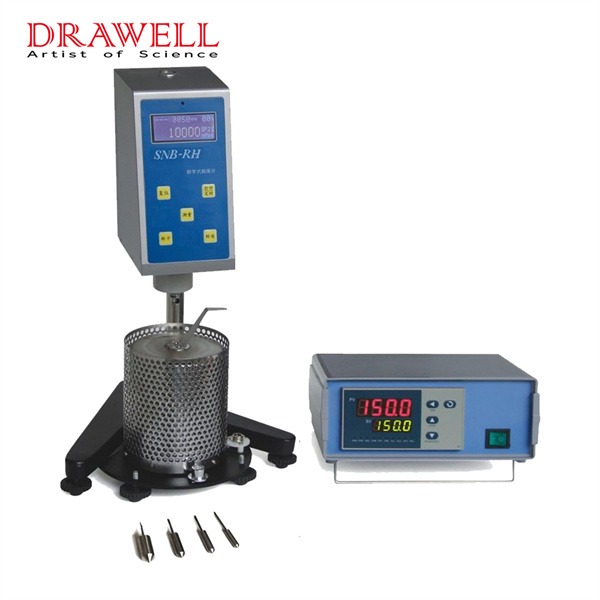
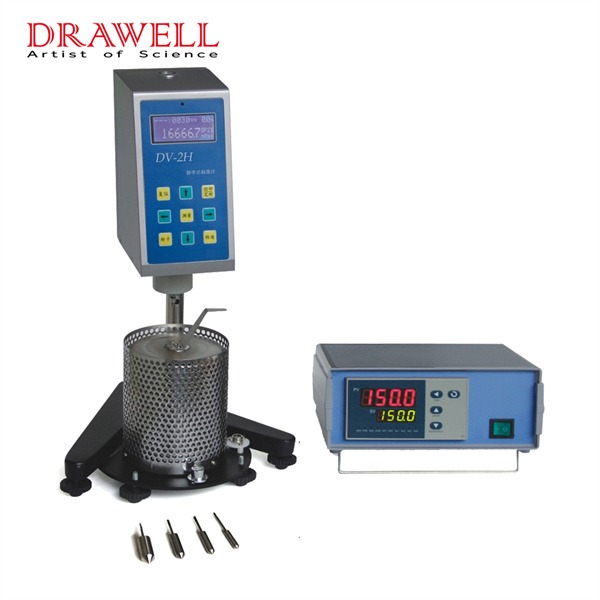
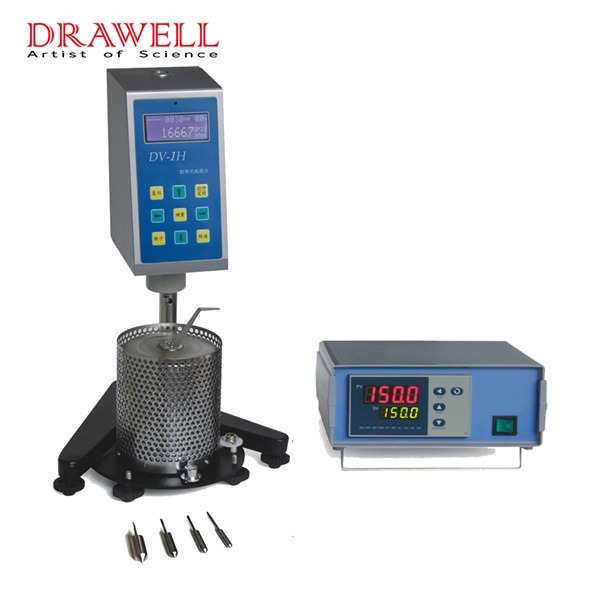
Rotational viscometers are essential tools in laboratories and industries. Understanding viscosity—the resistance of a fluid to flow—helps in evaluating product consistency, quality, and performance. Learning to use a rotational viscometer is vital for anyone involved in product formulation, quality assurance, or process management, as it provides insights that support quality, safety, efficiency, and innovation across various fields. Here let’s learn together.
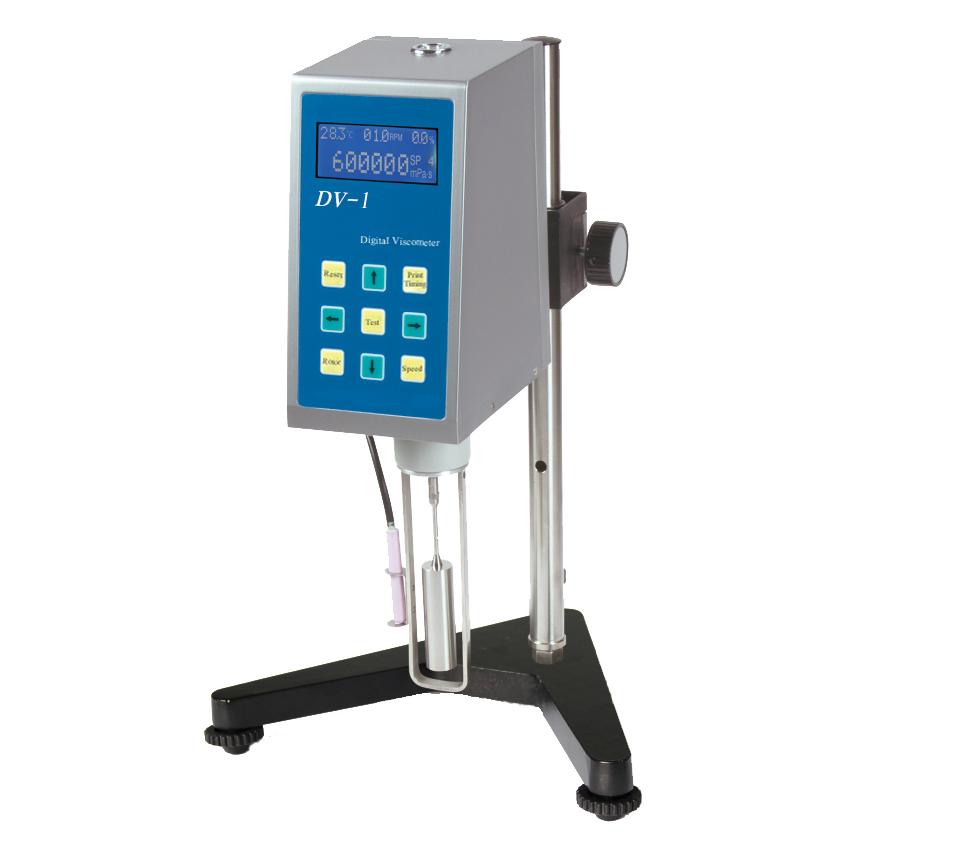
What is Rotational Viscometer?
A rotational viscometer measures the viscosity of a fluid by determining the resistance it exerts on a rotating spindle. It calculates viscosity based on the force required to rotate the spindle at a controlled speed within the sample fluid. This instrument is widely used because it can handle a variety of fluids—from thin liquids to thick pastes—and provides quick, reliable results.
Components of Rotational Viscometer:
- Spindle: A rotating element submerged in the fluid. The spindle’s resistance to movement, caused by the fluid’s viscosity, generates data for viscosity calculation.
- Motor: Drives the spindle’s rotation at a constant speed, critical for consistency in measurement.
- Torque Sensor: Measures the force needed to rotate the spindle. This force correlates with viscosity, giving a direct reading of the fluid’s resistance.
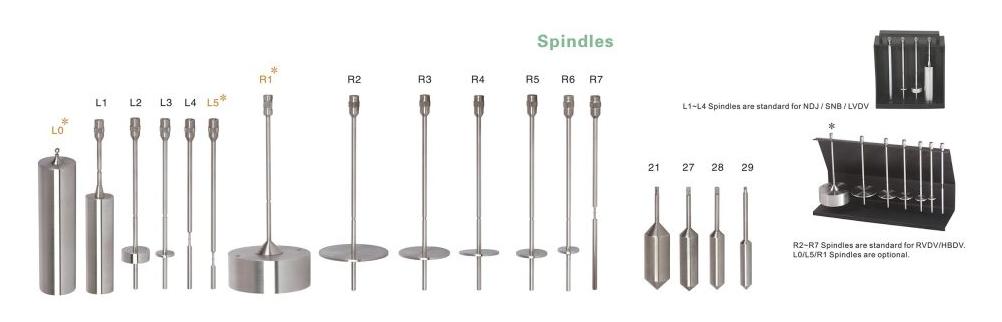
Rotational viscometers come in several types, such as Brookfield Viscometer, Cone and Plate Viscometer, and Coaxial Cylinder (Couette) Viscometer etc. Each designed to measure viscosity in specific ways to suit various fluid properties and application requirements. Drawell can provide you digital rotational viscometers such as NDJ and DV series viscometers. Feel free to contact us when you need.
Understanding the components, functions and types are crucial to using rotational viscometer effectively. Let’s diving in how to use it.
Step-by-Step Guide to Use the Rotational Viscometer
To achieve reliable and accurate readings, each stage in using a rotational viscometer is important. Below are detailed steps for setting up, preparing the sample, operating the device, and interpreting the results.
1. Setting Up the Rotational Viscometer
Setting up the rotational viscometer properly is essential for accuracy. Before taking any measurements, the device must be calibrated and configured to suit the characteristics of the sample fluid. The setting including:
- Assemble the Spindle and Motor: Ensure the spindle is securely attached to the motor and that the connection is tight to prevent vibration.
- Calibrate the Device: Perform an initial calibration using a known standard fluid. This process will vary by device, so consult the manual to ensure you’re following the correct procedure.
- Select the Correct Spindle and Speed: Based on the fluid’s expected viscosity range, choose a spindle size and rotation speed that matches your sample. Manufacturers often provide tables for spindle and speed selection to optimize measurement accuracy.
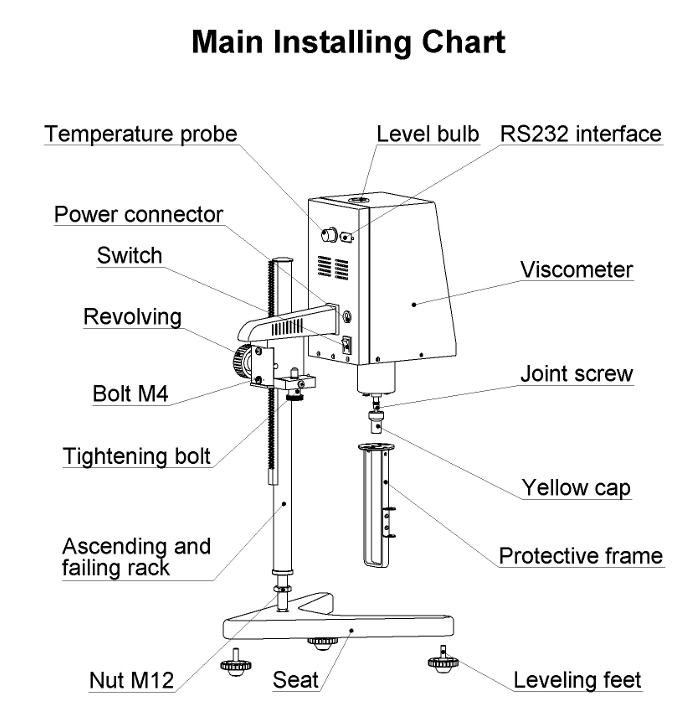
2. Preparing the Sample
Sample preparation is a key step in obtaining accurate viscosity measurements. Variables like sample volume, temperature, and cleanliness all affect the reading outcome, so careful preparation is essential. The preparing should including:
- Control the Temperature: Viscosity changes with temperature, so bring the sample to the desired temperature before testing. Many viscometers include a temperature control option, but if not, use an external thermometer.
- Measure the Correct Volume: Use the recommended sample volume indicated by the viscometer’s specifications. Overfilling or underfilling the sample container can affect the reading and damage the spindle.
- Avoid Contamination: Use a clean sample container and ensure no contaminants are introduced, as foreign particles or residue from previous tests can interfere with measurements.
3. Using the Rotational Viscometer
With the viscometer set up and the sample prepared, it’s time to conduct the measurement. This part involves specific actions to ensure smooth and accurate testing. Some using tips are:
- Immerse the Spindle Properly: Lower the spindle into the fluid until it reaches the recommended depth, ensuring it is neither too deep nor too shallow.
- Start the Device and Set Speed: Power on the viscometer, and choose the preset speed as indicated during setup. Allow the spindle to rotate until the display shows a stable reading.
- Record the Measurement: Once the viscosity reading stabilizes, document the value. Repeat the process if necessary to confirm accuracy.
4. Interpreting Results
- Evaluate Viscosity Values: Compare your recorded viscosity with the expected values for the sample type to verify if it meets specifications.
- Understand Viscosity Units: Viscosity is usually recorded in centipoise (cP) or Pascal-seconds (Pa·s). Ensure you’re interpreting values in the correct units for your application.
- Identify Anomalies: If viscosity values fall outside the expected range, consider potential causes such as incorrect setup, improper sample preparation, or device calibration issues.
Proper operation ensures that the rotational viscometer yields accurate viscosity data. Staying attentive to the process helps avoid errors and maintains consistency in readings.

Maintenance and Care of the Rotational Viscometer
Regular maintenance is essential to ensure the longevity and accuracy of a rotational viscometer. Proper care, cleaning, and storage practices keep the equipment in good working order and minimize measurement errors over time. Some tips are:
- Clean the Spindle After Each Use: Use a suitable cleaning agent to remove any residue from the spindle after each test. Avoid abrasive cleaners that could damage the spindle’s surface.
- Check Calibration Regularly: Regular calibration with standard fluids ensures continued accuracy, ideally every few months or after heavy usage.
- Store in a Stable Environment: Keep the viscometer in a clean, dry area where it is safe from dust, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations. Proper storage prevents deterioration of sensitive components.
Using a rotational viscometer involves more than simply turning on the device and recording data. Each stage—from setup to sample preparation, operation, and interpretation—contributes to the overall accuracy and reliability of your measurements. By adhering to the guidelines outlined above and regularly maintaining the equipment, you’ll maximize the rotational viscometer’s potential and ensure that it delivers precise viscosity data.








