Polarimeters are indispensable tools in pharmaceutical quality control, widely used to analyze the optical properties of chiral compounds. These instruments measure optical rotation, a property of optically active substances that rotate polarized light. Since many active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and drugs are chiral, polarimetry plays a critical role in ensuring the safety, efficacy, and consistency of pharmaceutical products.

Understanding the Role of Polarimetry in Pharmaceutical Quality Control
Polarimetry measures the rotation of polarized light as it passes through optically active substances. Many pharmaceutical compounds, particularly APIs, are optically active due to their molecular structure. By analyzing optical rotation, polarimeters provide information about the compound’s chiral nature, concentration, and potential impurities.
This data is crucial for compliance with stringent regulatory standards in pharmaceutical manufacturing, where even minor deviations in chirality or concentration can affect a drug’s therapeutic efficacy or safety profile.
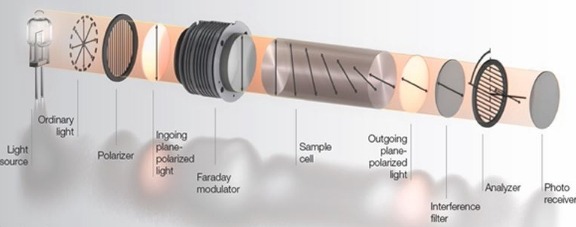
Key Applications of Polarimeters in Pharmaceutical Quality Control
1. Chiral Purity Analysis
Many drugs consist of enantiomers, which are molecules that are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. These enantiomers can have vastly different effects in biological systems. For instance, one enantiomer might be therapeutic, while the other could be inactive or even harmful.
Polarimeters are used to measure the optical rotation of pharmaceutical compounds, providing data on the enantiomeric excess and ensuring the desired enantiomer is predominant. This is essential for drugs where chiral purity directly influences their therapeutic effectiveness and safety.
2. Concentration Verification
Polarimetry allows for accurate determination of the concentration of optically active substances in solutions. By comparing the measured optical rotation to standard values, manufacturers can verify that formulations meet the required specifications. This is a non-destructive and highly efficient method for assessing concentration in both raw materials and finished products.
3. Quality Control of Raw Materials
The identity and purity of raw materials used in drug production are critical to ensuring consistent product quality. Polarimeters help verify the authenticity of optically active raw materials, such as sugars, amino acids, and other chiral compounds. This prevents the use of substandard or counterfeit materials that could affect product performance.
4. Impurity Detection
Impurities or by-products can alter the optical rotation of a compound. By analyzing deviations in optical rotation, polarimeters can detect these impurities, enabling corrective actions to maintain the purity and integrity of pharmaceutical products.
5. Stability Studies
Pharmaceutical products are subjected to stability testing to evaluate their shelf life and resistance to degradation under various conditions. Polarimeters are used in these studies to monitor changes in optical rotation over time. Any variation can indicate chemical changes, such as isomerization or degradation, providing insights into the product’s stability and storage requirements.

Advancements in Polarimeters for Pharmaceutical Quality Control
Over the years, technological advancements have significantly improved the capabilities of polarimeters, making them even more reliable, efficient, and user-friendly in pharmaceutical applications.
1. Digital Polarimeters with Enhanced Precision
Digital polarimeters have drastically improved measurement precision compared to their analog predecessors. They utilize advanced electronics and algorithms to calculate optical rotation with greater accuracy. This increased precision is essential in pharmaceutical quality control, where even the smallest deviations in optical rotation can indicate impurities, incorrect formulations, or inconsistencies in chiral purity.
Advanced digital polarimeters are capable of measuring optical rotation at higher resolutions and with faster response times. This allows for more sensitive detection of changes in optical rotation, which is critical for ensuring that active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) are within the required specifications for purity and concentration.

2. Temperature Control for Stable Measurements
Many pharmaceutical compounds are sensitive to temperature variations, which can lead to shifts in optical rotation. Modern polarimeters incorporate advanced temperature control systems to maintain a stable and consistent environment during measurements. This feature ensures that the optical rotation readings are not influenced by temperature fluctuations, providing more accurate and reproducible results.
Temperature-controlled polarimeters are particularly important when analyzing substances with narrow optical rotation ranges or substances that are susceptible to degradation or isomerization when exposed to temperature changes. These advancements allow for more reliable results in stability studies, concentration verification, and purity assessments.
3. Multi-Wavelength Polarimetry
The development of multi-wavelength polarimeters has expanded the scope of polarimetry in pharmaceutical applications. Traditional polarimeters use a single wavelength of light to measure optical rotation. However, multi-wavelength polarimeters allow for the use of multiple wavelengths, enabling the analysis of a wider range of compounds, particularly those that exhibit wavelength-dependent optical rotation.
By using multiple wavelengths, multi-wavelength polarimeters can analyze more complex substances, including those with varying molecular structures and optical characteristics. This versatility is especially useful when working with complex drug formulations or substances that may exhibit different optical properties at different wavelengths, such as certain sugars, amino acids, and biologically active compounds.
4. Automation and Integration with LIMS
Automatic polarimeters have become a key advancement, streamlining the measurement process and reducing the potential for human error. Automated sample handling systems allow for the precise and consistent analysis of multiple samples in a shorter amount of time. These systems can be programmed to handle a variety of sample types, ensuring that the correct procedures are followed for each analysis.
Furthermore, many modern polarimeters are now integrated with Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS). This integration allows for seamless data transfer, storage, and analysis, making it easier to track sample history, monitor trends, and maintain regulatory compliance. Automated reporting features reduce the need for manual data entry, ensuring that results are accurately recorded and easily accessible for further analysis or regulatory review.

5. Improved User Interfaces
Advancements in user interfaces have made modern polarimeters more accessible and easier to operate. Touchscreen displays, intuitive software, and simplified control systems allow for faster setup and smoother operation. These user-friendly interfaces reduce training time for personnel and minimize the likelihood of errors during operation.
Many polarimeters now feature software with built-in data analysis tools, allowing users to instantly analyze results and generate reports. The ability to customize analysis parameters and automate data processing ensures that pharmaceutical quality control professionals can quickly obtain the information they need without manual calculations.
6. Enhanced Sensitivity and Detection Limits
In pharmaceutical quality control, detecting even minute changes in optical rotation is critical. Advancements in detector technology have enhanced the sensitivity of modern polarimeters, allowing them to measure very small changes in optical rotation. This is especially important for applications such as impurity detection, where low levels of contaminants can have significant effects on drug safety and efficacy.
The increased sensitivity also makes it easier to analyze low-concentration substances, enabling polarimeters to be used in a wider range of pharmaceutical applications, from raw material verification to finished product testing.

Regulatory Compliance of Polarimeters in Pharmaceutical Quality Control
This chart outlines the key aspects of how polarimeters contribute to ensuring compliance with regulatory standards in pharmaceutical quality control, including their role in calibration, documentation, and validation.
| Regulatory Compliance Aspect | Role of Polarimeters in Compliance |
| Pharmacopeial Standards | Polarimeters are validated by pharmacopeial standards such as USP and EP for measuring optical rotation to ensure purity, identity, and concentration of chiral substances. |
| Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) | Polarimeters ensure consistency, reliability, and reproducibility in measurements, which are essential for maintaining GMP standards in pharmaceutical production. |
| Validation & Calibration | Polarimeters must be calibrated and validated according to regulatory guidelines to ensure accuracy and reliability in measurements for compliance with regulatory bodies. |
| Audit Trails and Data Integrity | Modern polarimeters provide audit trails, data security, and traceability, ensuring that data is documented and available for inspection, facilitating compliance with regulatory requirements. |
| Quality Control Documentation | Polarimeter data is required for regulatory submissions to prove the quality, potency, and purity of pharmaceutical products, ensuring compliance during inspections and product approvals. |
| Regulatory Inspections & Audits | Polarimeters are used to demonstrate regulatory compliance during inspections by showing consistent and accurate measurement of optical rotation in APIs and finished products. |
| Product Labeling Requirements | Accurate optical rotation measurements ensure compliance with product labeling regulations, confirming the enantiomeric purity and concentration of pharmaceutical products. |
| Environmental Conditions | Polarimeters equipped with temperature control systems help maintain consistent measurement conditions, complying with regulations that demand precise environmental control during testing. |

Summary
The applications of polarimeters in chiral purity analysis, concentration verification, impurity detection, stability testing, etc, make them indispensable for maintaining the high standards required in pharmaceutical production. The ability of digital polarimeters to measure optical rotation with higher accuracy, maintain stable conditions during testing, and automate sample handling has greatly improved the efficiency and reliability of polarimetric analysis in the pharmaceutical industry.


