In laboratory environments, achieving proper mixing of substances is crucial for obtaining accurate and reproducible results. Two commonly used laboratory mixing instruments are orbital shakers and vortex mixers, both designed to agitate liquids and solids. While they share a common purpose, their mechanisms, applications, and performance differ significantly. In this article, we will explore the key differences between orbital shakers and vortex mixers with their specific uses in laboratory settings to help you choose the right lab mixing instrument.

Key Differences between Orbital Shakers and Vortex Mixers
1. Principle of Operation
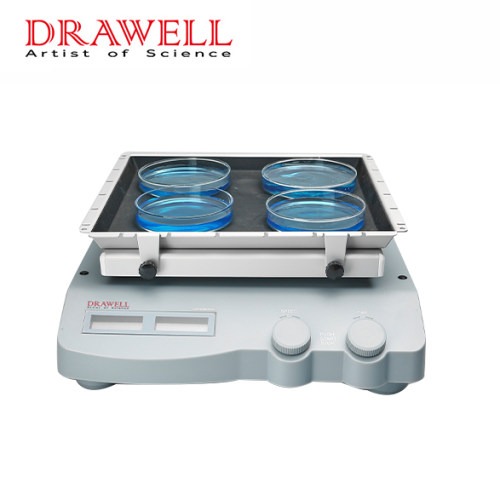
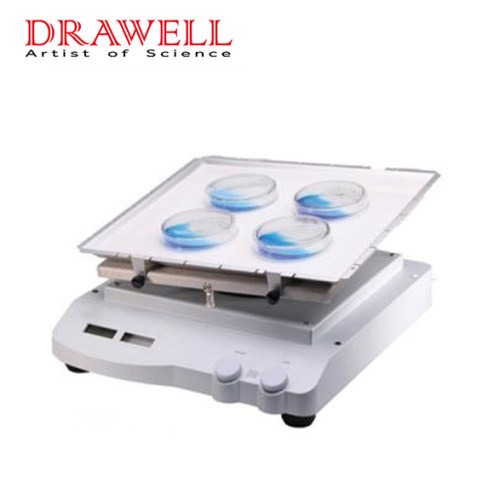
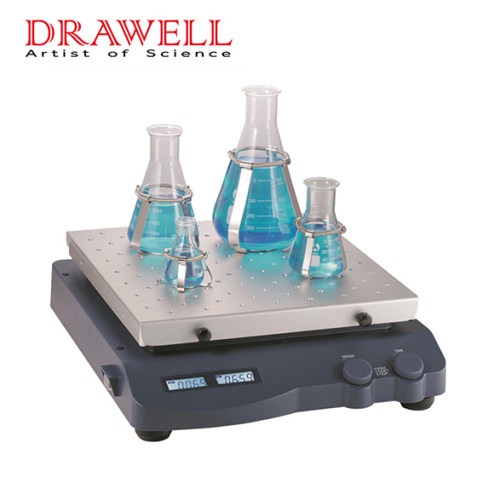
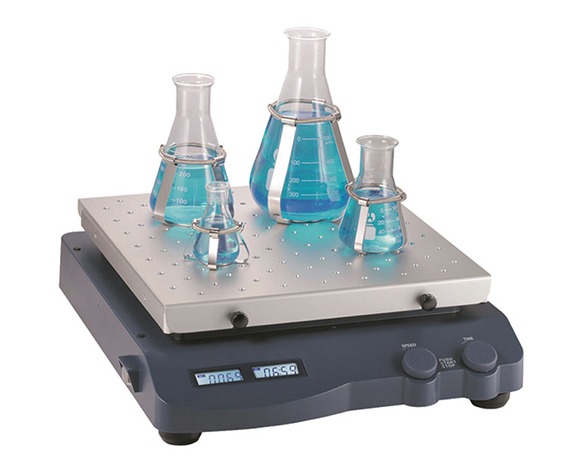
Orbital Shaker: An orbital shaker operates by gently moving samples in a circular or elliptical motion. The shaking platform, where the sample containers are placed, moves in a consistent orbit. This continuous motion helps mix the contents of flasks, bottles, or petri dishes in a controlled manner. Orbital shakers are designed for consistent and uniform agitation over a prolonged period, making them ideal for large volumes or multiple samples.

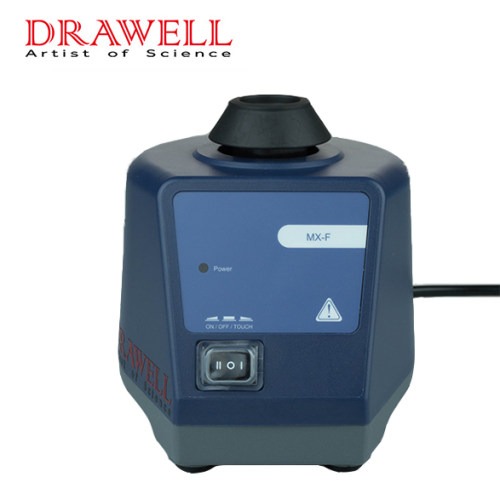
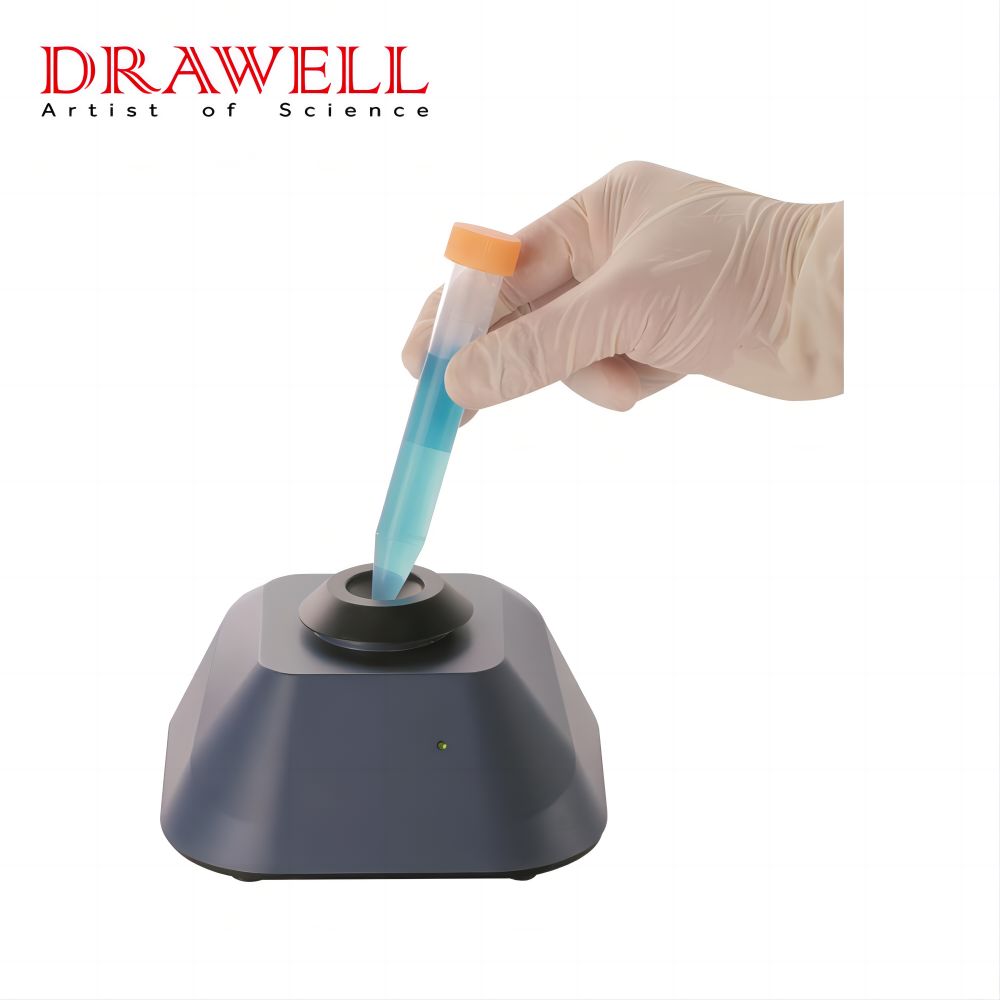
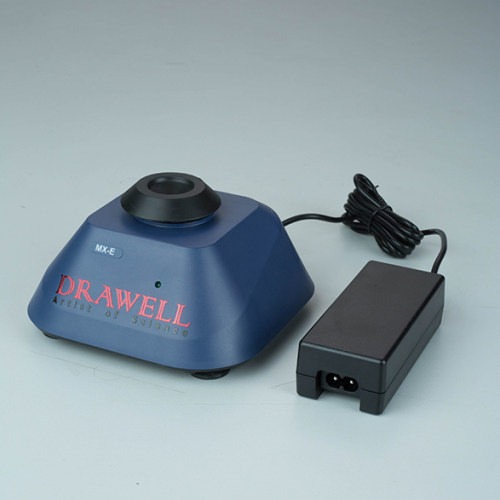
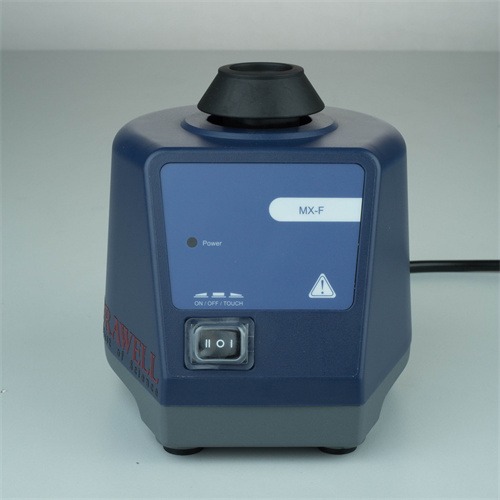
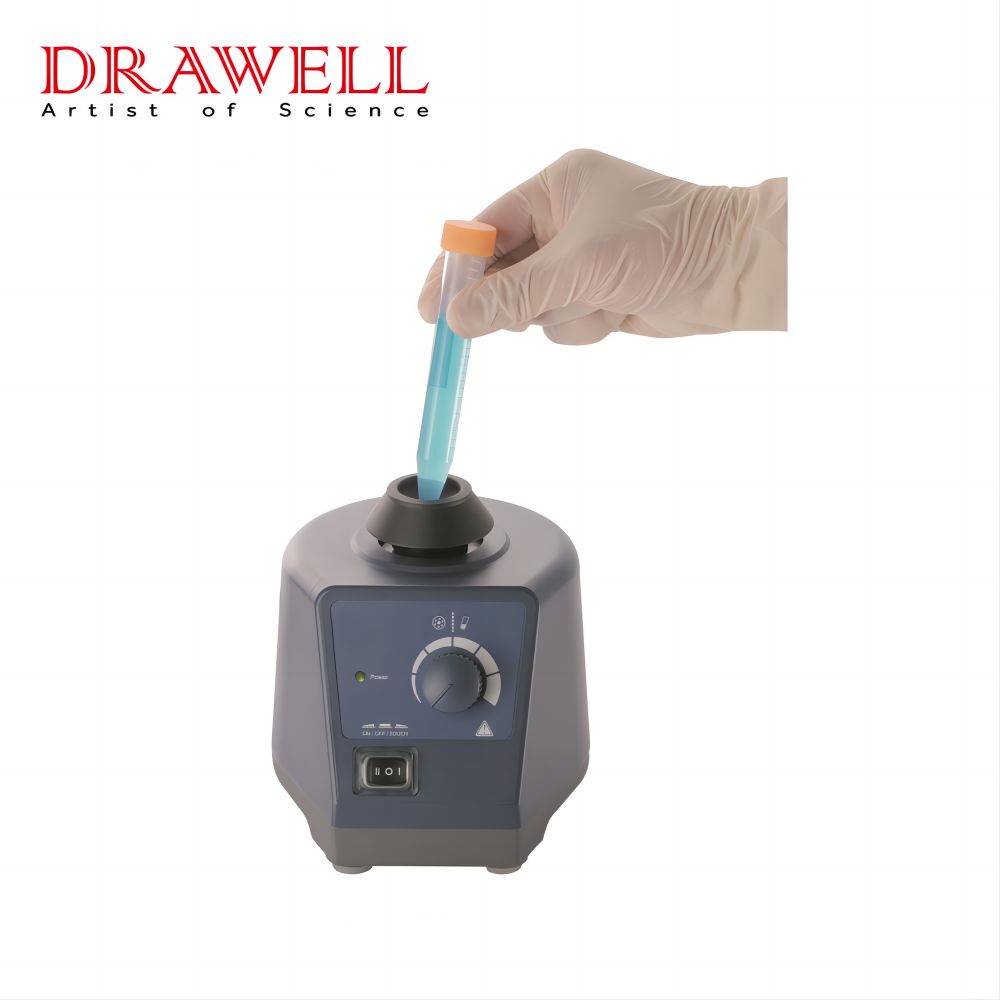
Vortex Mixer: A vortex mixer, on the other hand, works by creating a rapid, localized motion, often in the form of a circular vortex in the center of the sample container. This is achieved through a motor-driven rotating shaft that creates a vigorous swirling action. Vortex mixers are ideal for quick, intense mixing of small quantities, typically used for handling individual tubes or vials.
2. Design and Functionality
Orbital Shaker:
- Design: Orbital shakers have a flat, horizontal shaking platform. The platform can accommodate a range of containers like flasks, beakers, and multi-tube racks.
- Functionality: Orbital shakers are best suited for mixing larger quantities of samples, providing a consistent, gentle mixing action. They can operate at various speeds, with some models offering temperature control and the ability to shake at higher speeds for intense agitation.
Vortex Mixer:
- Design: Vortex mixers are typically compact and come with a holder to support sample containers such as test tubes, vials, or microcentrifuge tubes.
- Functionality: The key advantage of vortex mixers is their ability to quickly mix small volumes, often within seconds. They typically offer a variable speed control and have a touch-sensitive operation (activated by pressing the sample container against the mixing pad).

3. Applications
Orbital Shaker
Orbital shakers are versatile and can be used in a variety of laboratory applications, including:
- Cell Culture: Orbital shakers are essential for growing bacterial cultures or maintaining the homogeneity of cell suspensions in culture flasks. The gentle motion prevents damage to sensitive cells while ensuring optimal growth conditions.
- Chemical Reactions: They are also used for mixing reagents in flasks or reaction vessels, allowing for more efficient chemical reactions due to consistent mixing.
- In-Vitro Studies: Used in studies requiring homogeneous conditions for long periods, like enzyme reactions or protein assays.
- Environmental Studies: Used in environmental testing, such as soil and water sample preparation or when creating uniform mixtures of liquid samples.
Vortex Mixer
Vortex mixers are ideal for rapid and localized mixing, making them suitable for:
- Sample Preparation: Vortex mixers are commonly used in scenarios that require thorough mixing of small volumes, such as DNA or RNA extraction protocols, protein assays, and PCR preparation.
- Homogenizing Suspensions: Used to mix reagents in small vials or tubes, ensuring the components are thoroughly blended.
- Centrifugation Pre-Treatment: Vortex mixers are often employed to mix samples before or after centrifugation to ensure uniformity, especially for delicate or small volume samples.
4. Performance and Efficiency
Orbital Shaker
- Performance: The digital orbital shaker is highly efficient at mixing large volumes or multiple samples simultaneously. Its ability to shake in a smooth and consistent orbit reduces the risk of splashing and ensures that all parts of the solution are equally agitated.
- Efficiency: Orbital shakers are designed for longer mixing periods, typically ranging from minutes to hours, depending on the specific application. Their speed and versatility in controlling the frequency and motion make them ideal for tasks requiring a long-term, stable agitation.

Vortex Mixer
- Performance: The vortex mixer excels in rapid and localized agitation. It can mix small amounts of liquid very effectively in a short amount of time, making it an excellent choice for quick tasks.
- Efficiency: Vortex mixers are highly efficient for small-scale operations, but their capabilities are limited when it comes to larger samples. They typically provide high-speed mixing in short bursts, which may not be suitable for applications requiring sustained or uniform mixing.
5. Size and Portability
- Orbital Shaker: Orbital shakers are usually bulkier than vortex mixers, as they need to accommodate a larger number of samples or more significant containers. However, many models are designed to be benchtop units, making them suitable for most laboratory environments. Some advanced versions are even stackable for maximizing space.
- Vortex Mixer: Vortex mixers are compact and portable, designed for use on smaller laboratory benches or workspaces. The small size and ease of use in vortex mixers make them ideal for situations where space is limited or when mixing needs to be performed quickly and occasionally.
6. Cost Considerations
- Orbital Shaker: The cost of orbital shakers can vary depending on the size, features, and brand. Generally, they are more expensive than vortex mixers due to their larger size, versatile functionality, and ability to handle multiple or larger samples.
- Vortex Mixer: Vortex mixers are typically more affordable and widely available in laboratory settings. Their cost-effectiveness, particularly for small-scale mixing tasks, makes them accessible for many laboratories, even with limited budgets.

How to Choose Between Orbital Shaker and Vortex Mixer
| Criteria | Orbital Shaker | Vortex Mixer |
| Principle of Operation | Circular, smooth orbital motion for uniform mixing | Rapid, localized swirling action creating a vortex |
| Design | Flat platform for larger containers, multiple racks | Compact unit for individual test tubes or small vials |
| Best For | Large-scale or multiple sample mixing | Quick, intense mixing of small volumes |
| Sample Volume | Handles large volumes (e.g., flasks, bottles) | Ideal for small volumes (e.g., test tubes) |
| Mixing Time | Longer durations (minutes to hours) | Short bursts (seconds to a minute) |
| Mixing Intensity | Gentle, uniform agitation | Intense, localized agitation |
| Speed Control | Variable speed, often adjustable | Variable speed, typically high-speed bursts |
| Temperature Control | Available in some models | Not available in most models |
| Portability | Bulky, stationary unit | Compact, portable |
| Cost | Higher due to versatility and size | More affordable, cost-effective |
| Applications | Cell culture, chemical reactions, protein assays, environmental testing | Sample preparation, DNA extraction, reagent mixing |
| Typical Use | Long-term, gentle mixing for large or multiple samples | Quick mixing of small volumes or individual samples |
| Space Requirement | Larger, takes up more bench space | Compact, requires minimal space |

Summary
- Choose an orbital shaker if you need to mix large volumes or multiple samples over a prolonged period with uniform, gentle agitation, ideal for applications like cell culture or chemical reactions.
- Choose a vortex mixer if you need to quickly mix small quantities, requiring intense but short bursts of agitation, particularly in high-speed protocols like DNA extractions or reagent preparation.
Understanding the differences between orbital shakers and vortex mixers, allows laboratory professionals to choose the most appropriate mixer for their specific needs, ensuring optimal results in their research and experiments.