Blood banks play a crucial role in healthcare, providing a vital resource for patients in need of blood transfusions. To ensure the safety and efficacy of blood products, meticulous storage and handling practices are essential. A key component in achieving this is the specialized equipment used in blood banks. Here we will delve into the types of blood bank equipment essential for safe blood storage and handling, their functions, highlighting their significance and providing tips for best practices.
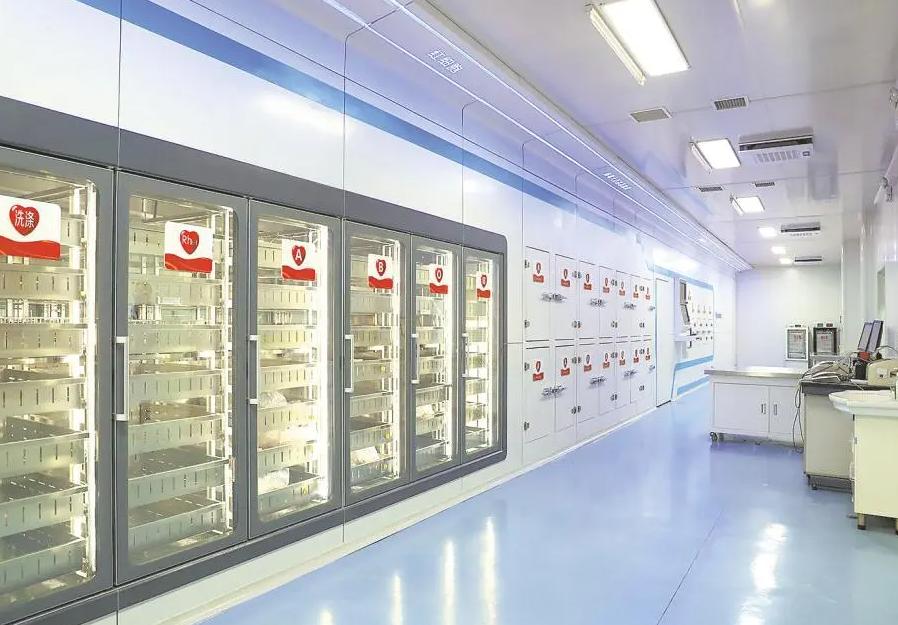

What Does Blood Bank Equipment Consist Of?
Blood bank equipment comprises a variety of specialized devices and systems designed to preserve the integrity, safety, and usability of blood and its components. These tools are critical at every stage of the blood handling process, from collection and processing to storage and eventual transfusion. Here are the key components:
| Category | Components |
| Blood Collection Equipment | Blood Collection Monitors, Blood Bags, Apheresis Machines |
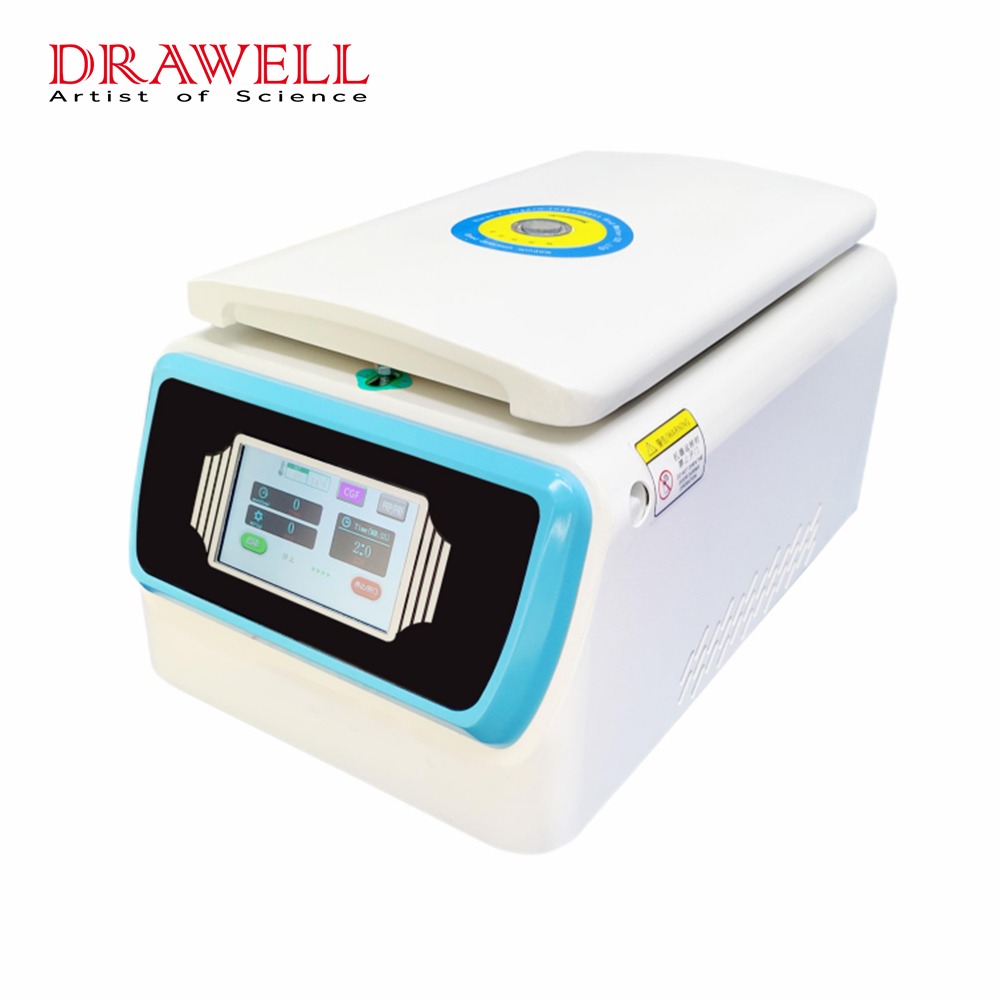
| Blood Processing Equipment | Centrifuges, Automated Blood Processing Systems, Plasma Thawing Devices |
| Blood Storage Equipment | Blood Storage Refrigerators, Plasma Freezers, Platelet Incubators and Agitators |
| Blood Testing & Quality Control | Automated Blood Analyzers, Microplate Readers, Hemovigilance Systems |
| Blood Transportation Equipment | Insulated Transport Boxes, Refrigerated Vehicles |
| Regulatory Compliance & Tools | Barcode Systems, Blood Bank Management Software |
The importance of this equipment cannot be overstated, as the highly sensitive nature of blood requires stringent handling and storage conditions. Specialized equipment ensures that blood is processed correctly, stored at the right temperature, and monitored continuously to prevent any compromise in quality. For instance, blood components like red cells, plasma, and platelets each require specific storage conditions. Without the right equipment, maintaining these conditions consistently would be impossible, leading to the risk of bacterial contamination, clotting, or degradation of vital components.
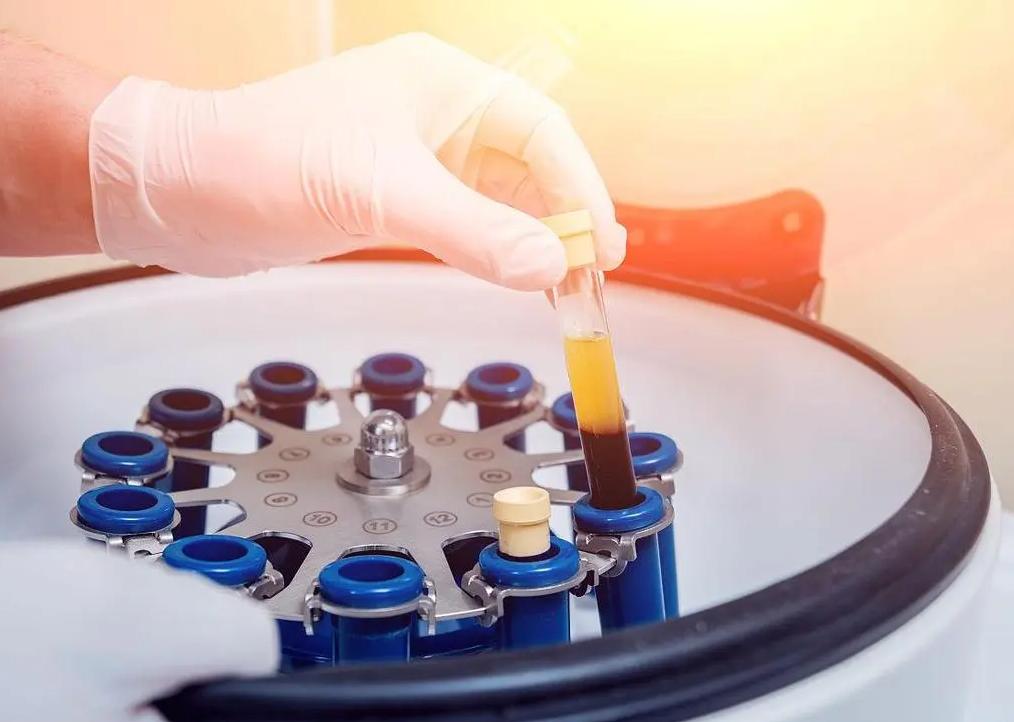

Types of Blood Bank Equipment
Blood bank equipment can be broadly categorized based on its role in processing or storing blood. Each category plays a vital part in ensuring that the blood remains safe and viable for use in medical procedures.
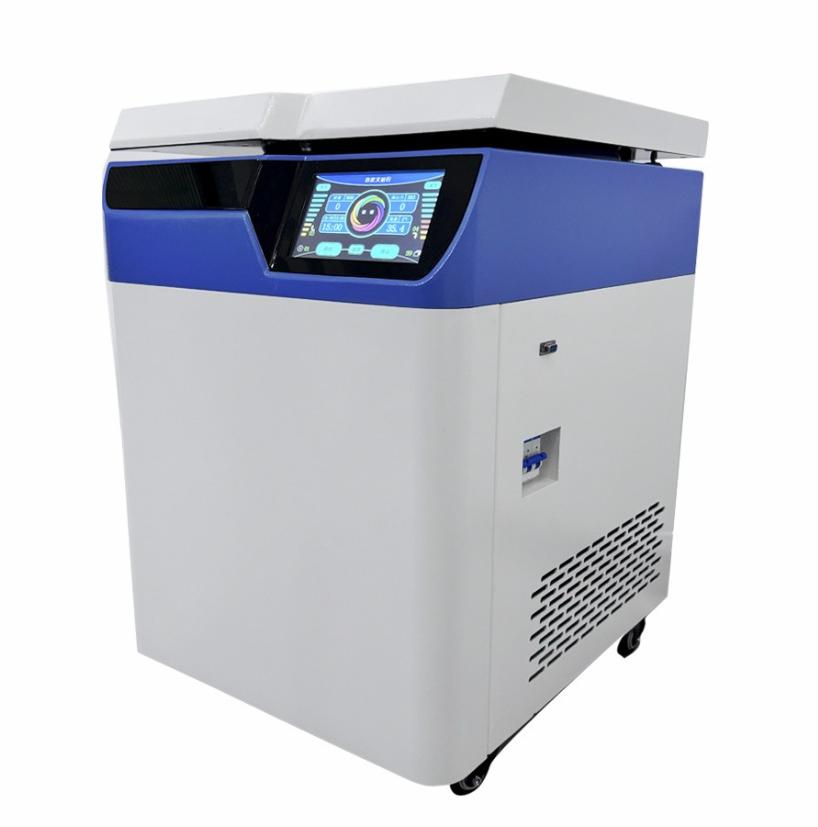

Blood Processing Equipment – Separation:
Blood processing equipment is primarily involved in the separation of whole blood into its individual components—red blood cells, plasma, and platelets. This separation is crucial because different components are used for various treatments and must be stored differently.
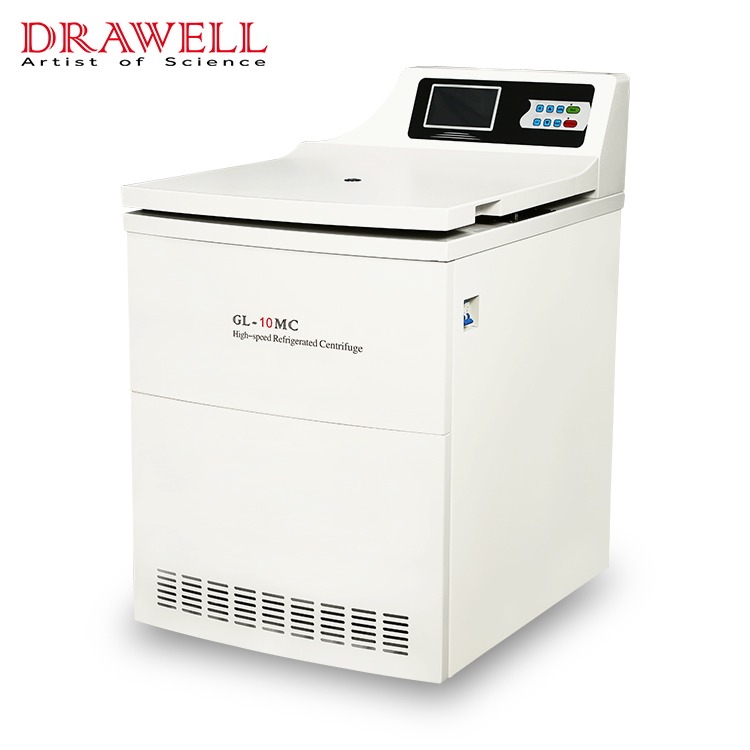
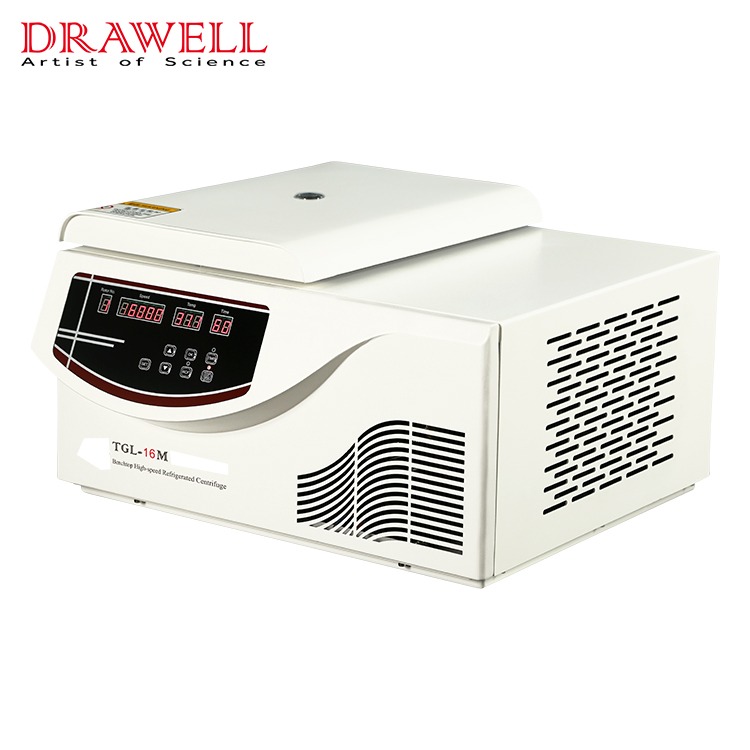
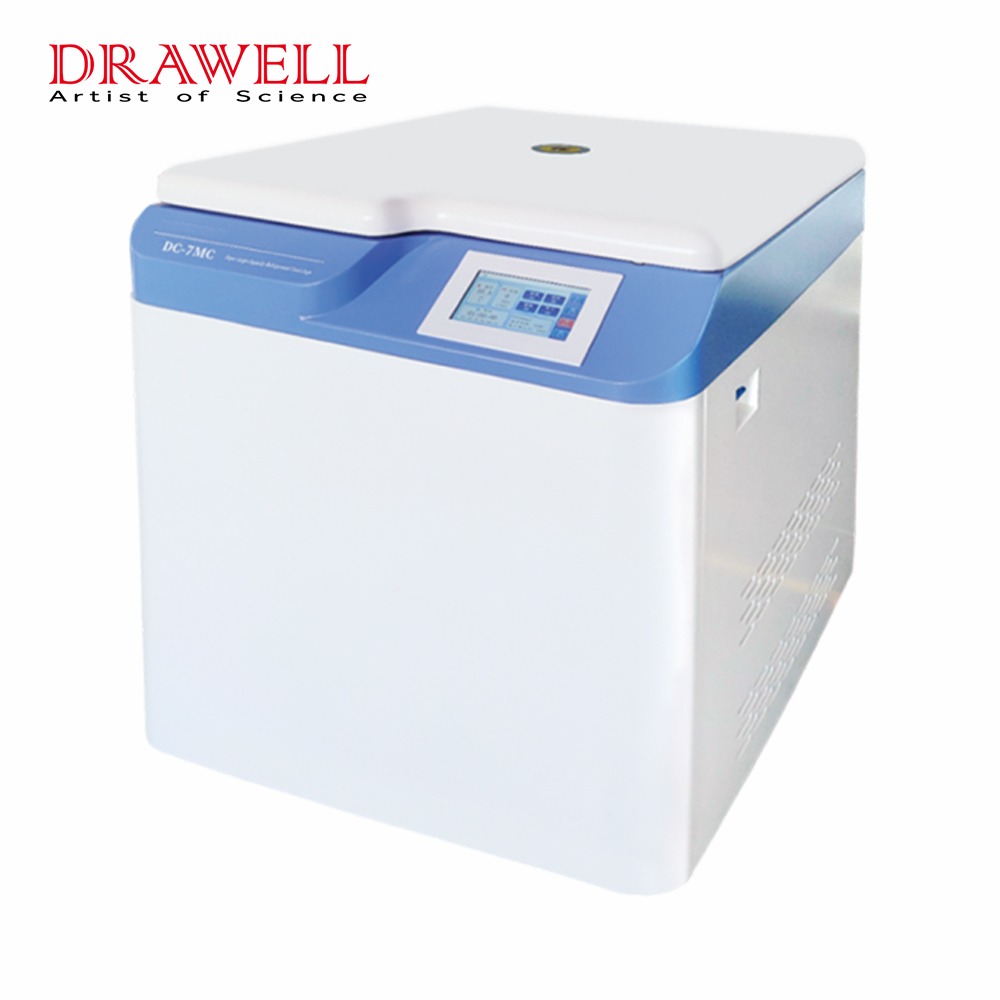
Centrifuges: Centrifuges are the cornerstone of blood processing. These machines spin blood at high speeds, causing its components to separate based on density. Red blood cells, being the heaviest, settle at the bottom, while plasma, the lightest, rises to the top. Platelets remain suspended between the two. This precise separation is essential for the correct storage and later use of these components.
Automated Blood Processing Systems: These systems further refine the separation process by automating the steps involved in isolating blood components. Automation reduces the risk of human error and increases the efficiency and consistency of blood processing, ensuring that each component is handled according to its specific requirements.
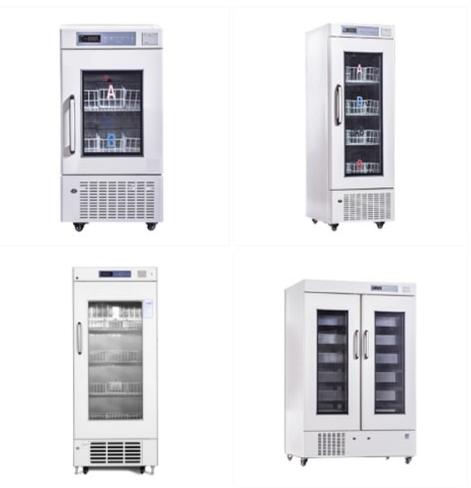

Blood Storage Equipment – Temperature Control:
Once blood has been processed, its components need to be stored under specific conditions to maintain their viability. This is where blood storage equipment comes into play.
Blood Storage Refrigerators: These are designed to store whole blood and red blood cells at a constant temperature between 1-6°C. Temperature control is crucial because even slight deviations can cause blood to degrade, making it unsuitable for transfusion.
Plasma Freezers: Plasma needs to be stored at much lower temperatures, typically below -30°C. Plasma freezers are equipped with advanced temperature monitoring and control systems to ensure that these low temperatures are maintained consistently, preserving the plasma’s clotting factors and other vital proteins.
Platelet Incubators and Agitators: Platelets require a controlled environment with constant agitation to prevent them from clumping together. Platelet incubators maintain the required temperature (20-24°C), while agitators ensure continuous gentle movement, preserving the platelets’ functionality for transfusion.
Safe Blood Storage and Handling Tips
Maintaining the safety and integrity of stored blood involves more than just using the right equipment. Proper handling protocols and regular maintenance of the equipment are equally important. Here are some essential tips:
- Regular Monitoring: Continuously monitor storage temperatures using automated systems with alarms to detect any deviations from the safe range.
- Proper Sterilization: Regularly clean and sterilize all blood bank equipment, including storage units and processing machines, to prevent contamination.
- Staff Training: Ensure that all personnel handling blood are well-trained in using blood bank equipment and follow established protocols for safe handling.
- Backup Power Systems: Install backup power systems for storage equipment to maintain the required temperatures during power outages, protecting the integrity of stored blood.
- Routine Maintenance: Perform regular maintenance and calibration of blood bank equipment to ensure it operates correctly and reliably, preventing equipment failure.
- Controlled Environment: Maintain a controlled environment in storage areas, avoiding exposure to direct sunlight, excessive humidity, or extreme temperatures that could compromise blood safety.
- Proper Labeling and Documentation: Ensure accurate labeling of blood products and maintain thorough documentation to track the storage conditions and handling history, aiding in traceability and quality control.
- Handling Protocols: Follow standardized handling protocols to minimize the risk of contamination or damage to blood products during processing, storage, and transportation.
- Compliance with Guidelines: Adhere to national and international guidelines and standards for blood storage and handling to ensure compliance and maintain the highest safety levels.
- Inventory Management: Implement effective inventory management practices to rotate stock, avoid overstocking, and ensure that blood products are used within their shelf life.
Find a Reliable Blood Bank Storage and Processing Equipment Supplier
Blood bank equipment plays a pivotal role in ensuring the safe storage and handling of blood, which is critical to patient safety during transfusions and other medical procedures. By understanding the types of equipment available, their purposes, and the best practices for using them, blood banks can maintain the highest standards of blood safety and integrity. Selecting the right blood bank equipment supplier further ensures that your blood bank is equipped to meet these rigorous demands, ultimately contributing to better patient outcomes.