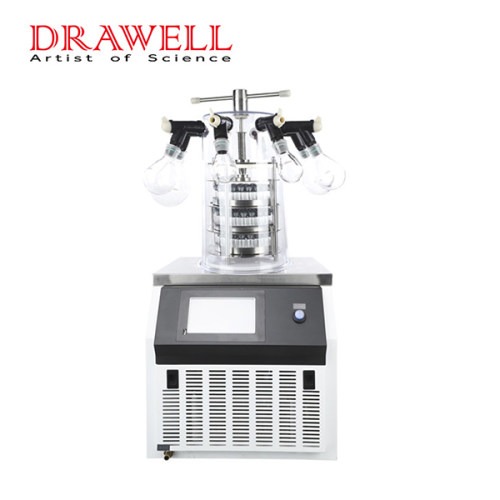
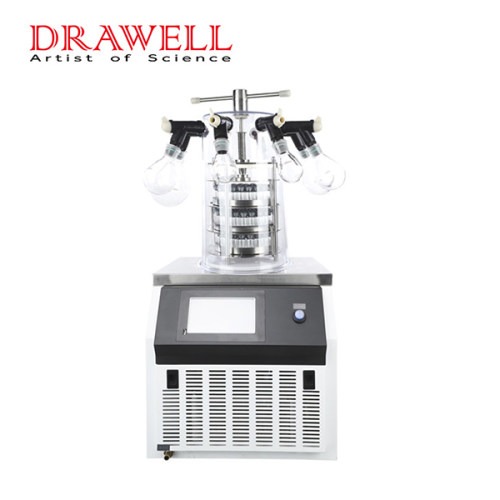
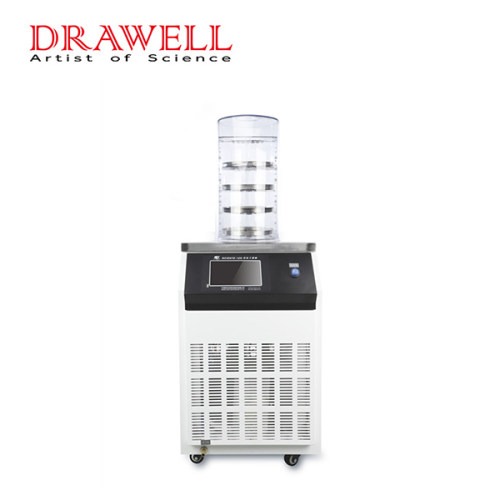
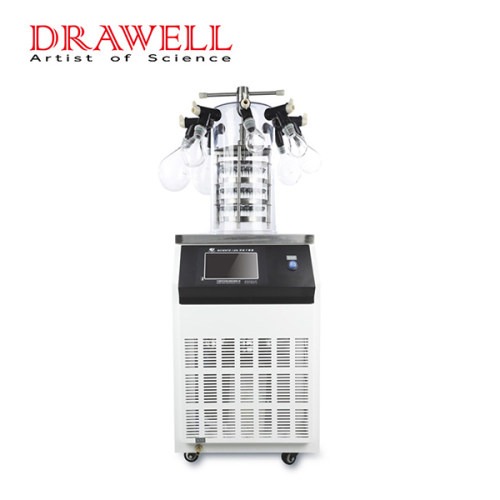
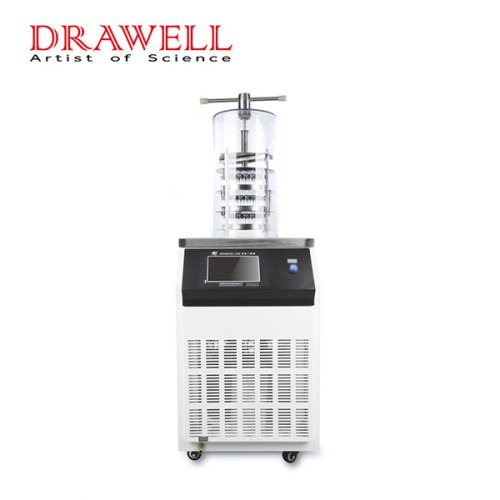
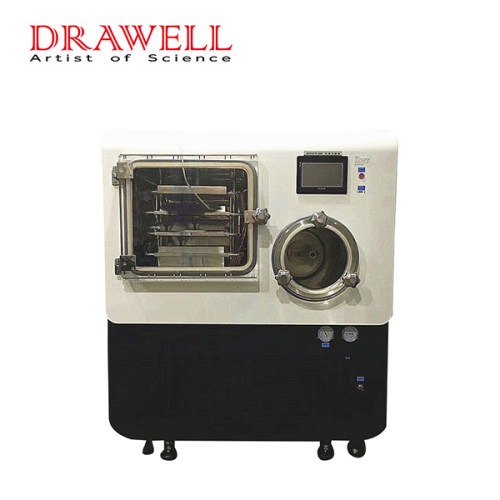
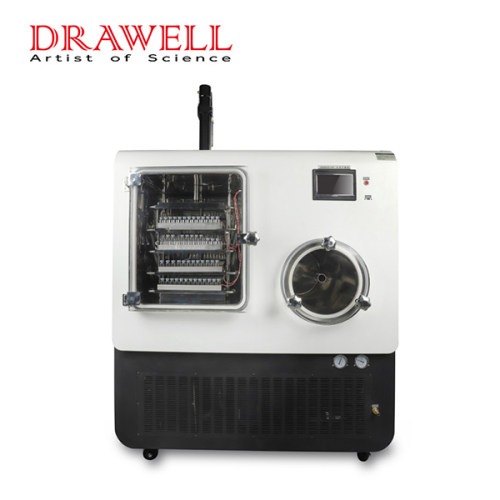
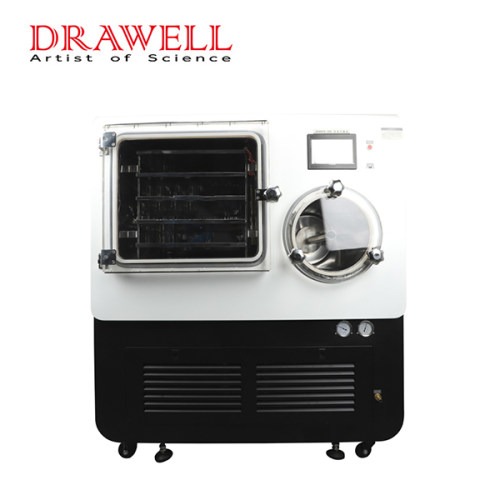
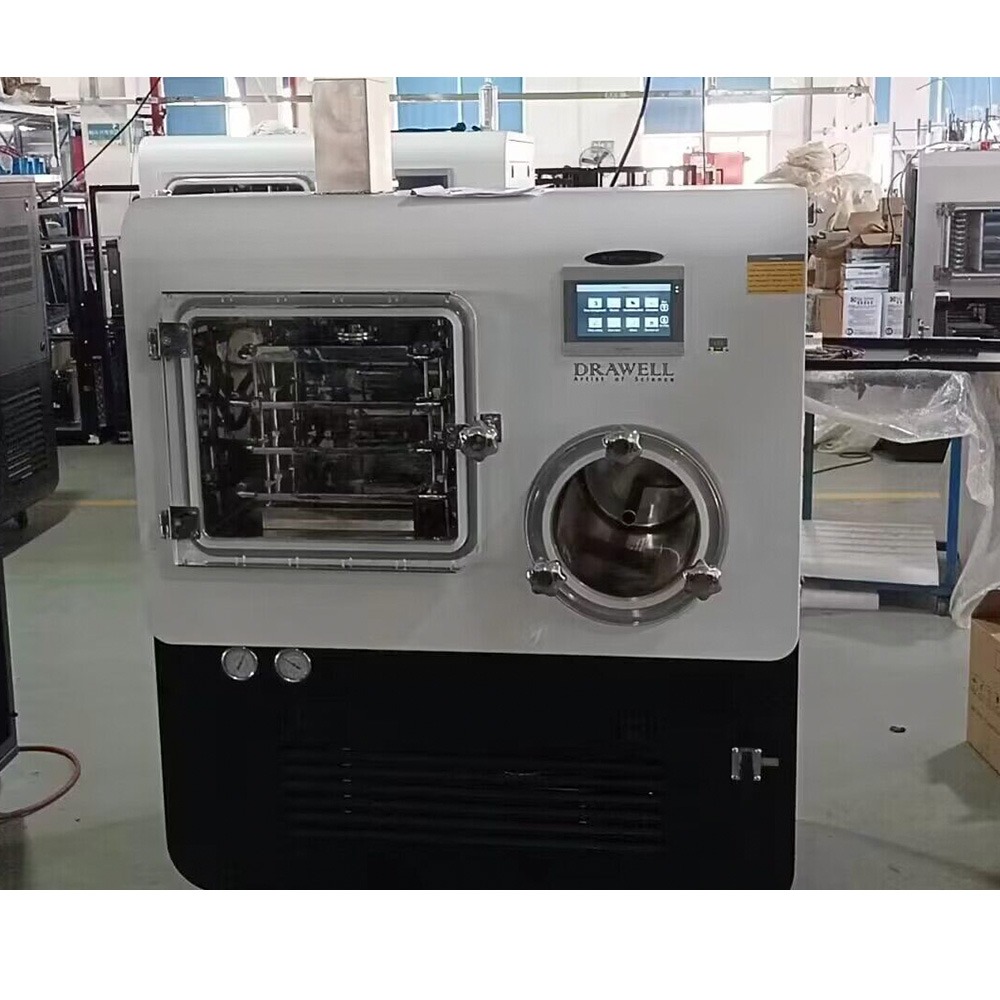
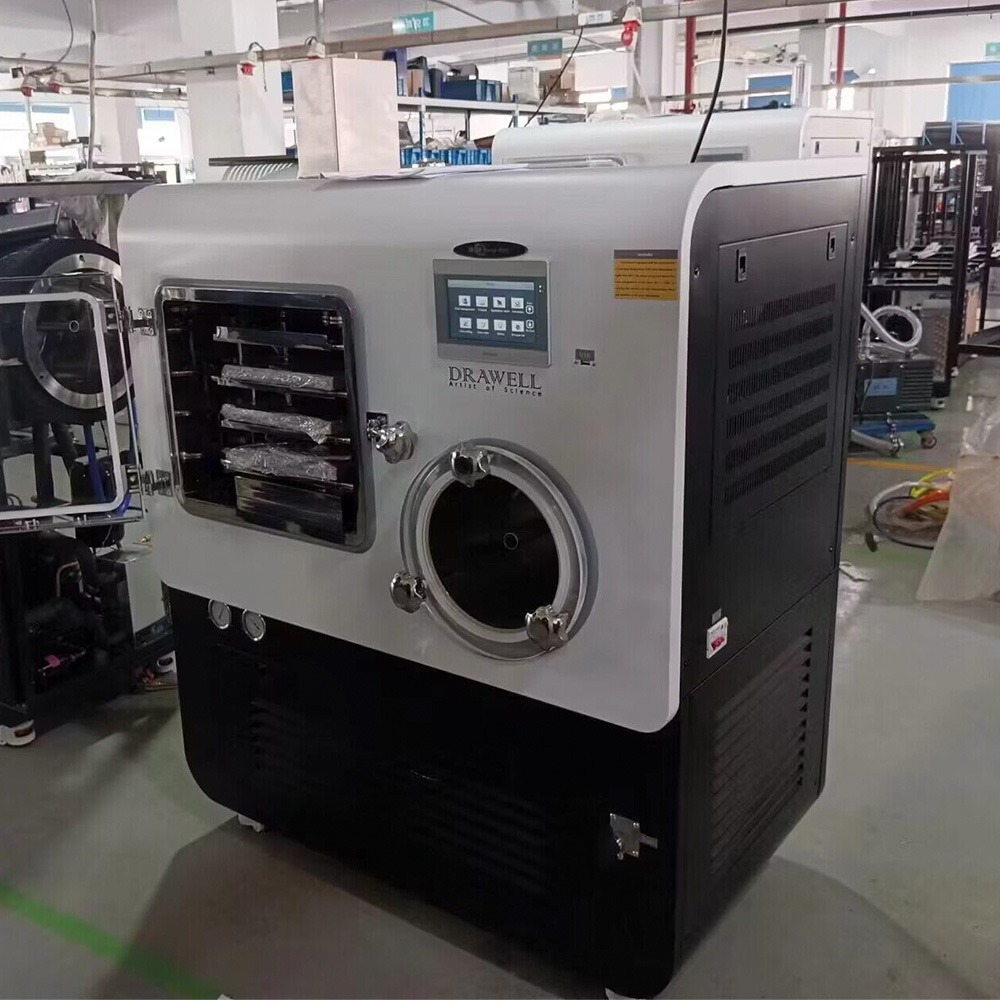
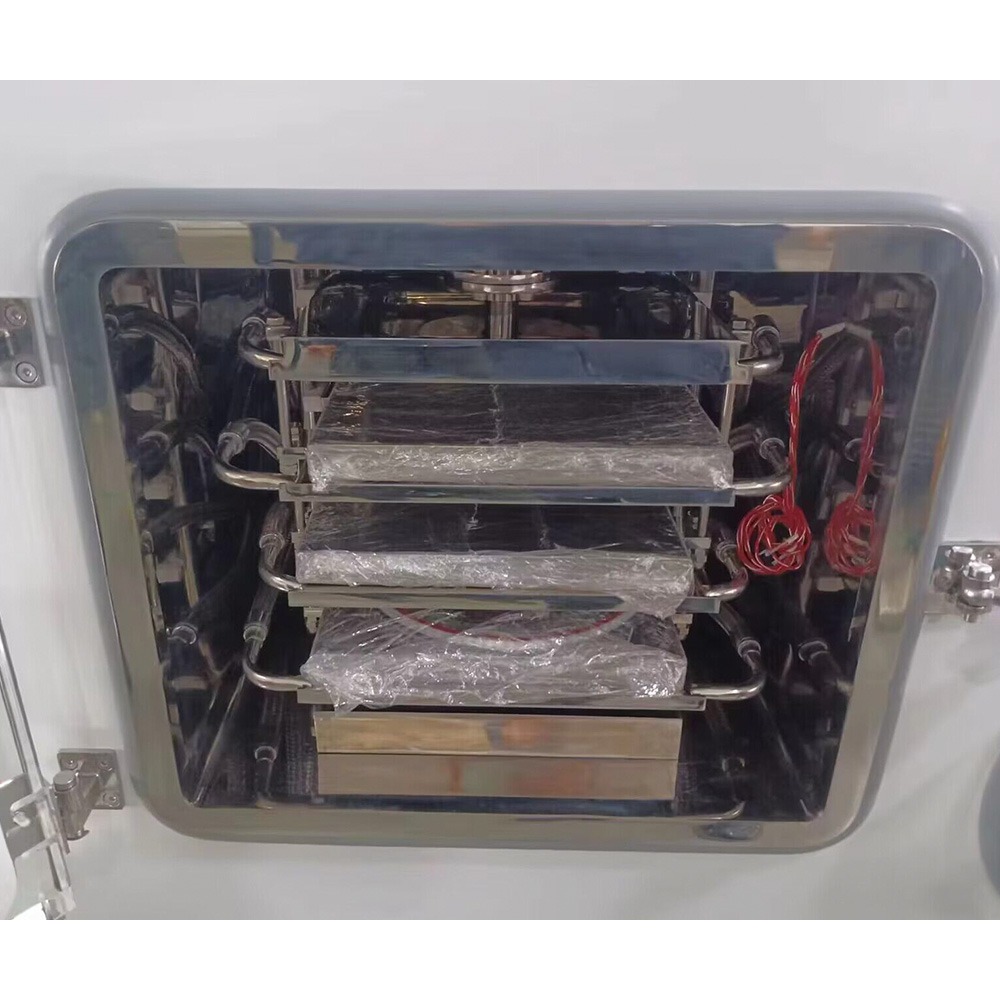
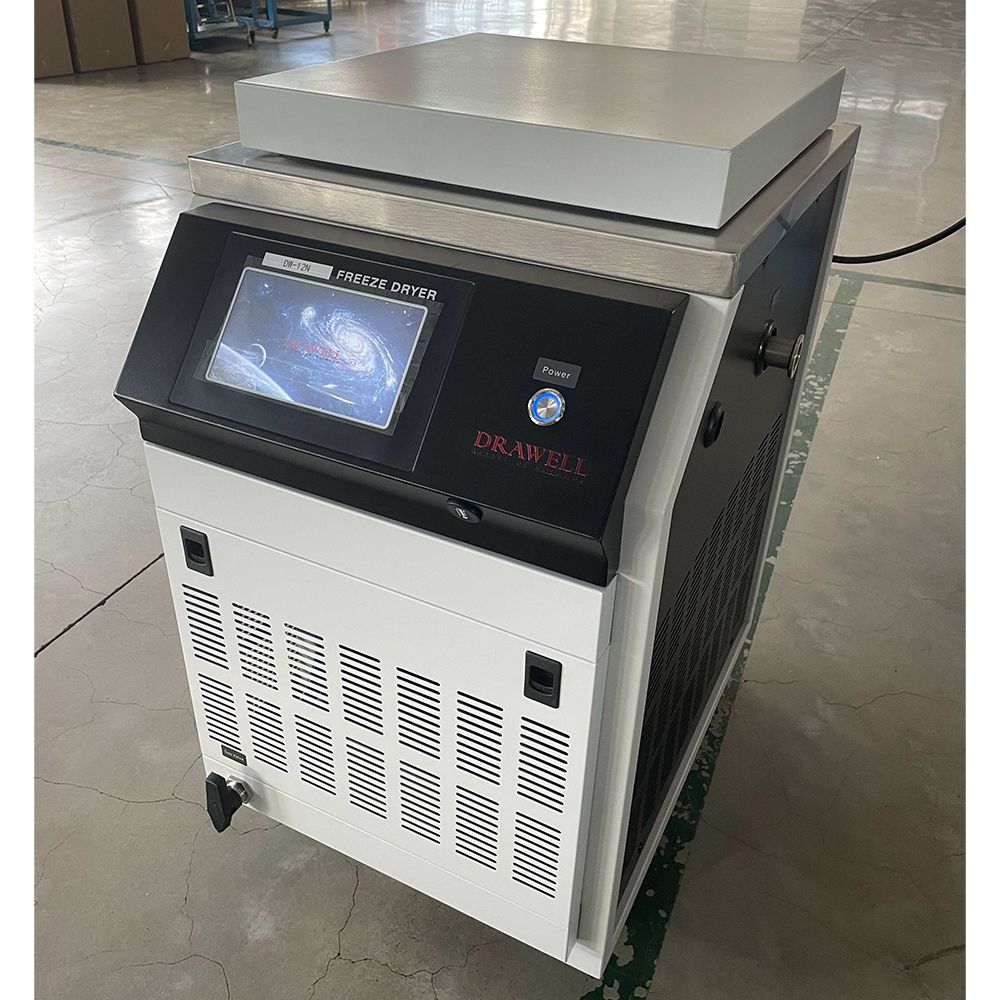
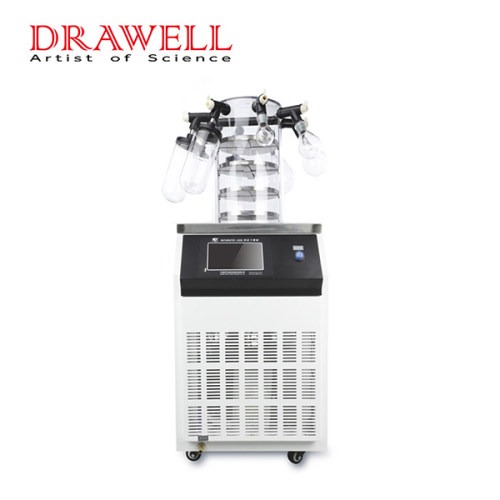
Lab Freeze Dryer
Features | Classification | Application | Image | Working steps | Why Choose Drawell | How to Operate/Maintain
The freeze dryer for laboratory, also known as lyophilizer, originated from the vacuum freeze-drying technology in the 1820s. It refers to a process in which solid materials are directly sublimated into a gaseous state under vacuum conditions without going through the liquid phase. During the freeze-drying process, the original chemical structure and morphology of the solute will not be destroyed. In addition, the biologically active material can still restore the conformation and biological function before freeze-drying after being re-dissolved. Compared with other drying methods, vacuum freeze-drying technology has incomparable advantages, so this technology is increasingly widely used in biology, medicine, food, environment, etc.
Drawell freeze dryers are mainly composed of six parts: drying box, condenser (water trap), heating system, vacuum system, refrigeration system and electrical control system.

Features of Lab Freeze Dryer
- Heat-sensitive substances will not be denatured or inactivated.
- Greatly reduce the loss of some volatile components in the substance.
- The growth of microorganisms and the action of enzymes are eliminated, so the original characteristics can be maintained.
- Keep the original structure without concentration.
- Avoid surface hardening caused by general drying methods.
- The product can be stored for a long time without deterioration.
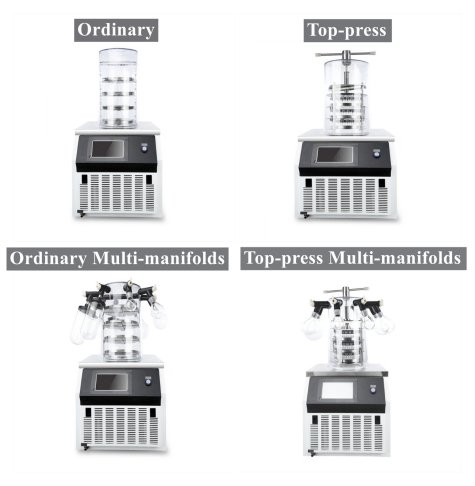
- Each model is available in 4 types: Ordinary, Top-Press, Ordinary Multi-Manifolds, and Top-Press Multi-Manifolds.
Classification of Lab Freeze Dryer
DW-10N Desktop Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 0.08㎡and 0.12㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water: 3Kg/batch
DW-10ND Desktop Freeze Dryer With Heating Function System
• Dryer area: 0.08㎡and 0.12㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water: 3Kg/batch
DW-12N Vertical Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 0.08㎡and 0.12㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water: 4Kg/batch
DW-12ND Vertical Freeze Dryer With Heating Function System
• Dryer area: 0.08㎡and 0.12㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water: 4Kg/batch
DW-18ND Vertical Freeze Dryer With Heating Function System
• 5 Dryer area: 0.09㎡and 0.18㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water : 6Kg/batch
DW-18N Vertical Freeze Dryer
• 5 Dryer area: 0.09㎡and 0.18㎡ optional
• Ability to capture water : 6Kg/batch
Silicone Oil Heating Freeze Dryer
DW-20F In-situ Silicone Oil Heating Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 0.21 ㎡
• Ability to capture water: 4Kg/batch
DW-30F In-situ Silicone Oil Heating Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 0.32 ㎡
• Ability to capture water: 6Kg/batch
DW-50F In-situ Silicone Oil Heating Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 0.54 ㎡
• Ability to capture water: 10Kg/batch
DW-100F In-situ Silicone Oil Heating Freeze Dryer
• Dryer area: 1.08 ㎡
• Ability to capture water: 15Kg/batch
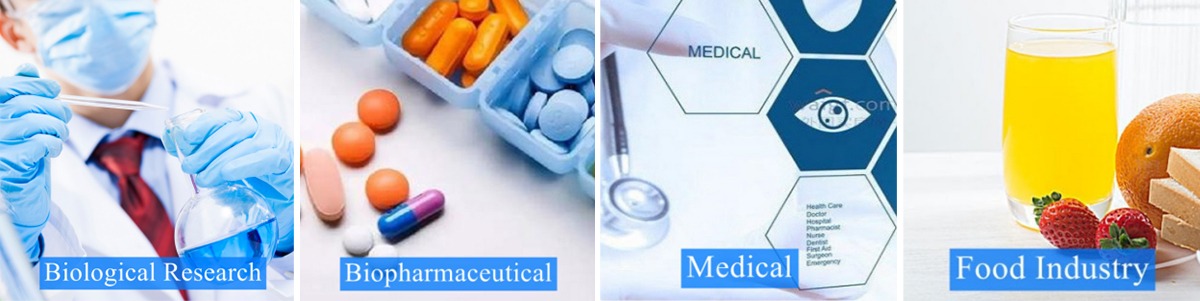
Applications of Lab Freeze Dryer
- Biological specimens and biological tissues: For example, the production of various animal and plant specimens, dry preservation of skin, bones, aorta, heart valves and other marginal tissues used for animal xenograft or allogeneic transplantation.
- Environmental protection: freeze-drying of soil and sludge samples.
- Food drying: coffee, tea, meat, fish and eggs, seaweed, fruits, vegetables, seasonings, tofu, convenience foods, etc.
- Biopharmaceuticals: vaccine powder injection, interferon, orally disintegrating tablets, serum protein and plasma, enzymes, cosmetic skin tissues, etc.
- Scientific research: freeze-drying samples of drug research and development, polymer synthesis, nanomaterials, soil testing, food testing, etc.
- Disease prevention and resistance: freeze-drying of bacteria, viruses, etc., pretreatment of physical and chemical laboratory samples.
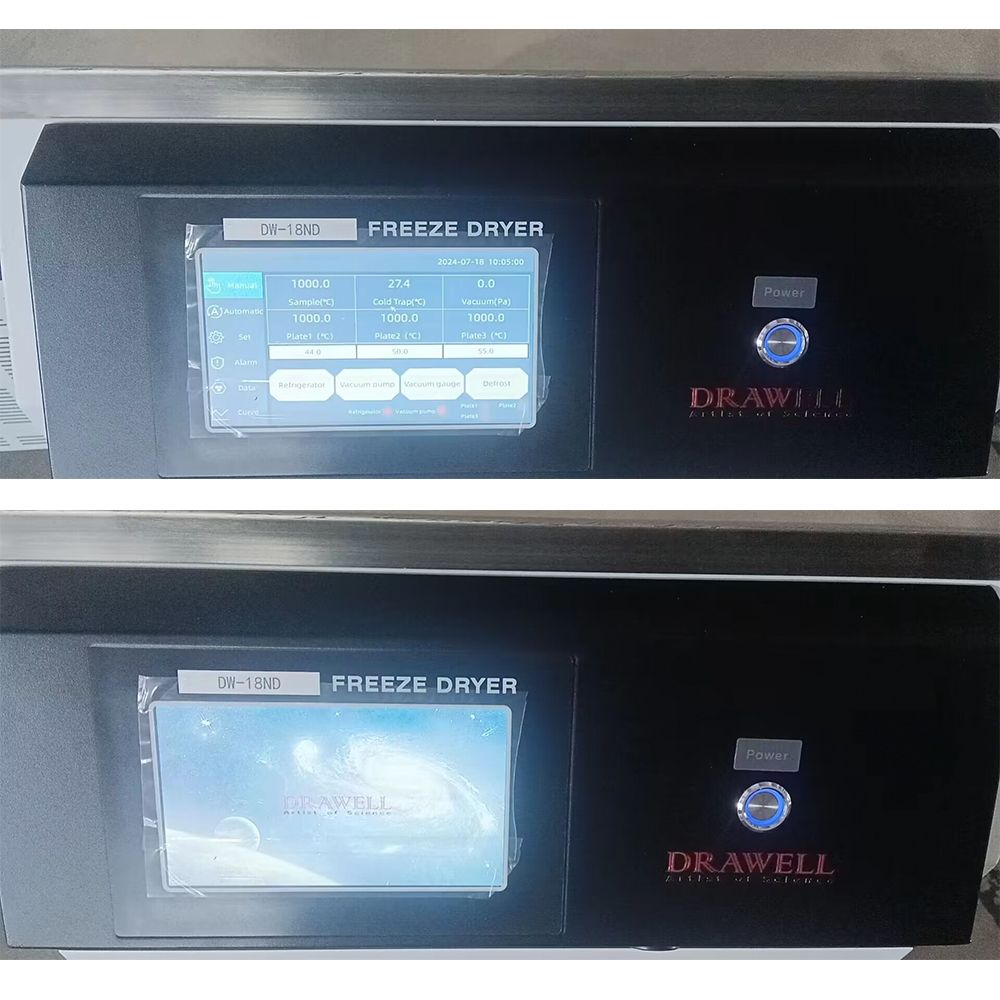
Lab Freeze Dryer Display
Working Steps of Lab Freeze Dryer
The basic principle of the freeze dryer is to utilize the phase change characteristics of water under low temperature conditions. By lowering the temperature and pressure, the water in the substance can be sublimated directly from solid to gas, thereby achieving the purpose of drying.
- Freezing: Rapidly freeze the liquid sample to form ice crystals.
- Vacuum: Establish an efficient vacuum environment to promote the sublimation process of ice crystals.
- Heating: Provide heat through the heating system to convert ice crystals directly from solid to gas without first becoming liquid.
- Collection: Collect the generated vapor to prevent pollution to the environment, and at the same time, the solvent can be recovered.
Why Choose Us for Lab Freeze Dryer?
“Multiple suppliers” have always been an issue in the procurement process. Drawell as a one-stop laboratory equipment and scientific instruments supplier, can perfectly solve this problem. In addition to manufacturing our own equipment, we also represent other laboratory equipment. Our product lines are rich and diverse at competitive prices. Provide one-stop service to customers.
User Training – Training by Drawell skilled engineers about installation, debug tests, technical services, etc. It can happen in our factory in China, or at the site in the customers’ country. Cost depends on where and when the training happens.
To discuss the problem and get it resolved, online chats, real-time video calls, and remote guidance. For the after-sales stage, our online technical guidance is free and ready forever.
1 year free official warranty, including repairing quality-damaged parts, and offering replacements of selected parts (shipping cost is extra). 5% of the product price is charged for extending the warranty before the end of the official warranty.
How to Operate Lab Freeze Dryer?
- Prepare the material for freeze-drying.
- Load the material into the freeze dryer.
- Close the chamber and start the freezing cycle.
- Once frozen, turn on the vacuum pump to start primary drying.
- Monitor the process and adjust the parameters as necessary.
- Start secondary drying when sublimation is completed.
- Once the desired moisture content is reached, terminate the cycle and remove the dried product.
- Turn off the main machine and vacuum and clean the chamber.
How to Maintain Lab Freeze Dryer?
- Check the power supply and wires regularly to ensure they are safe and reliable;
- Clean the surface of the condenser regularly to maintain its good cooling effect;
- Check the drainage pipe regularly to ensure smooth drainage;
- Regularly maintain and service the vacuum pump to keep it in good operating condition;
- Clean and remove dust from the inside of the freeze dryer regularly to keep it in good working condition.