Biosafety cabinets are essential for ensuring a safe and controlled environment in laboratories when handling hazardous materials. These cabinets are intended to protect both laboratory personnel and the environment from potential biological agent exposure. There are various types of biosafety cabinets, each with its own set of features and applications. In this article, we focus on topic of types of biosafety cabinets, exploring the different types of biosafety cabinets, their distinctive characteristics and the key factors to consider for choosing the right type of biosafety cabinet.

What are the Different Types of Biosafety Cabinets?
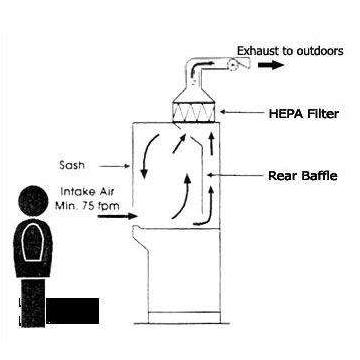
1. Class I Biosafety Cabinets
Purpose: Class I BSCs are intended to protect both personnel and the environment. They do not, however, protect the samples being handled.
Features:
A protective sash covers the front opening.
The laboratory’s airflow is drawn in, passed through a HEPA filter, and then exhausted.
Inward airflow provides personnel protection.
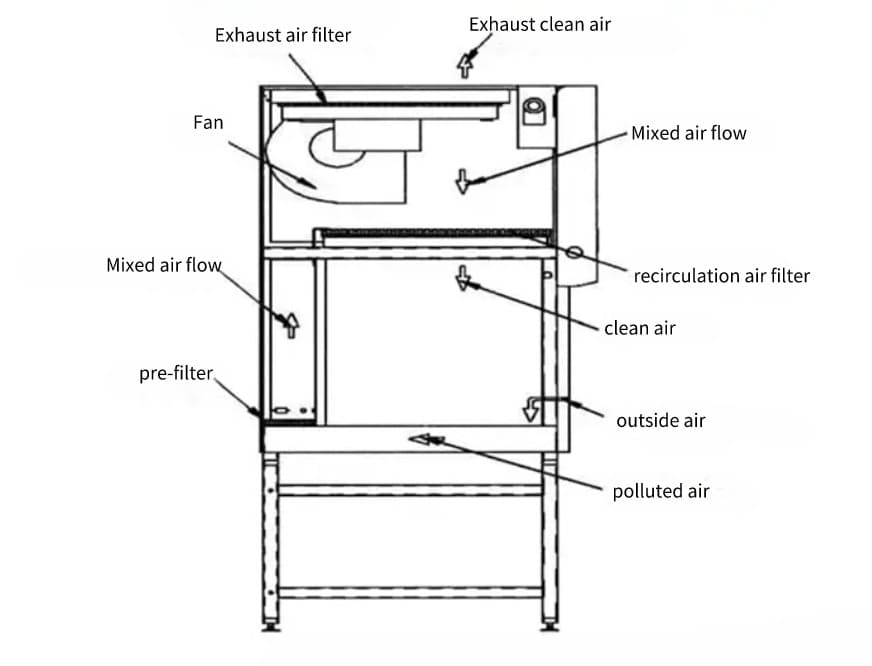
2. Class II Biosafety Cabinets
Purpose: Class II BSCs protect both personnel and the environment, making them the most commonly used biosafety cabinets.
Features:
Divided into four types (A1, A2, B1, B2) based on design and airflow patterns.
Air is drawn through a front grille, and then it is recirculated through HEPA filters.
Exhaust air is also HEPA-filtered before release into the environment.
Suitable for Biosafety Levels 1, 2, and 3.
3. Class III Biosafety Cabinets
Purpose: Class III BSCs provide the highest level of containment, making them ideal for working with highly infectious and hazardous agents, such as those that require Biosafety Level 4 (BSL-4) containment.
Features:
All operations are carried out through attached gloves in a completely enclosed and gas-tight environment.
Supply and exhaust air is HEPA-filtered.
Maintains negative pressure to prevent hazardous materials from escaping.
4. Animal Transfer Stations
Purpose: Animal transfer stations are designed to ensure the safe movement of animals into and out of containment.
Features:
Typically comes with a HEPA-filtered exhaust system.
Allows for the safe handling of animals while avoiding the exposure of personnel to potential contaminants.
Animals and biohazardous materials are used in research.
5. PCR Workstations
Purpose: PCR workstations provide a clean environment for polymerase chain reaction (PCR) applications, preventing sensitive samples from becoming contaminated.
Features:
To maintain a sterile workspace, use laminar airflow.
Equipped with UV lights for decontamination.
Used in molecular biology laboratories for DNA and RNA work.

What are the Key Factors to Consider for Choosing the Right Type of Biosafety Cabinets?
The right type of biosafety cabinet is a critical decision that is influenced by a number of factors such as the laboratory’s specific requirements, the nature of the materials being handled, and the desired level of protection.
1. Risk Level and Biosafety Level (BSL)
Determine the level of risk associated with the biological materials you will be working with. BSL-1, BSL-2, BSL-3, and BSL-4 are the various levels of containment. Select a biosafety cabinet that meets the requirements of your work’s specific biosafety level.
2. Type of Research or Application
Biosafety cabinets are tailored to specific applications. Consider the type of research or procedures you intend to carry out. Class II cabinets, for example, are commonly used for microbiological research, whereas Class III cabinets are appropriate for working with highly infectious agents.
3. Airflow Patterns and Containment
Understand the airflow patterns of the biosafety cabinet. Class I cabinets have unidirectional airflow, while Class II cabinets have laminar airflow. Class III cabinets provide total containment. Choose the one that aligns with your containment needs and the nature of your work.
4. Sample Protection
Consider whether the biosafety cabinet needs to protect the samples being handled. Class I and Class II cabinets offer protection to personnel and the environment but may not safeguard the samples. Class III cabinets, on the other hand, provide complete sample containment.
5. Personnel Safety
Evaluate the level of protection provided to personnel. Class II and Class III cabinets offer a higher degree of personnel protection compared to Class I cabinets. Class III cabinets, in particular, provide a fully enclosed, gas-tight system with gloves for handling materials.
6. Decontamination and Sterilization
Consider the decontamination and sterilization methods of the biosafety cabinet. Some cabinets are equipped with UV lights for decontamination, while others may have built-in systems for gas decontamination. The ease of cleaning and decontaminating the cabinet is crucial for maintaining a safe environment.
7. Size and Configuration
Examine the biosafety cabinet’s physical dimensions and configuration. Check that it fits within the available laboratory space and accommodates the equipment and procedures that you intend to use.
8. Regulatory Compliance
Ensure that the chosen biosafety cabinet complies with relevant regulatory standards and guidelines, such as those from organizations like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), the National Institutes of Health (NIH), or the International Organization for Standardization (ISO).
9. Cost Considerations
Determine the available budget for purchasing and maintaining the biosafety cabinet. While safety should be prioritized, consider the cost-effectiveness of the chosen option as well as the long-term operating costs.
10. User Training and Familiarity
Ensure that laboratory personnel are adequately trained to use the chosen biosafety cabinet. Familiarity with the specific type of cabinet is crucial for maintaining a safe working environment.
Conclusion
Biosafety cabinets (BSCs) are essential tools in laboratories where potentially hazardous materials are handled. Choosing the appropriate biosafety cabinet is critical for maintaining a safe and controlled laboratory environment. Understanding the characteristics and applications of each type of biosafety cabinet is critical for ensuring laboratory personnel safety and the integrity of the research being conducted.

