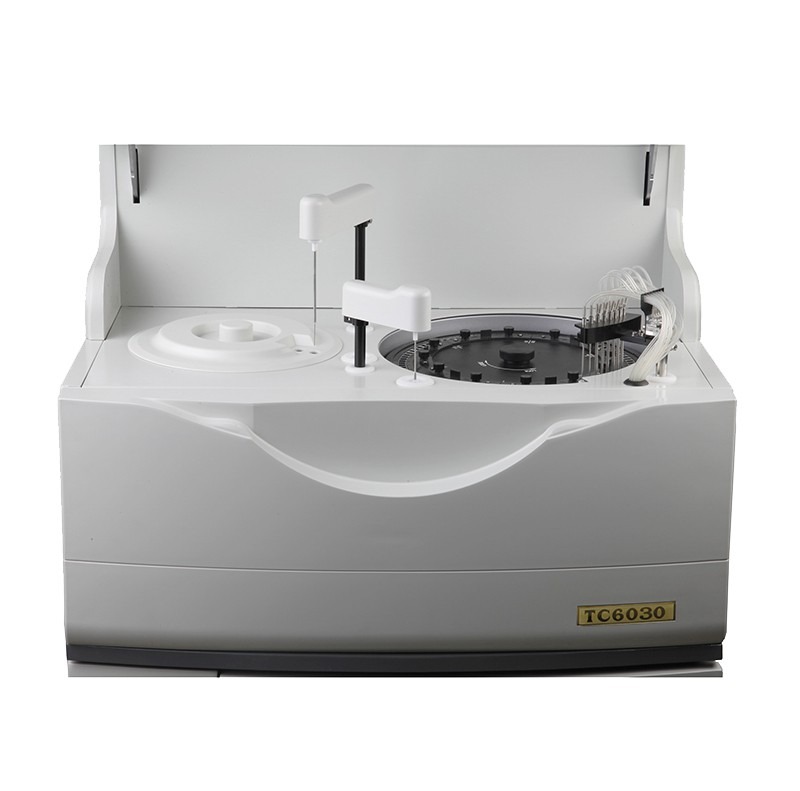
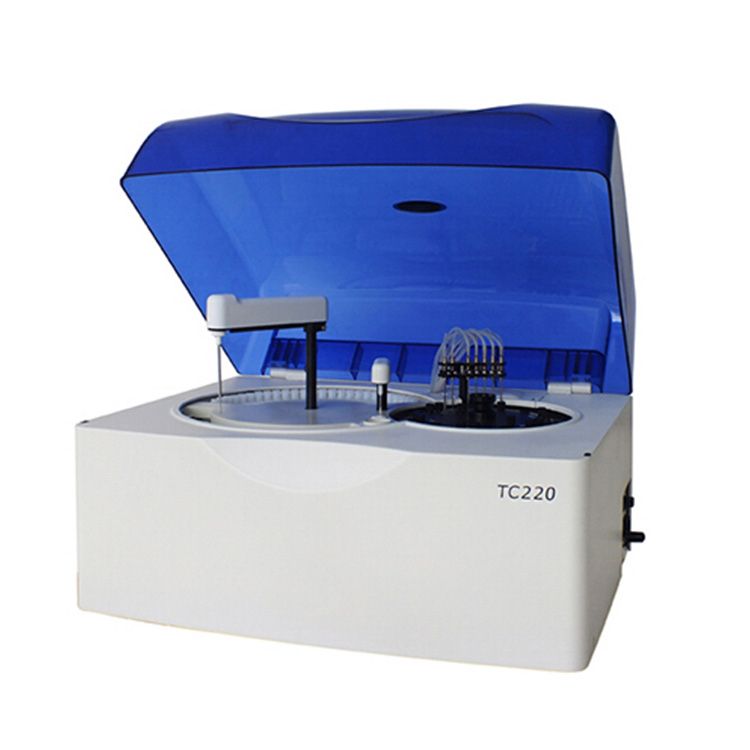
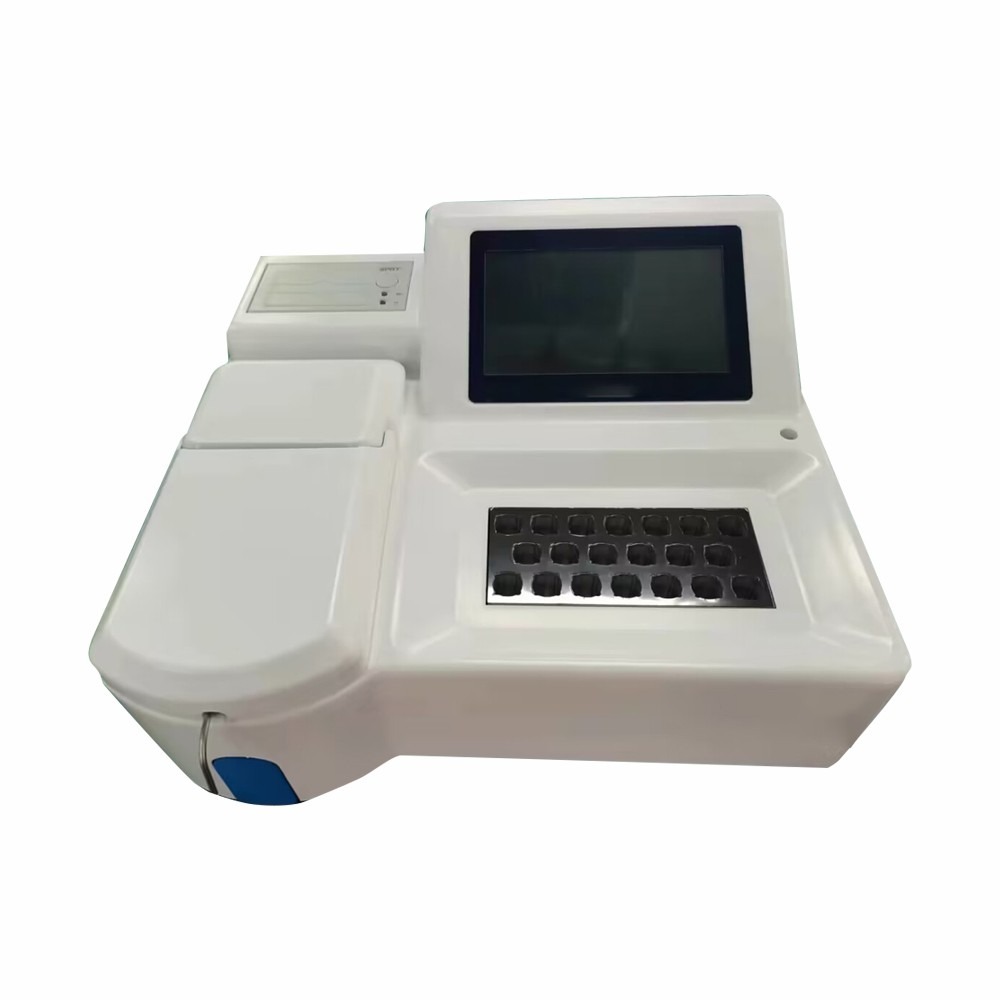
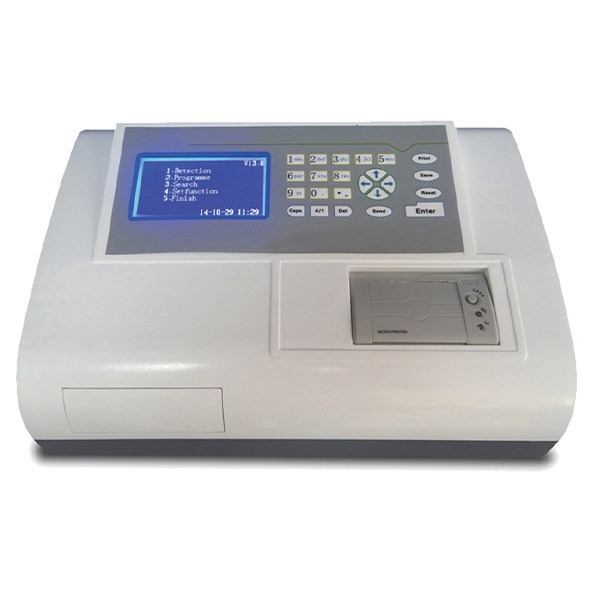
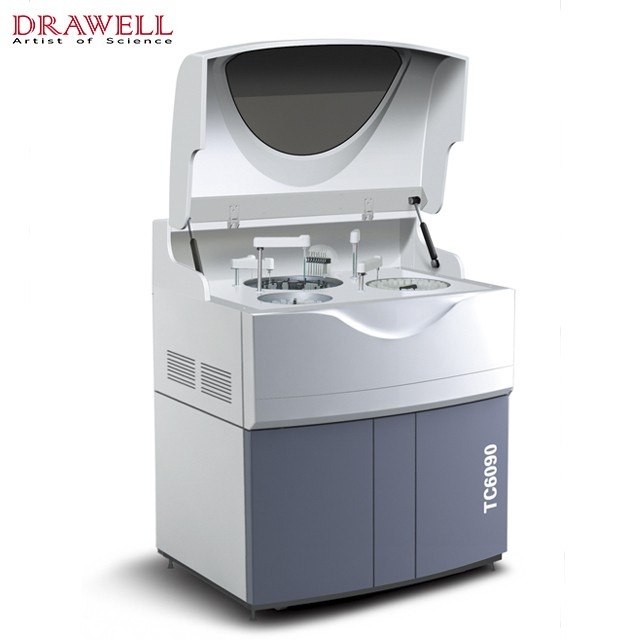
Biochemistry Analyzer
Biochemistry analyzers are automated laboratory instruments used to measure the concentration of various biochemical substances in blood, serum, or plasma. They employ a variety of analytical techniques, such as spectrophotometry, colorimetry, and enzymatic reactions, to detect and quantify analytes such as glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, liver enzymes, kidney function markers, and electrolytes.
Biochemistry analyzers provided by Drawell, are equipped with advanced optical systems, and data analysis software, and can handle large sample volumes efficiently. They are essential tools in clinical laboratories for diagnosing diseases, monitoring patient health, and conducting medical research.
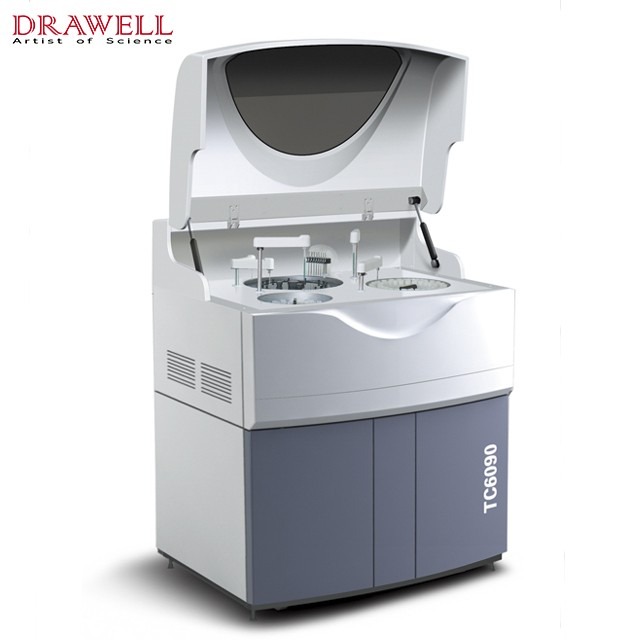
Features of Biochemistry Analyzer
- Fully automatic, discrete, random STAT function.
- Online test items.
- Analysis Method: end-point, kinetic, two-point, double-reagents, double-wavelength, multi-standard, etc, open to various reagents.
- Data Processing.
- Various QC managements, insert QC randomly; save, display & print QC chart; define different QC in advance.
- Calibration: linear/nonlinear multi-point calibration.
- Re-test: retest the sample automatically when the result is out of the linearity range or the sample is not sufficient
- Cleaning System,8-step automatic washing, automatic cuvette dry function.
Applications of Biochemistry Analyzer
The biochemical analyzer can be used in hospital laboratories for various tests, such as clinical blood routine, myocardial enzyme spectrum, blood lipid, liver function, kidney function, albumin detection, blood sugar detection and other routine biochemical indicators, or detection of enzymes and muscle in blood Anhydride levels. Clinically, some types of biochemical analyzers can be used to measure antigen-antibody interactions in biochemical reactions. Such as:
1. Liver function test: total bilirubin, direct bilirubin, total protein, albumin, alanine aminotransferase, aspartate aminotransferase, γ-glutamyltransferase, alkaline phosphatase.
2. Examination of renal function: urea (UREA), creatinine (CREA), uric acid (UA).
3. Blood lipids: total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), apolipoprotein (ApoA1), apolipoprotein ( ApoB).
4. Blood sugar: Glucose (Glu), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1C) detection.
5. Three items of rheumatism: C-reactive protein, antistreptolysin O, and rheumatoid factor.

How to Choose the Biochemistry Analyzer?
1)What are the differences between our models?
The main reason is that the complexity of the instruments is inconsistent, and there are differences between automatic and semi-automatic.
2)Testing speed
Testing speed is one of the important parameters for users to choose a biochemical analyzer.
3)Optical parameters
In addition to the characteristics of spectroscopic technology, the instrument in a certain wavelength range of monochromatic light wavelength (or filter) number should be able to meet the needs of laboratory testing work, usually in the wavelength range of 300 ~ 800 nm, the number of fixed wavelengths should be more than 11.
4)Reagent position and sample loading
The fully automated biochemical analyzers used in clinical laboratories now generally use multi-channel analysis. Biochemistry analyzers can be loaded with sample trays or sample racks.
5)Environmental requirements
To ensure the normal use of biochemical analyzers, there are certain requirements for their installation environment, such as temperature, humidity, water quality and water (discharge), power supply power, and use of space.
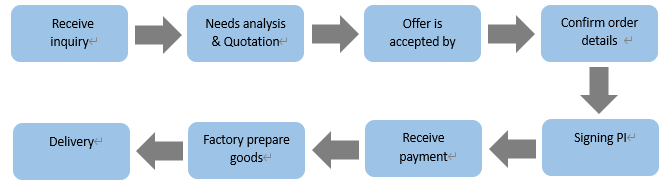
Order Process
Why Choose Us?
- Rich categories
- The products are market-oriented and exported to many countries in the world
- Perfect sales system, efficient and fast after-sales service
- On-time delivery rate reaches 100%
- High-cost performance