Freeze drying, a sophisticated preservation method celebrated for its ability to maintain the integrity and longevity of various products, undergoes a transformative journey when transitioning from laboratory-scale experimentation to industrial production. This journey is fraught with challenges, yet armed with strategic approaches, these obstacles can be overcome. In this article, we delve into the intricacies of scaling up laboratory freeze drying processes to industrial scale, exploring the hurdles encountered and strategies employed to overcome them.
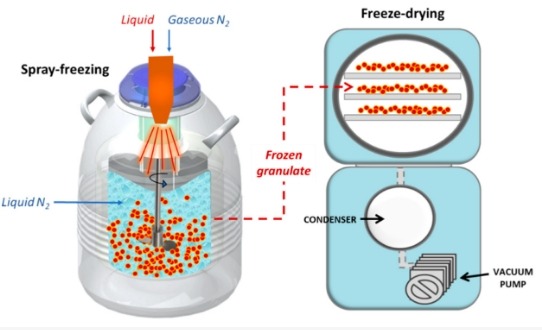
Understanding Laboratory Freeze Drying
Here’s a simplified table outlining the key aspects of laboratory freeze drying processes:
1. Processes
| Stage | Description |
| Freezing | Product is frozen to solidify water content |
| Freezing conditions affect ice crystal size | |
| Primary Drying | Primary drying removes ice through sublimation |
| Low temperature and reduced pressure | |
| Secondary Drying | Secondary drying removes bound water molecules |
| Elevated temperature and reduced pressure |
2. Equipment
| Equipment | Features |
| Freeze Dryer | Vacuum chamber for reduced pressure |
| Condenser for capturing evaporated water vapor | |
| Shelves for holding product |
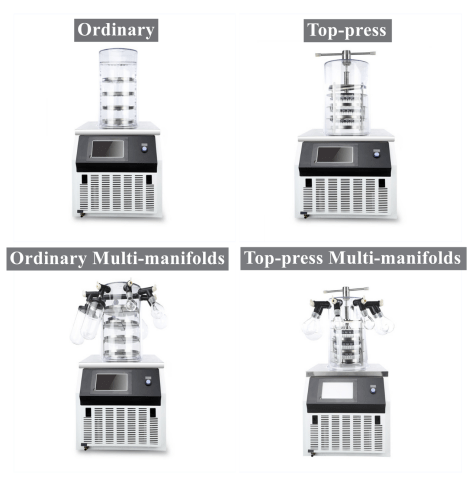

3. Key Aspects of Control and Monitoring
| Control and Monitoring | Aspects |
| Temperature | Controlled to facilitate freezing and drying |
| Pressure | Adjusted to optimize sublimation and desorption |
| Vacuum Level | Maintained to promote water vapor removal |
| Product Moisture Content | Monitored to determine drying progress |
4. Key Factors to Considered in Maintaining Product Quality
| Product Quality | Considerations |
| Structure Preservation | Maintain integrity of product structure |
| Shelf Life Extension | Extend shelf life by removing moisture |
| Retention of Bioactivity | Preserve biological and pharmaceutical activity |
| Minimal Damage or Loss | Minimize damage or loss of volatile compounds |
5. Applications
| Applications | Examples |
| Pharmaceuticals | Drug formulations, vaccines, biologics |
| Food | Freeze-dried fruits, vegetables, instant coffee |
| Biological Samples | Cells, tissues, enzymes |
| Chemicals | Laboratory reagents, standards |
Challenges in Scaling Up Laboratory Freeze Drying Processes to Industrial Production
1. Equipment Design and Capacity
Lab freeze dryers are typically smaller and have limited capacity compared to industrial-scale equipment. Upscaling requires the design and installation of larger freeze dryers capable of handling increased volumes of materials while maintaining optimal drying conditions. Ensuring that the industrial equipment is robust, efficient, and meets regulatory standards is essential.
2. Uniformity of Drying
Achieving uniform drying across large-scale batches is crucial for maintaining product quality and consistency. Laboratory setups often offer better control over drying conditions, leading to more uniform results. However, in industrial settings, variations in temperature, pressure, and airflow can impact drying uniformity. Optimizing process parameters and implementing strategies to ensure even distribution of heat and mass transfer is necessary to overcome this challenge.
3. Process Control and Monitoring
Lab freeze drying processes are closely monitored and controlled to ensure reproducibility and product quality. Scaling up requires the implementation of advanced control systems capable of managing larger batches and maintaining tight control over critical parameters such as temperature, pressure, and drying time. Real-time monitoring and feedback mechanisms are essential to detect and correct deviations from desired conditions promptly.
4. Energy Consumption and Efficiency
Freeze drying is an energy-intensive process, and scaling up can significantly increase energy consumption. Industrial production facilities need to invest in energy-efficient equipment and optimize process parameters to minimize energy usage while maximizing productivity. Implementing energy recovery systems and optimizing cycle designs can help reduce operating costs and environmental impact.
5. Regulatory Compliance
Meeting regulatory requirements is a critical aspect of scaling up freeze drying processes to industrial production. Industrial facilities must comply with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other regulatory standards to ensure product safety, quality, and consistency. This involves implementing robust quality control measures, documentation practices, and validation protocols to demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
6. Cost Considerations
Scaling up laboratory freeze drying processes to industrial production involves significant capital investment in equipment, infrastructure, and personnel. Manufacturers need to carefully assess the costs associated with scaling up and develop a comprehensive budget that accounts for all expenses, including equipment procurement, facility modifications, and operational costs. Balancing upfront investment with long-term profitability is essential for successful scale-up.

Strategies for Scaling Up Laboratory Freeze Drying Processes to Industrial Production
Scaling up laboratory freeze drying processes to industrial production requires careful planning and strategic implementation to ensure a smooth transition while maintaining product quality and efficiency.
1. Pilot-Scale Studies
Before scaling up, conduct pilot-scale studies to evaluate the feasibility and challenges of transitioning to industrial production. These studies involve replicating industrial conditions on a smaller scale to identify potential issues, optimize process parameters, and validate equipment performance.
2. Equipment Selection and Design
Choose industrial-scale freeze dryers that are suitable for the specific requirements of the intended production volume and product characteristics. Ensure that the selected equipment is capable of handling larger batches, maintaining uniform drying conditions, and meeting regulatory standards. Customization of equipment may be necessary to accommodate specific process requirements.

3. Process Optimization
Optimize process parameters such as shelf temperature, chamber pressure, and drying time to achieve desired product characteristics while maximizing efficiency and productivity. Utilize mathematical modeling and computational simulations to predict the behavior of the freeze drying process at an industrial scale and optimize process parameters accordingly.
4. Control Systems and Monitoring
Implement advanced control systems and monitoring technologies to ensure consistent and reproducible product quality. Real-time monitoring of critical process parameters such as temperature, pressure, and product moisture content enables proactive control and adjustment of process conditions to minimize variability and maintain product integrity.
5. Energy Efficiency
Invest in energy-efficient equipment and optimize process designs to minimize energy consumption and operating costs. Implement energy recovery systems such as heat exchangers and condensers to capture and reuse waste heat generated during the freeze drying process, thereby improving overall energy efficiency.
6. Quality Assurance and Regulatory Compliance
Develop and implement robust quality assurance protocols to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements such as Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and product quality standards. Establish comprehensive validation procedures for equipment, processes, and products to demonstrate compliance and ensure product safety and efficacy.
7. Training and Personnel Development
Provide training and education to personnel involved in the scaling-up process to ensure they are proficient in operating industrial-scale equipment and following established protocols. Develop standard operating procedures (SOPs) and documentation practices to maintain consistency and traceability throughout the production process.
8. Risk Management
Identify potential risks and develop mitigation strategies to minimize their impact on the scaling-up process. Conduct thorough risk assessments to identify critical process parameters, failure modes, and potential hazards, and implement measures to prevent or mitigate their occurrence.

Conclusion
Scaling up laboratory freeze drying processes to industrial production presents a myriad of challenges that demand careful planning, technical expertise, and regulatory compliance. By employing advanced equipment, process optimization techniques, and quality-driven approaches, manufacturers can navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring efficient, reliable, and compliant production of high-quality freeze-dried products at an industrial scale.