Traditionally, low-speed centrifuges have been operated manually, but the integration of digital technologies is transforming their functionality, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and ease of use. This article explores the integration of digital technologies with low-speed centrifuges and the significant benefits this brings to laboratory workflows.
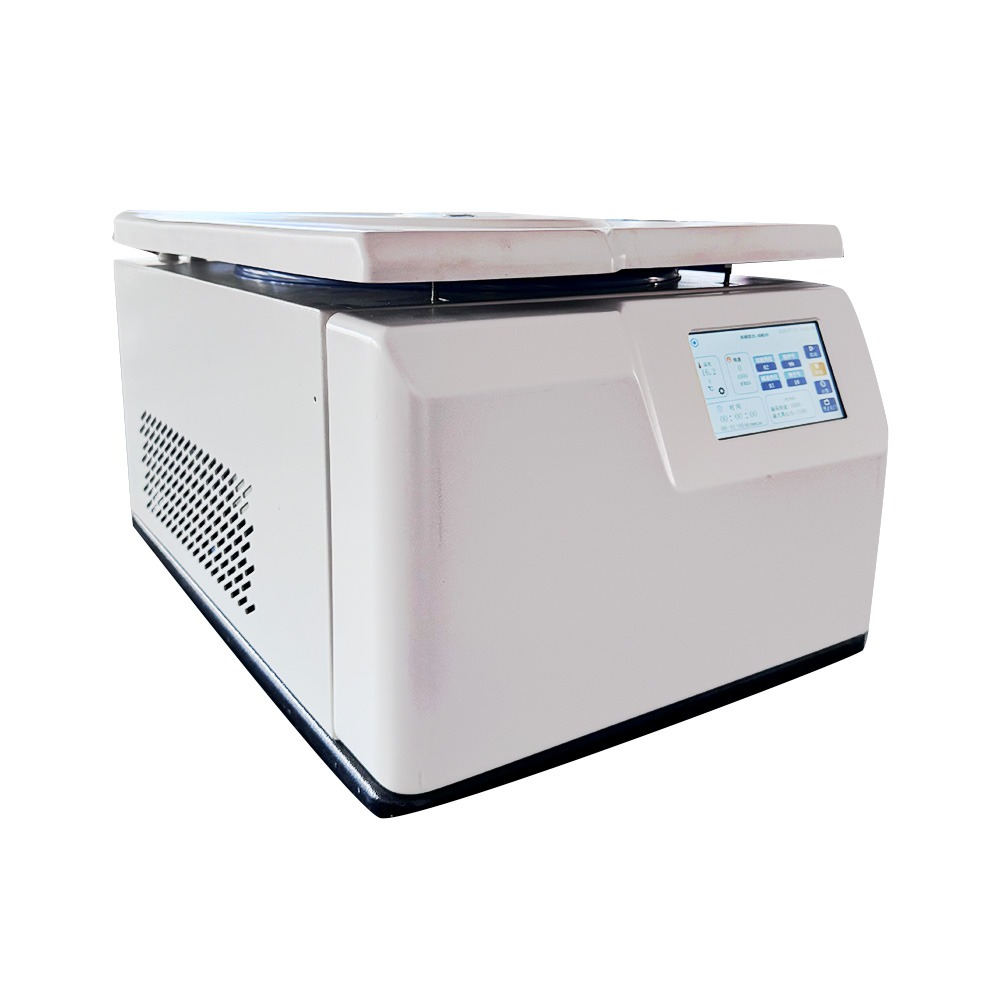

The Role of Low-Speed Centrifuges
This chart provides a concise overview of the role and functionality of low-speed centrifuges in laboratory settings.
| Category | Details |
| Primary Function | Separates substances of different densities by spinning samples at low speeds. |
| Typical Speed Range | 300 to 6000 revolutions per minute (RPM). |
| Common Applications | Clinical Laboratories: Routine sample preparation for diagnostic testing.Blood Sample Processing: centrifuges for separating blood components such as plasma, serum, and cells.Cell Culture: Harvesting cells from culture media. Research Laboratories: General sample separation and preparation tasks. |
| Key Components | RotorMotorSpeed Control SystemTemperature Control (optional)Safety Lid Locking Mechanism |
| Examples of Use | Blood Banks: Separating plasma for transfusions.Medical Labs: Preparing samples for biochemical analysis.Biotechnology: Harvesting bacterial or yeast cells from culture media. |
| Technological Enhancements | Digital controls for precise speed and time settings.Automated imbalance detection and correction.Connectivity for remote monitoring and data logging. |
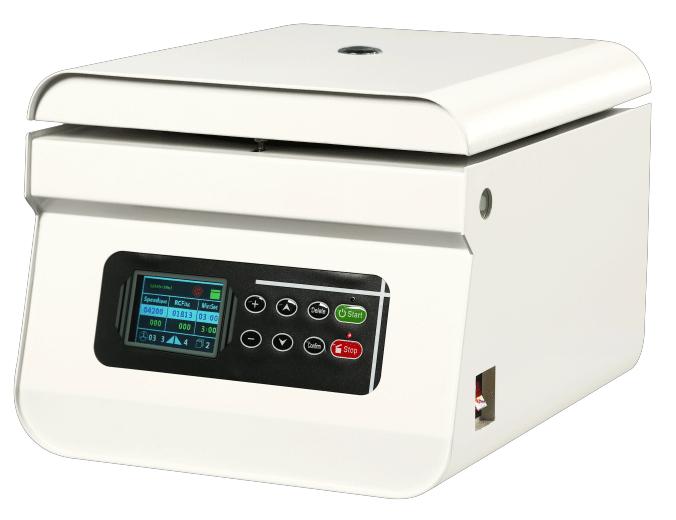

How Digital Technologies Transforming Low-Speed Centrifuges?
The advent of digital technologies is revolutionizing the operation, monitoring, and efficiency of low-speed centrifuges, which are essential tools in various laboratory applications.
1. Automation and Smart Controls
Automation significantly reduces the need for manual intervention, enhancing consistency and reproducibility in centrifuge operations.
- Programmable Settings: Modern intelligent low-speed centrifuges allow users to input specific protocols, ensuring precise control over speed, duration, and temperature. This eliminates the variability associated with manual settings.
- Automated Balancing: Automatic balance centrifuge adopting digital sensors detect imbalances in the rotor and automatically adjust to maintain smooth and safe operation. This not only enhances the longevity of the centrifuge but also ensures the safety of the samples.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Continuous digital monitoring of operational parameters such as speed, temperature, and run time provides instant feedback and alerts users to any deviations from the set protocols.

2. Connectivity and IoT Integration
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) facilitates seamless communication between the centrifuge and other devices, enhancing remote access and data sharing.
- Wireless Connectivity: Centrifuges equipped with Wi-Fi or Bluetooth can be controlled and monitored remotely using smartphones, tablets, or computers. This is particularly useful in large laboratories where equipment is spread across different locations.
- LIMS Integration: Connecting centrifuges to Laboratory Information Management Systems (LIMS) automates data transfer, ensuring that all operational data is accurately recorded and easily accessible for analysis.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: Laboratory managers and technicians can monitor the status and performance of centrifuges in real-time, receive notifications, and make adjustments from any location, thus enhancing operational flexibility and response times.
3. Data Management and Analysis
Advanced data management capabilities are crucial for maintaining accurate records and enabling detailed analysis of centrifuge operations.
- Digital Logging: Automatic logging of operational data such as run times, speeds, and temperature profiles ensures comprehensive record-keeping and enhances data integrity.
- Data Analytics: Integration with software tools allows for sophisticated analysis of operational data, helping to identify trends, optimize protocols, and predict maintenance needs.
- Error Tracking and Reporting: Automated error detection and logging provide insights into recurring issues, helping to refine maintenance strategies and prevent future problems.
4. Enhanced User Interfaces
User interfaces have evolved to become more intuitive and user-friendly, reducing training requirements and improving ease of use.
- Touchscreen Displays: High-resolution touchscreens offer easy navigation through centrifuge settings and protocols. Users can quickly set up and adjust parameters with minimal effort.
- User-Friendly Software: Simplified software interfaces make it easier for users to create, save, and recall customized protocols tailored to specific applications.
- Visual and Audio Alerts: Digital interfaces provide immediate visual and audio alerts for any deviations from the set parameters, ensuring prompt corrective actions.
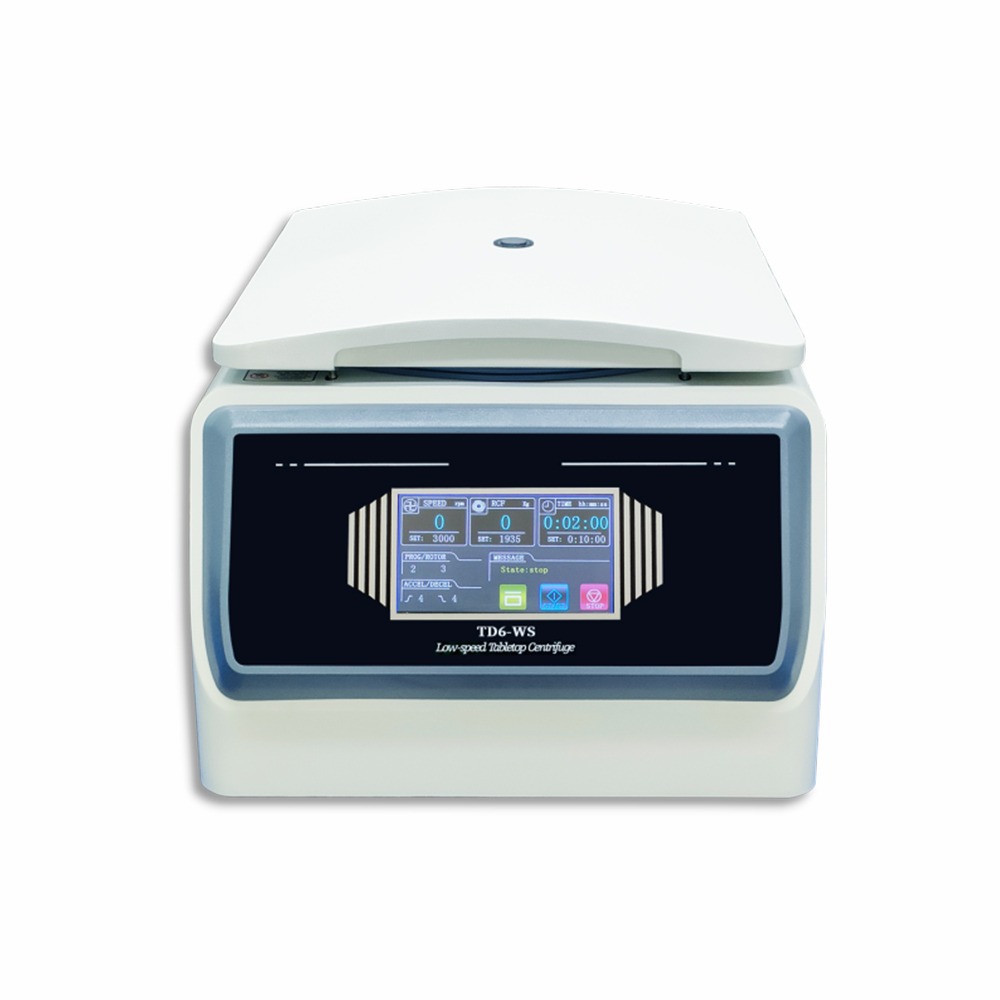

Benefits of Integrating Digital Technologies with Low-Speed Centrifuges
Integrating digital technologies with low-speed centrifuges significantly improves their efficiency, accuracy, and user experience. These advancements enhance laboratory workflows and ensure reliable and consistent results.
1. Increased Efficiency
Automation and smart controls in low-speed centrifuges streamline operations and reduce the need for manual intervention.
- Automated Protocols: Users can pre-program specific protocols, ensuring consistent and reproducible results with minimal user input.
- Real-Time Adjustments: Digital sensors detect and correct imbalances or other issues, maintaining optimal performance without manual correction.
2. Enhanced Accuracy
Intelligent technologies used in low-speed Large capacity centrifuge provide precise control over operational parameters.
- Precision Sensors: Advanced sensors monitor and control speed, temperature, and time with high accuracy, ensuring each run meets the specified parameters.
- Consistent Results: Automation reduces variability between runs, leading to more reliable and reproducible outcomes.
3. Improved Data Management
Seamless data logging and integration with laboratory information management systems (LIMS) enhance data integrity and accessibility.
- Automatic Data Logging: Operational data such as run times, speeds, and temperature profiles are automatically recorded, ensuring comprehensive and accurate record-keeping.
- Data Integration: Easy integration with LIMS facilitates centralized storage and management of data, allowing for efficient data retrieval and analysis.
4. Remote Access and Control
Connectivity features enable remote operation and monitoring, providing greater flexibility and convenience.
- Remote Monitoring: Laboratory managers and technicians can monitor centrifuge performance in real-time from any location using connected devices such as smartphones, tablets, or computers.
- Remote Adjustments: Operational parameters can be adjusted remotely, allowing for quick responses to any issues that may arise during a run.
5. Enhanced Safety
Digital integration contributes to safer operation and reduces the risk of accidents.
- Error Detection: Advanced error tracking and reporting systems identify issues early, allowing for timely maintenance and reducing the risk of equipment failure.
6. Cost Savings
The increased efficiency, accuracy, and reliability of digital-integrated centrifuges lead to significant cost savings.
- Reduced Downtime: Automated maintenance alerts and real-time monitoring minimize downtime, ensuring continuous operation and reducing productivity losses.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Predictive maintenance strategies enabled by digital technologies help prevent costly repairs and extend the lifespan of the centrifuge.
- Minimized Sample Waste: Enhanced accuracy and consistency in centrifuge operations reduce the likelihood of sample loss or damage, saving resources and materials.
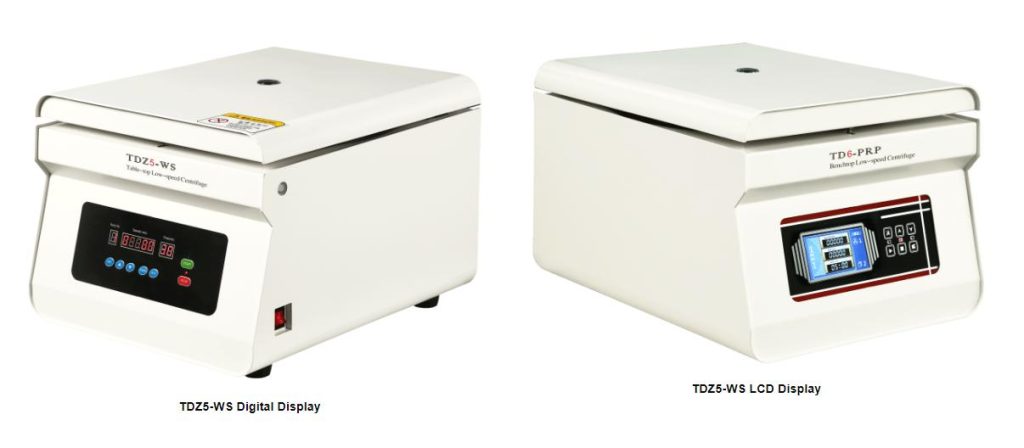

TDZ5-WS Benchtop Low-speed Large Capacity Centrifuge
In Summary, the integration of digital technologies with low-speed centrifuges is revolutionizing laboratory workflows. Automation, connectivity, data management, and enhanced user interfaces are key advancements that are driving this transformation, which are not only enhancing the functionality of these essential laboratory tools but also significantly improving the workflow and productivity in laboratories.