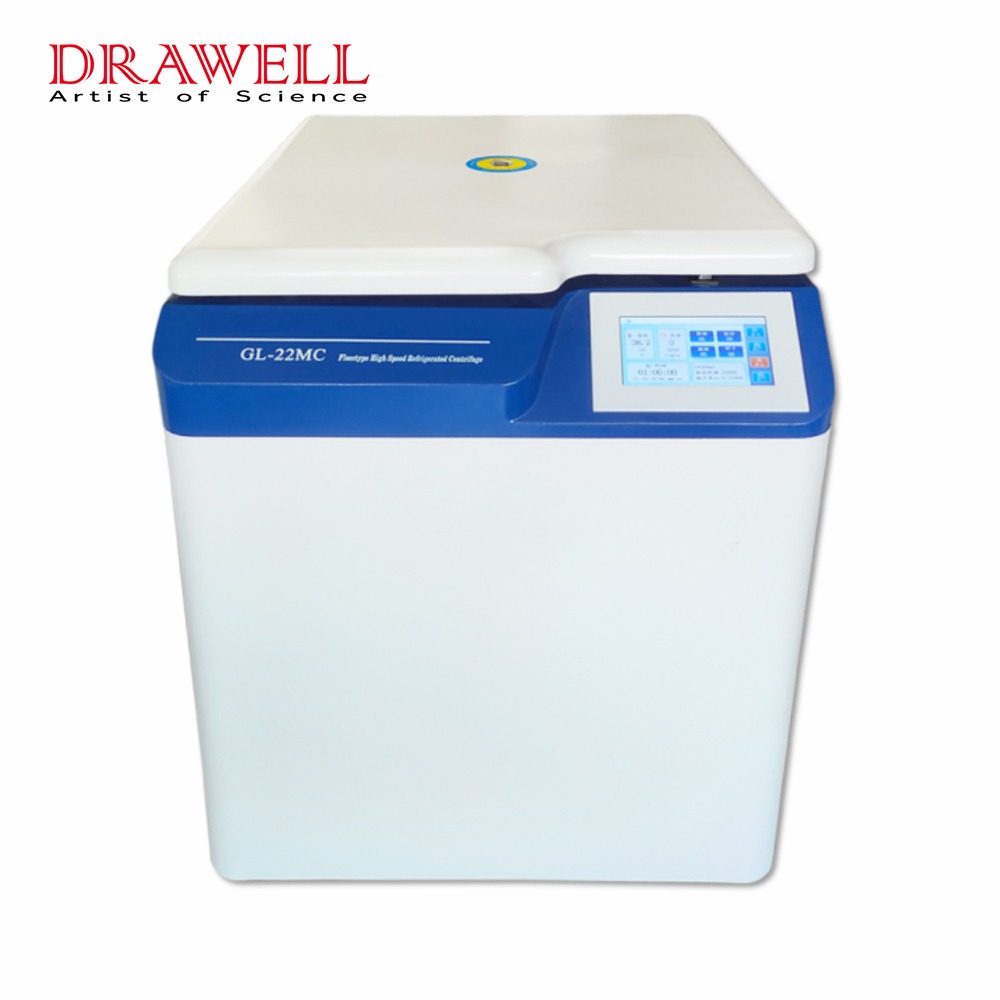
A laboratory centrifuge is a device used in scientific and medical laboratories to separate substances of different densities or particle sizes from a sample mixture. It utilizes centrifugal force to rapidly spin samples, causing heavier components to move towards the outer edges while lighter components collect in the center. This separation allows for further analysis and study of the isolated components. Centrifuges are commonly used in various applications such as blood tests, DNA research, and particle analysis.

The Common Applications of A Lab Centrifuge
A laboratory centrifuge has a wide range of applications in scientific and medical research. Some common applications include:
- Separation of Blood Components: Centrifuges are extensively used in clinical settings to separate red blood cells, white blood cells, and plasma for diagnostic purposes, such as blood cell counting, plasma protein analysis, and blood typing.
- DNA and RNA research: Centrifuges play a crucial role in DNA and RNA extraction, purification, and isolation. They help separate nucleic acids from other cellular components, enabling further analysis and study.
- Cell Culture and Microbiology: Centrifuges are used in cell culture laboratories to separate cells from growth media, harvest cell pellets, and isolate subcellular components. They are also used in microbiology to concentrate microbial cells or separate different types of microorganisms.
- Protein Purification: Centrifugation is employed to separate proteins from cell lysates or other mixtures, enabling purification and analysis of specific proteins. This technique is crucial for biochemistry and biotechnology research.
- Environmental Analysis: Centrifuges are used in the analysis of environmental samples, such as soil, water, and air, to separate and concentrate target analytes for further characterization and measurement.
- Pharmaceutical research and development: Pharmaceutical scientists use centrifuges to separate and purify active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) and for pharmaceutics formulation studies.
- Industrial Applications: Centrifugation is utilized in various industries, including food and beverage, oil and gas, chemical engineering, and wastewater treatment. It is used for separation, clarification, and purification processes.
How to Properly Install A Laboratory Centrifuge?
Proper installation of a laboratory centrifuge is crucial to ensure its safe and effective operation. The specific installation steps may vary depending on the centrifuge model and manufacturer, but here are some general guidelines to follow:
- Location: Choose a suitable location for the centrifuge that meets the recommended environmental conditions. Ensure the area is well-ventilated, away from direct sunlight, and free from excessive vibrations or temperature fluctuations. Consider any specific requirements mentioned in the centrifuge’s user manual.
- Power Supply: Ensure that the power supply in the chosen location meets the electrical requirements of the centrifuge. Use a grounded electrical outlet and avoid using extension cords or power strips whenever possible.
- Leveling: Place the centrifuge on a sturdy and level surface. Use a spirit level to check and adjust the levelness of the instrument. This step is crucial to ensure proper balance and prevent excessive vibrations during operation.
- Clearance: Provide adequate clearance around the centrifuge for proper airflow and maintenance access. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations regarding minimum clearance distances for ventilation purposes.

- Rotor Installation: Install the appropriate rotor and any necessary adapters or buckets according to the centrifuge’s specifications. Ensure that the rotor is securely seated and properly balanced. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for rotor installation and removal to ensure safety and prevent accidents.
- Lid and Safety Precautions: Attach and secure the lid or cover of the centrifuge properly. Ensure that all safety features, such as interlocks or control mechanisms, are functioning correctly. Familiarize yourself with the safety precautions and operating instructions provided by the manufacturer. Always close the lid before starting the centrifuge.
- Operational Verification: Before using the centrifuge, perform an operational verification check as described in the user manual. This may include verifying the display, control settings, and any alarms or safety features.
- Training and Maintenance: Make sure that the operators are adequately trained in using the centrifuge safely and correctly. Follow the recommended maintenance schedule and procedures to maintain the centrifuge’s performance and longevity.
Note: These are general guidelines, and it is important to refer to the specific instructions provided by the centrifuge manufacturer for precise installation steps. Additionally, always prioritize your safety and consult with experts if you have any doubts or questions during the installation process.
How to Safely Operate A Laboratory Centrifuge?
Operating a laboratory centrifuge safely is essential to protect yourself and others from potential hazards. Here are some guidelines for safe operation:
- Read the manual.
- Personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Load balancing.
- Secure the lid.
- Proper rotor installation.
- Balance the rotor.
- Set appropriate parameters.
- Pre-run inspection.
- Start and monitor operation.
- Post-run precautions.
- Regular maintenance.

How to Work Safely With A Centrifuge?
Working safely with involves following proper procedures and precautions to minimize the risk of accidents or injuries. Here are some key guidelines for safe operation:
- Familiarize Yourself: Read and understand the manufacturer’s instructions, user manual, and safety guidelines specific to the centrifuge model you are using. Be aware of any limitations, precautions, or potential hazards associated with the device.
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment, including lab coats, gloves, and safety goggles or glasses, when working with the centrifuge. Adhere to the PPE requirements set by your laboratory or institution.
- Training and Competence: Ensure you receive adequate training on the operation of the centrifuge before using it independently. Seek guidance from experienced personnel or supervisors and familiarize yourself with the specific protocols and procedures established in your laboratory.
- Safe Sample Handling: Handle all samples and materials with care. Use properly sealed, labeled, and leak-proof containers suitable for centrifugation. Follow guidelines for proper preparation, loading, and balancing of samples in accordance with the centrifuge and rotor specifications.
- Load Balancing: Ensure equal weight distribution within the rotor to prevent imbalance and minimize the risk of accidents or damage. Use complementary tube or vial pairs, or balance the rotor with empty containers or counterweights as recommended by the manufacturer.
- Secure the Lid: Always close and latch the centrifuge lid securely before initiating a run. The lid is designed to contain samples and protect against rotor failure. Do not override or disable any lid interlocks.

- Speed and Time Settings: Set the centrifugation parameters, such as speed, time, and temperature (if applicable), based on the specific requirements of your experiment or protocol. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and respect the limitations of the rotor and centrifuge model.
- Avoid Overloading: Do not exceed the maximum load capacity specified by the manufacturer. Overloading a centrifuge can cause imbalance, rotor failure, or compromise the safety of the centrifuge and its operators.
- Monitoring the Run: Stay nearby and monitor the centrifuge closely during operation. Be attentive to unusual noises, vibrations, or any signs of malfunction. If an abnormality is detected, immediately stop the centrifuge, allow it to come to a complete stop, and investigate the cause before proceeding.
- Post-run Precautions: After completing a centrifugation run, ensure the rotor has come to a complete stop before opening the lid. Handle the samples and rotors with caution, following any necessary safety protocols or biohazard containment procedures if applicable.
- Maintenance and Inspections: Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule and inspection procedures. Regularly clean the centrifuge, check for any signs of damage or wear, and promptly report any issues to the appropriate personnel for rectification.
- Emergency Preparedness: Familiarize yourself with the location and operation of emergency shut-off switches, fire extinguishers, and emergency contact information. Be prepared to respond appropriately to any emergencies or incidents that may occur during centrifuge operation.