannel Pipette
• Fully autoclavable. ( 121℃ for 20 minutes )
• Volume Range options: 1-10ul, 2-20ul, 5-50ul, 20-200ul, 30-300ul
EPP12 MultiChannel Pipette
• Fully autoclavable. ( 121℃ for 20 minutes )
• Volume Range options: 1-10ul, 2-20ul, 5-50ul, 20-200ul, 30-300ul
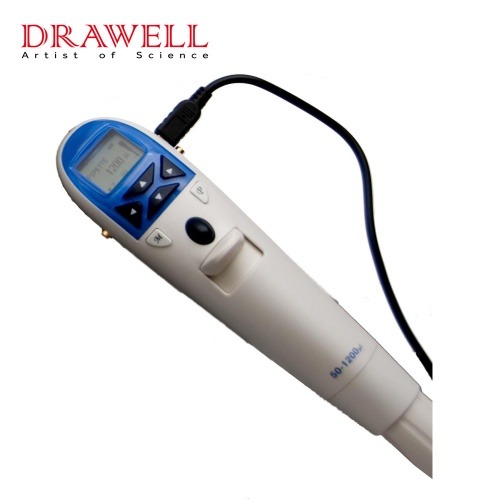
Electronic Pipette:
- High accuracy and precision.
- High-quality stepper motor and piston control system provide outstanding accuracy and repeatability in results, which reduce manual operation errors.
- High-level ergonomic handle design
- Lightweight and compact to protect users from repetitive strain injury.
- Simple to use and versatile
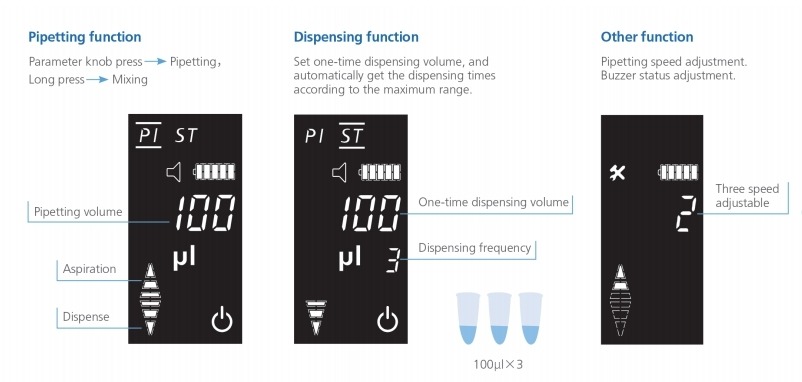
- Double knobs for simple and versatile control. Dispensing function reduces the pipetting steps and speeds up work.
- Dual charging mode
- Using the USB charge or charging stand to ensure uninterrupted use.
ESP Electronic Single Pipette
• Volume Range options: 0.5-10ul, 5-100ul, 20-300ul, 50-1200ul
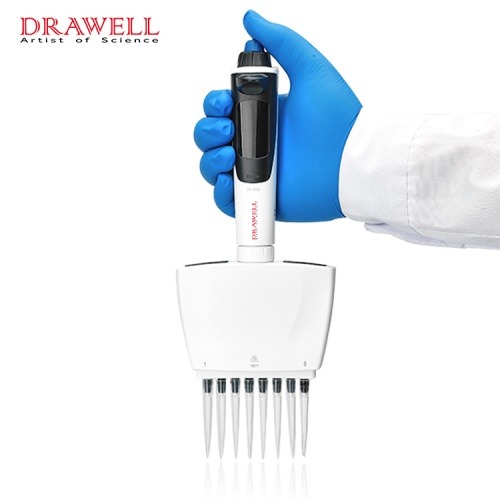
dPette Multifunctional 8-channel Electronic Pipette
• Volume Range options: 0.5-10ul, 10-100ul, 15-300ul, 30-300ul
Application of Pipette
1. Laboratory demand. The laboratory is the main use scenario of pipettes. With the rapid development of the bio pharmaceutical industry, the demand for laboratories is also increasing. Especially in the fields of molecular biology, cell biology and clinical diagnosis, the demand for pipettes is particularly urgent.
2. Medical demand. In addition to the laboratory field, the medical field also has a certain demand for pipettes. For example, in clinical diagnosis, sample analysis and testing are required, and pipettes can help medical staff to accurately divide and mix samples.
3. Industrial manufacturing demand. In the production of bio pharmaceuticals and medical devices, pipettes are also needed to transfer and mix various liquids. Therefore, the industrial manufacturing field is also a potential market for pipettes.
Components of Electronic Pipette(ESP series)

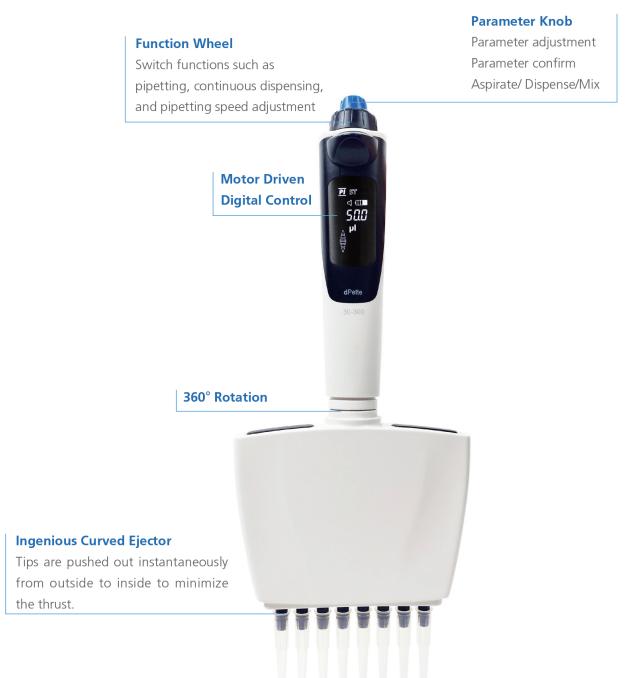
Main Structure of Electronic Pipette(dPette series )


.jpg)