The incubator is a very common laboratory instrument, but we often encounter various incubators, such as constant temperature incubators, constant temperature, and humidity incubators, carbon dioxide incubators, anaerobic incubators, mold incubators, light incubators, and many more. So many types, what’s the difference?

The incubator simulates a growth environment similar to that of cells/tissues/microorganisms in a living organism or a specific situation in the incubator. Such as a certain temperature, a certain humidity, a certain light or a certain CO2 level, a certain pH, and so on.
It can also be a device for in vitro culture of cells/tissues/organisms and is widely used in the fields of plants, biology, microorganisms, genetics, viruses, medicine, and environmental protection. It is widely used in low-temperature and constant-temperature tests, culture tests, environmental tests, and so on.
5 Most Common Types of Incubators: Functions and Differences
1. Constant Temperature Incubator
The constant temperature incubator is suitable for common bacterial culture and closed cell culture, and is often used for pre-warming equipment and reagents related to cell culture.
Features: heating control, without refrigeration.
The constant temperature incubator is divided into a water-proof constant temperature incubator and electric heating constant temperature incubator.
Waterproof electric heating constant temperature incubator: The heating tube heats the water in the interlayer and uses the convection of the water to form four-sided heating, which effectively ensures the uniformity of heating.
The water jacket can still be kept at a constant temperature in case of power failure, and two temperature control methods are adopted: a microcomputer intelligent temperature controller and a bimetal regulator. Temperature control range: room temperature +5 ℃-60 ℃, can only stabilize the temperature above room temperature, not refrigeration.
Electric heating constant temperature incubator: It adopts the method of electric heating, the outer shell is made of cold-rolled plate electrostatic spray, the inner tank is made of stainless steel, the insulation layer is made of asbestos as the insulation material, and a heating tube is arranged at the bottom, and the box is heated through the heating tube.
Its disadvantage is that the temperature uniformity is relatively poor, and the temperature impulse is relatively high. It is mainly composed of a box, heater, blower, and temperature controller.
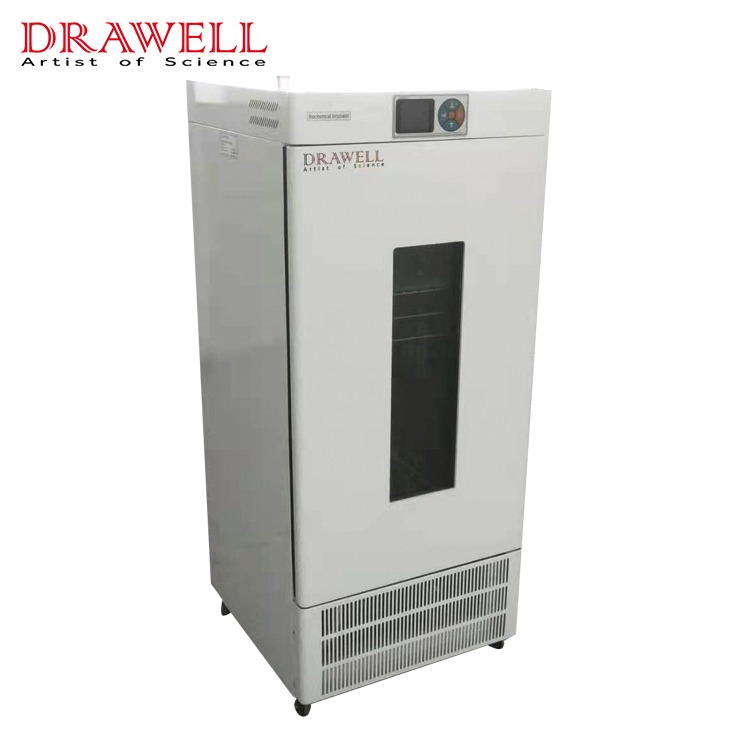
2. Biochemical Incubator
The biochemical incubator is equipped with electric heating wire heating and compressor cooling at the same time. Therefore, it can adapt to a large range and can be maintained at a constant temperature throughout the year, so it is gradually popularized.
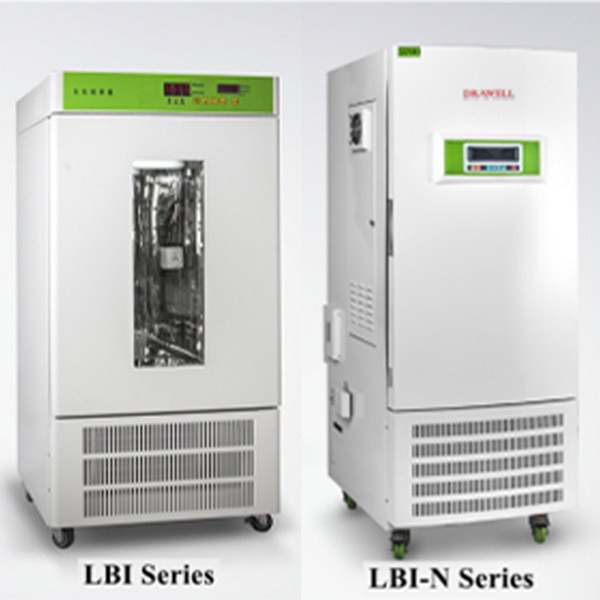

The use and maintenance of this incubator are similar to that of an electric heating incubator. Due to the installation of a compressor, the precautions for maintenance of the refrigerator should also be observed, such as keeping the voltage stable, not tilting too much, and cleaning the dust on the radiator in time.
Features: Biochemical incubators generally do not have humidity control and antivirus functions. With dual-type cold and hot temperature control. Generally with a glass observation window.
Biochemical incubators are indispensable laboratory equipment for scientific research and education departments such as plants, biology, microorganisms, genetics, viruses, medicine, environmental protection, etc., and are widely used in low-temperature and constant-temperature experiments, culture experiments, and environmental experiments.
3. Mold Incubator
A mold incubator is test equipment suitable for cultivating eukaryotic microorganisms such as mold.
Because most molds are suitable for growth at room temperature (25 degrees Celsius) and need to maintain a certain humidity when culturing on solid substrates, the general mold incubator consists of a refrigeration system, a heating system, an air humidifier, and a cultivation room, and a control circuit. and operation panel.
And it uses a temperature sensor and a humidity sensor to maintain a stable temperature and humidity inside the cultivation chamber. Some special mold incubators can also set the temperature and humidity to change with the incubation time.
Features: dual-type cooling and heating control, heating, cooling, and humidity control
This product is suitable for environmental protection, sanitation and epidemic prevention, agriculture and livestock, drug inspection, aquatic products, and other scientific research, college experiments, and production departments. It is a special constant temperature and constant temperature oscillation equipment for water body analysis; BOD determination of bacteria and molds; microbial culture and preservation; plant cultivation and breeding experiments.
4. CO2 Incubator
CO2 incubator simulates a growth environment similar to that of cells/tissues in vivo in the incubator. The incubator requires a stable temperature (37°C), stable CO2 level (5%), and constant PH (PH value). : 7.2-7.4), high relative saturated humidity (95%), a device for in vitro culture of cells/tissues.

Features: temperature control, generally only with heating, high-temperature sterilization, individual refrigeration, CO2 level control, pH control, and humidity control.
CO2 incubators are widely used in the cell, tissue culture, and the culture of some special microorganisms, commonly used in cell dynamics research, collection of mammalian cell secretions, carcinogenic or toxicological effects of various physical and chemical factors, antigen research, and Production and cultivation of hybridoma cells to produce antibodies, in vitro fertilization (IVF), stem cells, tissue engineering, drug screening, and other research fields.
Due to the increase in carbon dioxide concentration control and the use of microcontrollers to accurately control the temperature of the incubator, the success rate and efficiency of biological cells, tissues, etc. have been improved. In short, the carbon dioxide incubator is a new type of incubator that cannot be replaced by ordinary electric heating incubators.
5. Anaerobic Incubator
Anaerobic incubators are also known as anaerobic workstations or anaerobic glove boxes. The anaerobic incubator is a special device for bacterial culture and operation in an anaerobic environment.
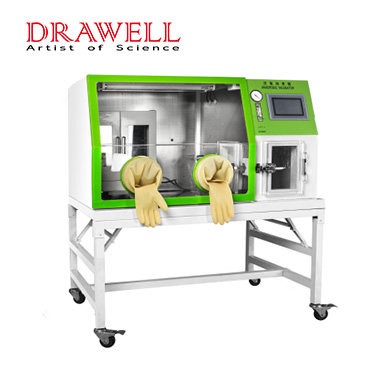
It can provide strict anaerobic constant temperature culture conditions and a systematic and scientific working area.
Features: anaerobic control, temperature control
This product is a special device that can cultivate and operate bacteria in an anaerobic environment. It can cultivate the most difficult anaerobic organisms to grow and can avoid the risk of death when anaerobic organisms are exposed to oxygen when they operate in the atmosphere. Therefore, this device is an ideal tool for anaerobic biological detection and scientific research.








