In blood banks, the precise separation of blood components is crucial for ensuring that patients receive the highest quality blood products. Refrigerated centrifuges play a vital role in this process, enabling the efficient separation of blood cells, plasma, and other components at controlled temperatures. This article will guide you through the key considerations for choosing the best refrigerated centrifuge for your blood bank, ensuring that you make an informed decision that enhances the efficiency and reliability of your operations.

Understanding the Role of Refrigerated Centrifuges
Refrigerated centrifuges are critical components in blood banks, playing a pivotal role in the processing and preservation of blood and its components. Their importance stems from several key functions that directly impact the quality, safety, and efficacy of blood products. Here are the main reasons why refrigerated centrifuges are indispensable for blood banks:
1. Temperature Control and Preservation
Maintaining Optimal Conditions: Blood components, such as plasma, platelets, and red blood cells, are highly sensitive to temperature changes. Refrigerated centrifuges ensure that these components are processed at optimal temperatures, preserving their functionality and extending their shelf life.
Preventing Degradation: High temperatures can lead to the degradation of proteins and other vital elements in blood. By maintaining a cold environment, refrigerated centrifuges prevent the breakdown of these components, ensuring that they remain effective for transfusions and other medical uses.
2. Efficient Separation of Blood Components
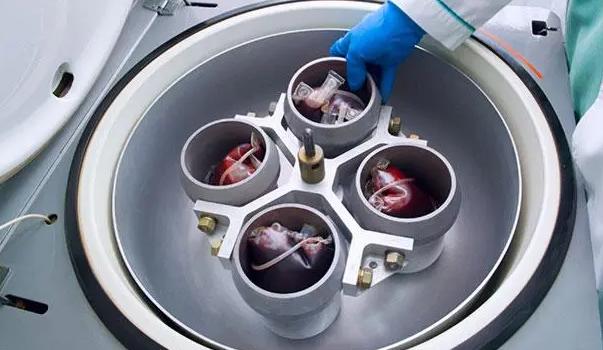
High-Speed Centrifugation: Refrigerated centrifuges apply high-speed centrifugal force to blood samples, enabling the efficient separation of different blood components. This is essential for isolating plasma, platelets, and red and white blood cells, each of which is used for different therapeutic purposes.
Precision and Consistency: These centrifuges provide precise control over speed and temperature, ensuring consistent and reproducible results. This consistency is crucial for maintaining the quality and reliability of blood products used in patient care.

3. Enhanced Safety and Quality Control
Preventing Contamination: The enclosed, temperature-controlled environment of refrigerated centrifuges reduces the risk of contamination during the separation process. This is vital for ensuring the safety of blood products and protecting patients from infections.
Automated Safety Features: Modern refrigerated centrifuges are equipped with automated safety features, such as imbalance detection, lid locking mechanisms, and emergency braking systems. These features protect operators and ensure the safe handling of blood samples.
Traceability and Documentation: Many refrigerated centrifuges come equipped with advanced monitoring and documentation features. These allow blood banks to maintain detailed records of each centrifugation process, supporting traceability and quality assurance efforts.
4. Supporting Specialized Applications
Advanced Research and Therapies: Refrigerated centrifuges are also essential for supporting advanced research and specialized medical therapies. They enable the preparation of specific blood components used in cutting-edge treatments, such as stem cell therapy and personalized medicine.
Flexibility and Versatility: With various rotor options and programmable settings, refrigerated centrifuges offer the flexibility needed to handle a wide range of applications. This versatility makes them invaluable tools in both routine blood processing and specialized research settings.
In summary, the role of refrigerated centrifuges is crucial in safeguarding the integrity of blood products and ensuring that patients receive the highest quality care.

Types of Refrigerated Centrifuges for Blood Banks
Refrigerated centrifuges come in various types, each designed to meet specific needs and applications within blood banks. Understanding the different types can help you choose the right equipment for your blood bank’s requirements. Here are the common types of refrigerated centrifuges used in blood banks:
| Type | Pros | Cons | Specific Applications in Blood Banks |
| Benchtop Refrigerated Centrifuges | Space-saving design | Limited capacity and speed | Routine blood component separation |
| Easy to use and maintain | Not suitable for high-volume processing | Small-scale research and diagnostics | |
| Lower initial cost | |||
| Floor-Standing Refrigerated Centrifuges | High capacity and speed | Requires more floor space | High-throughput blood component separation |
| Suitable for continuous operation | Higher initial cost | Processing large volumes of blood samples | |
| Robust and durable | |||
| High-Speed Refrigerated Centrifuges | Fast and efficient separation | Higher noise levels | Rapid separation of platelets and plasma |
| Capable of handling a wide range of samples | May require specialized training | Research applications requiring high-speed | |
| Precision control over speed and temperature | |||
| Ultracentrifuges | High separation efficiency | Very high cost | Advanced research applications |
| Ability to process very small particles | Requires specialized training and maintenance | Isolating viruses, DNA, and proteins | |
| Essential for specialized applications | |||
| Swing-Bucket Refrigerated Centrifuges | Gentle and uniform separation | Slower than fixed-angle centrifuges | Separation of blood components like plasma and cells |
| Ideal for large volume samples | Can be more expensive | Applications requiring minimal sample disruption | |
| Reduced risk of sample mixing or disruption | |||
| Fixed-Angle Refrigerated Centrifuges | Faster sedimentation of particles | May cause disruption to sensitive samples | Pelleting cells, bacteria, and other particles |
| High-speed operation | Less gentle than swing-bucket centrifuges | Routine blood processing | |
| Efficient for routine applications |
In summary, the common types of refrigerated centrifuges for blood banks include benchtop, floor-standing, high-speed, ultracentrifuges, swing-bucket, and fixed-angle centrifuges. Each type has specific features and advantages, making them suitable for different applications and processing needs within blood banks.
Key Features to Consider When Choosing
Selecting the right refrigerated centrifuge involves evaluating several key features:
Temperature Control and Stability: Ensure the centrifuge can maintain consistent temperatures throughout the run to protect sensitive blood components.
Speed and Capacity: Consider the maximum RPM and the capacity of the centrifuge, ensuring it meets the demands of your blood bank’s workflow.
Rotor Types and Compatibility: Different rotors are designed for various applications. Ensure the centrifuge supports the rotors you need for your specific processes.
Noise Levels and Ergonomics: Look for centrifuges with low noise levels and ergonomic designs to create a comfortable working environment for staff.
Safety Features: Features such as imbalance detection, lid locking mechanisms, and emergency braking systems are crucial for ensuring operator safety and preventing accidents.
Reliability and Maintenance: Choose a centrifuge known for its reliability and ease of maintenance to minimize downtime and ensure long-term performance.
Get Refrigerated Centrifuge for Blood Bank From Drawell
At Drawell, we understand the critical role refrigerated centrifuges play in blood bank operations. We offer a comprehensive selection of high-quality, reliable centrifuges specifically designed for blood processing. Our centrifuges boast features like:
- Versatile rotors to accommodate various blood processing applications.
- Precise temperature control for optimal blood component preservation.
- Quiet operation for a peaceful working environment.
- Intuitive controls for ease of use.
- Advanced safety features to ensure operator and product safety.
- We also provide exceptional after-sales service and warranty support.
Contact Drawell today to discuss your blood bank’s specific needs and find the perfect refrigerated centrifuge for optimal performance and patient safety.